Ventilation Mechanisms
This lesson covers:
- What ventilation is
- The muscles involved in ventilation
- The process of inspiration
- The process of expiration
What is ventilation? Ventilation, or breathing, consists of inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out). It allows air to enter and leave the lungs, providing the body with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. |
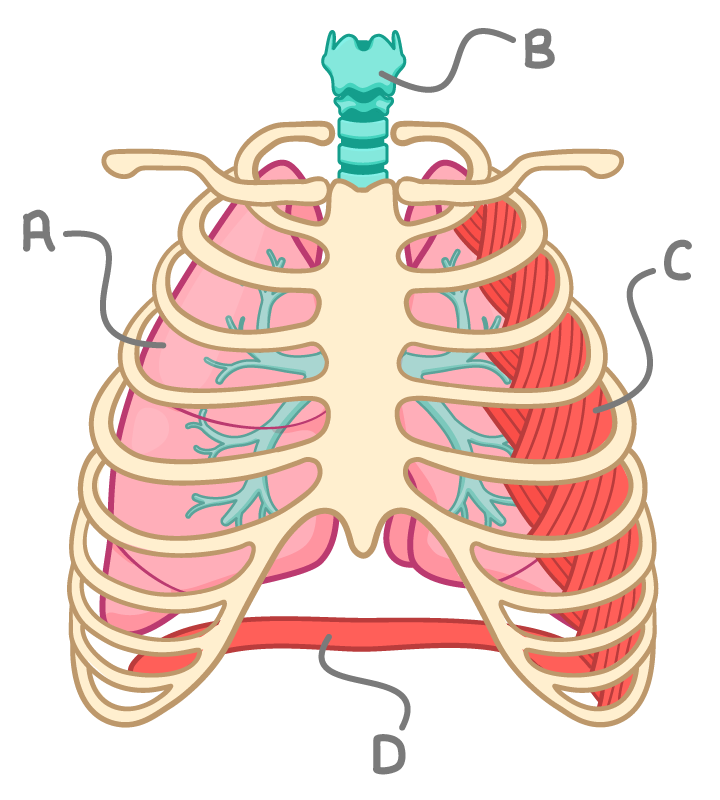
Muscles involved in ventilation The ribcage is made up of bones called ribs that enclose the thorax - the cavity where the lungs are located. In mammals, ventilation is controlled by muscles that change the volume of the thorax. When the muscles attached to the ribcage contract and relax, they move the ribs to change the volume in the thoracic cavity. This affects the pressure in the lungs and controls ventilation. |
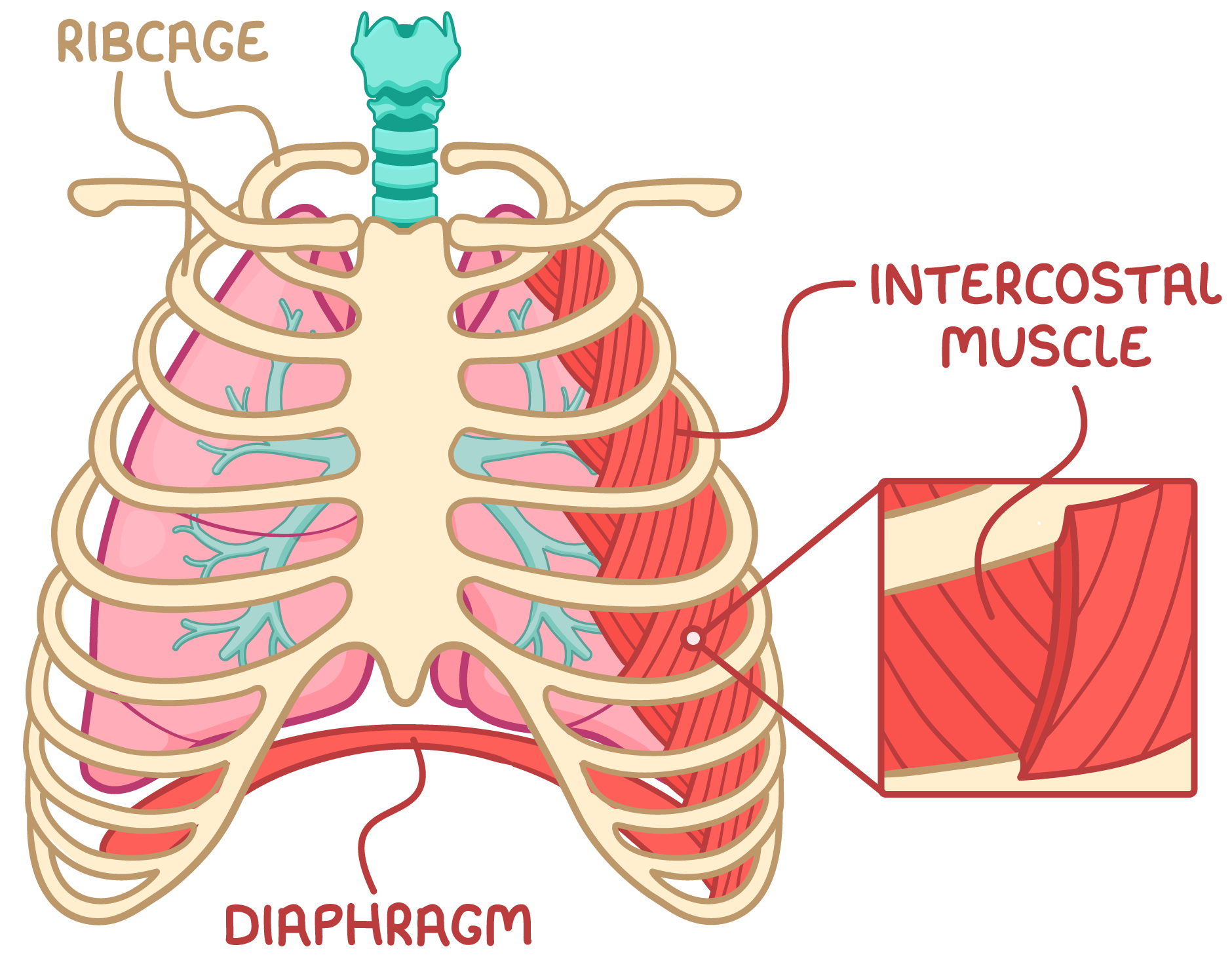 There are two sets of muscles that act on the ribcage:
|
Inspiration Inspiration is an active process requiring energy for muscle contraction. |
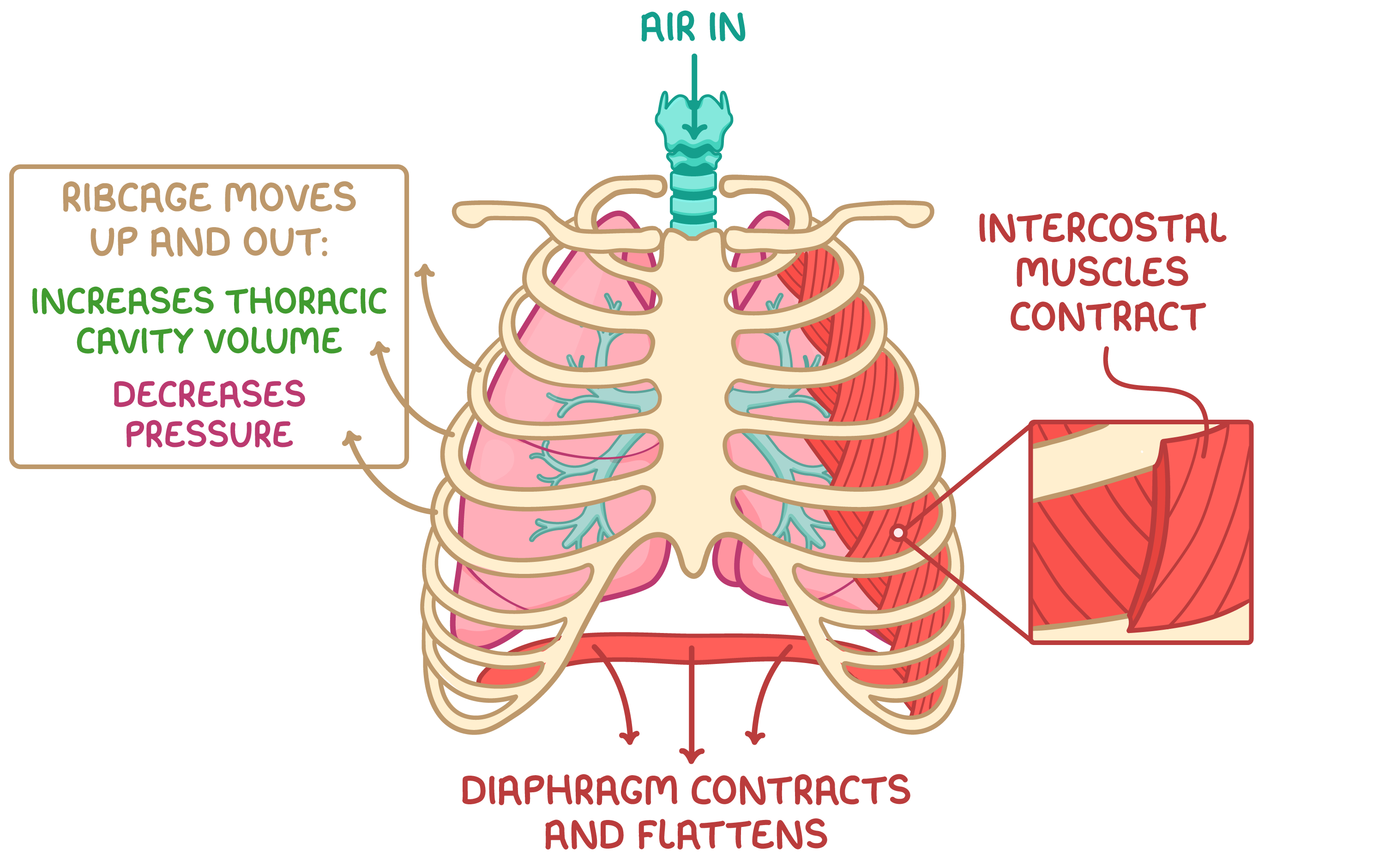 During inspiration:
|
Expiration Normal expiration at rest is a passive process so it does not require energy. |
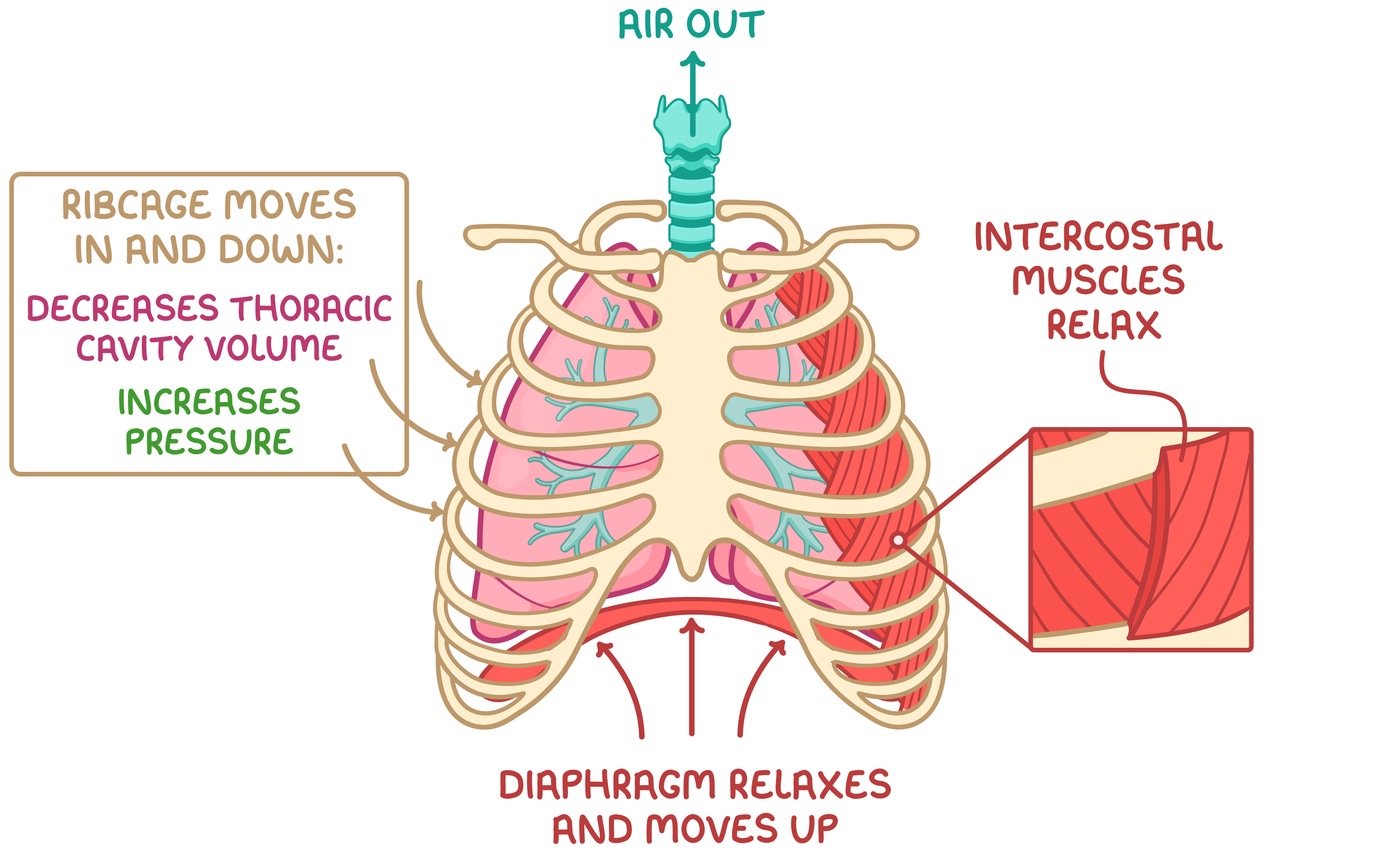 During expiration:
|
Which of the following parts of the respiratory system contain rings made of cartilage?
diaphragm
alveoli
intercostal muscles
trachea
|
Which of the parts A, B, C or D, represents the intercostal muscles?
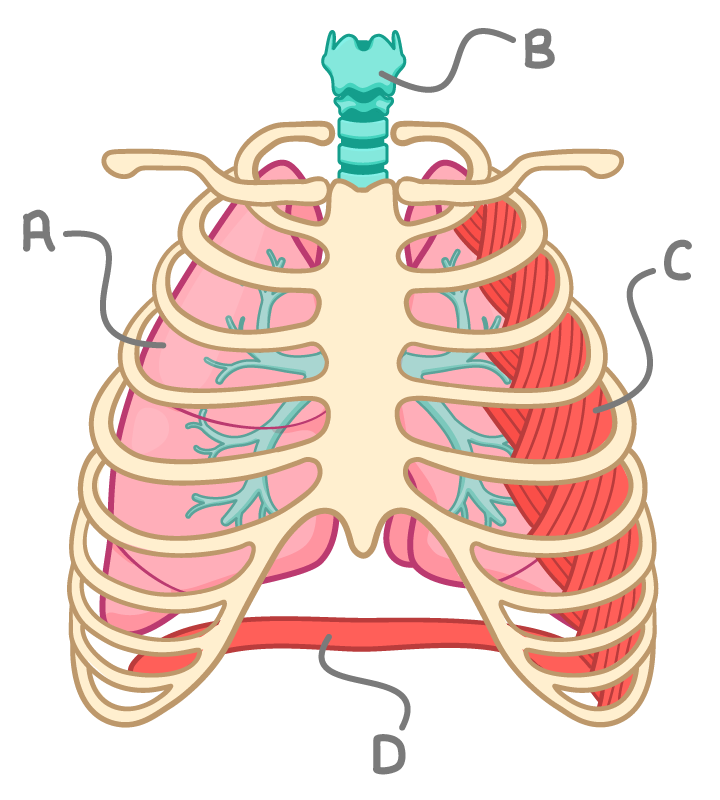
A
B
C
D
|
What is the name of the structure labelled B?
|
Which one of the following protects the lungs?
trachea
cranium
ribcage
diaphragm
|
Which of the parts A, B, C or D, represents the diaphragm?
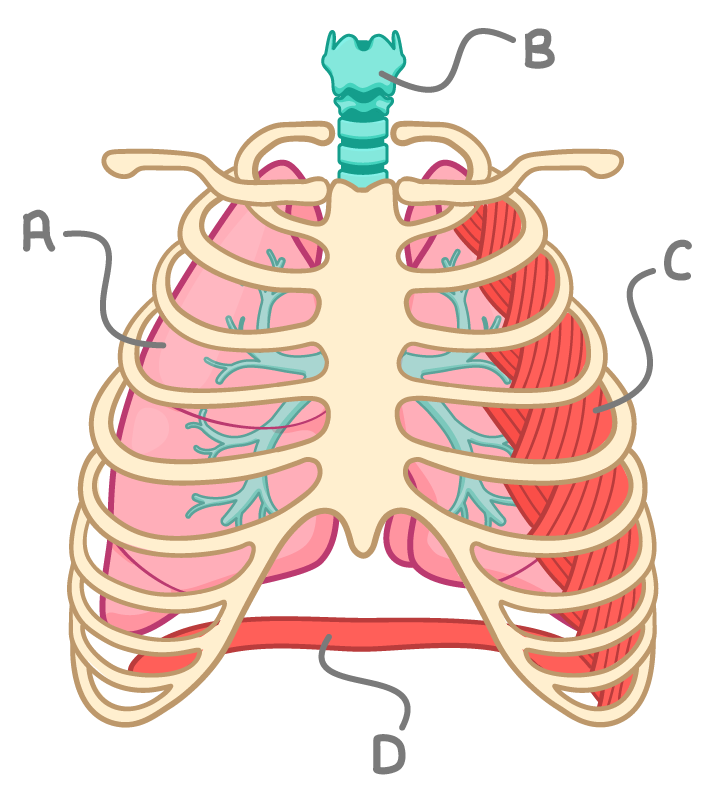
A
B
C
D
|
What happens to the lungs during inhalation?
They push up the diaphragm
They contract
They expand
They produce oxygen
|