Food Chains & Foodwebs
This lesson covers:
- What food chains show
- What 'producers', 'primary consumers', 'secondary consumers', and 'tertiary consumers' are
- What food webs show
A model that shows how energy passes from organism to organism is called a .
|
Organisms at the very start of a food chain that can create glucose using photosynthesis are known as .
|
Which two of the following groups of organisms are producers?
Apex predators
Plants
Algae
Herbivores
|
Which resource do plants not compete for?
Light
Space
Food
|

What do primary consumers feed on?
Other primary consumers
Decomposers
Secondary producers
Producers
|
consumers are organisms that eat secondary consumers.
|
As energy passes along a food chain, most of the energy is _________.
conserved
lost
|
Which is the secondary consumer in the following food chain?
tree → caterpillar → shrew → owl
Caterpillar
Tree
Shrew
Owl
|
What is a predator?
An animal that is hunted and killed for food by another animal
An animal that makes its own food
An animal that hunts and kills other animals for food
|
An organism that is killed and eaten by a predator is known as .
|
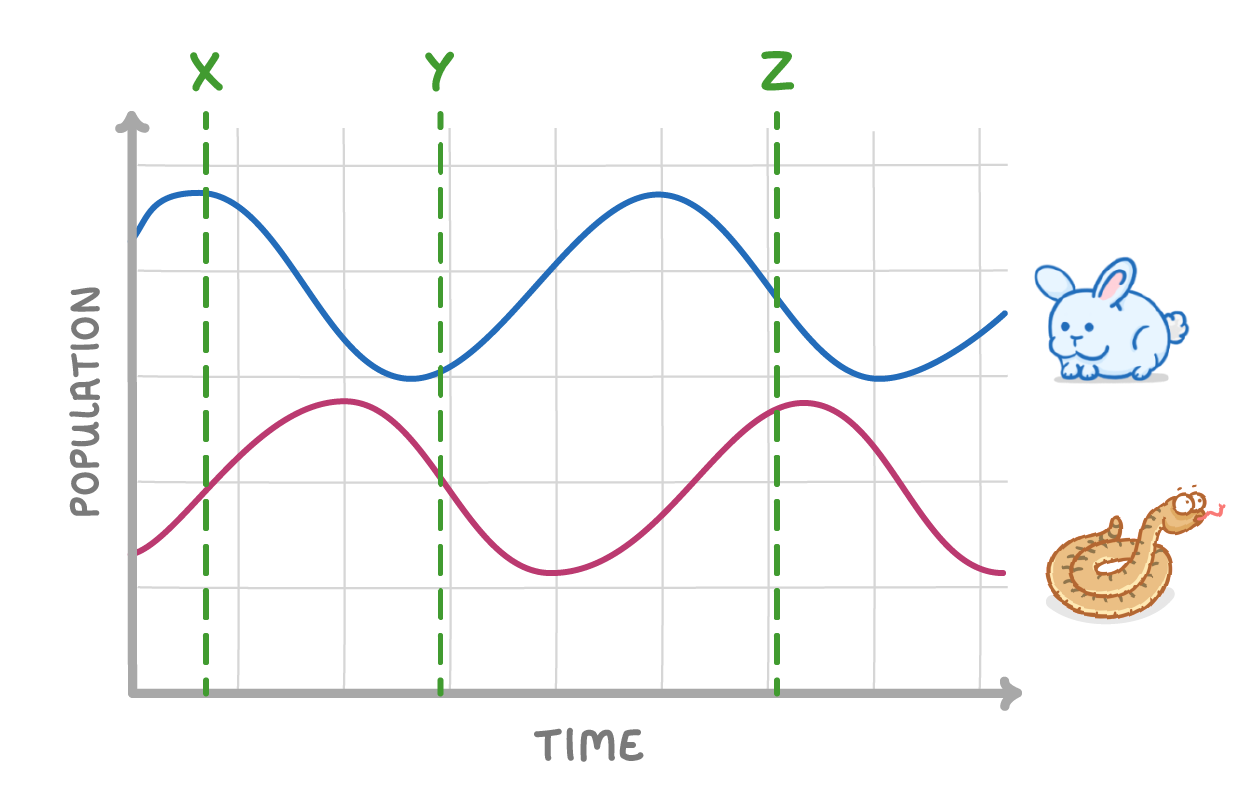
The diagram above shows the predator-prey cycle between snakes and rabbits.
increasing / decreasing
- At time X, the number of predators is because there is a lot of prey.
- At time Y, the number of predators is because there is less prey.
- At time Z, the number of prey is because there are now more predators.
|