Fish Farming
This lesson covers:
- What fish farming is
- How saltwater fish can be grown in sea cages, using the example of salmon farming
- How freshwater fish can be grown in tanks or ponds, using the example of carp farming
Why do we farm fish?
Overfishing threatens the existence of many fish species in the wild.
We use fish farming and sustainable fishing methods as an alternative way of sourcing fish that avoids overfishing.
- Fish farms are large enclosures or tanks designed to provide controlled environments for the growth of fish for human consumption. Obtaining our fish from fish farms allows wild fish stocks to recover.
- Opting for fish sourced from sustainable fisheries, in addition to fish farming, helps maintain fish stocks.
Seawater fish farming using sea cages In fish farms, large numbers of fish are bred in small enclosures, and fed high-quality food in order to maximise growth and reproduction rates, in order to meet the high demand for fish. |
Salmon farming in Scotland is an example of marine fish farming. 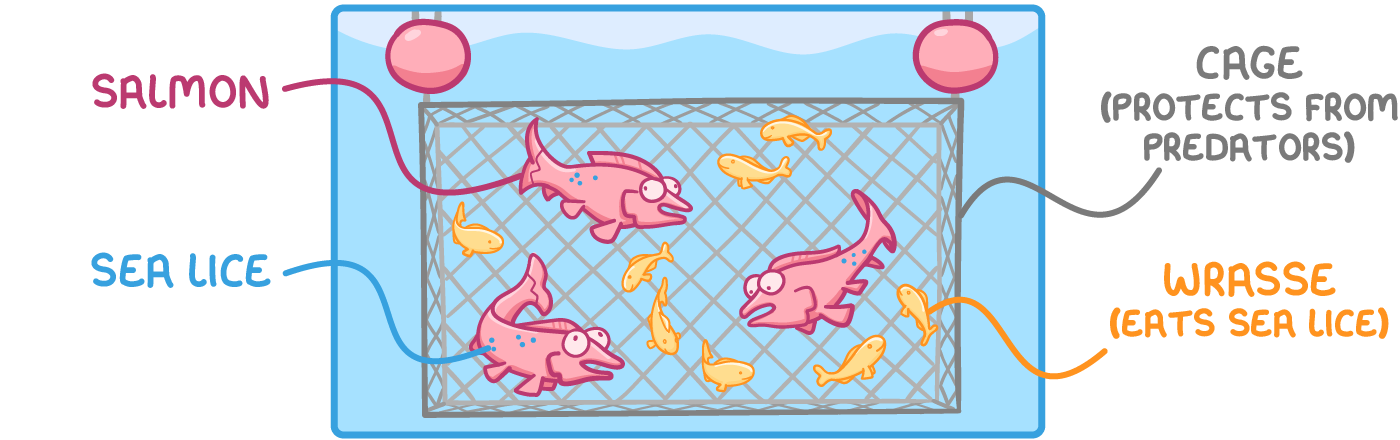 |
Fish farming overview:
|
Tank farming Aquatic species such as carp can also be farmed in controlled environments like ponds or indoor tanks. Tank farming is particularly useful when the water needs to be tightly controlled. |
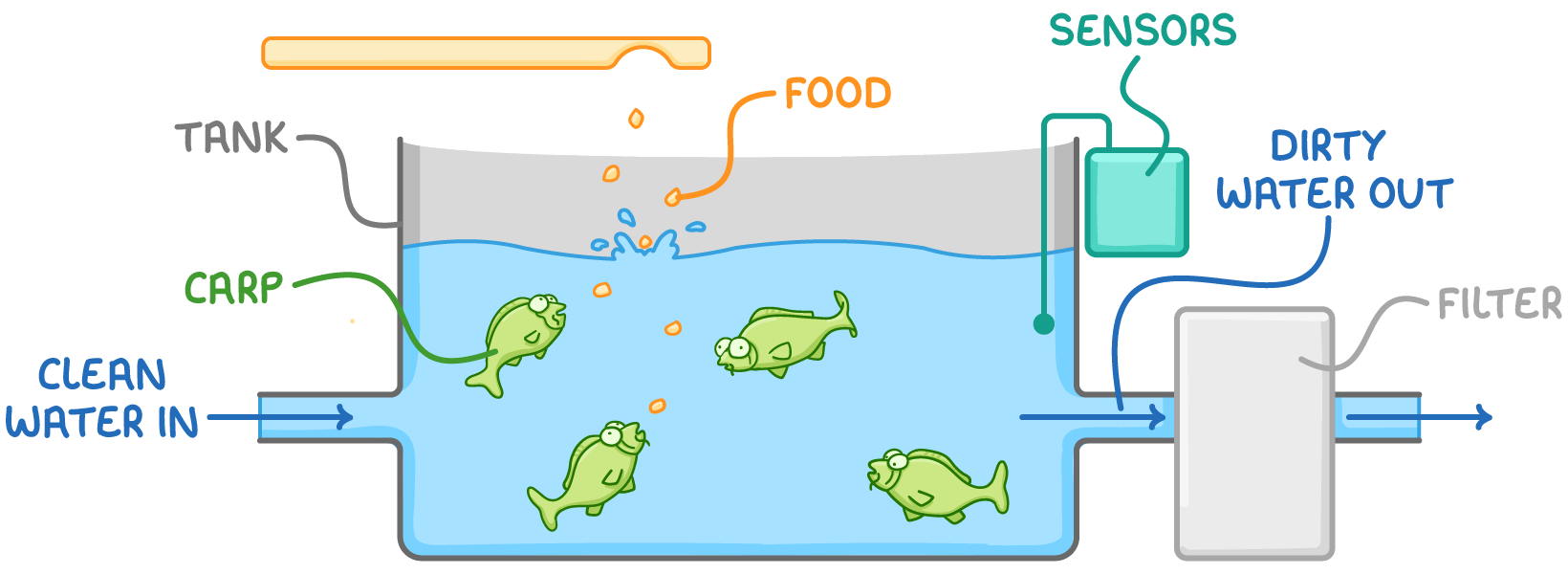 |
Tank farming overview:
|
In fish farms, what role do tanks or enclosures play in the cultivation of fish?
Decoration
Amphibious habitats
Fish feeding stations
Controlled environments
|
What is a primary purpose of providing fish in fish farms with high-protein food?
To enhance their colouration
To encourage natural foraging behavior
To promote rapid growth for human consumption
To increase their size for aesthetic appeal
|
What is the purpose of using wrasses in salmon farming?
To enhance productivity through selective breeding
To control diseases and parasites
To separate juvenile fish from adult fish
|