Cloning Plants & Tissue Culture
This lesson covers:
- Two techniques used to clone plants:
- Cuttings
- Micropropagation (also known as tissue culture)
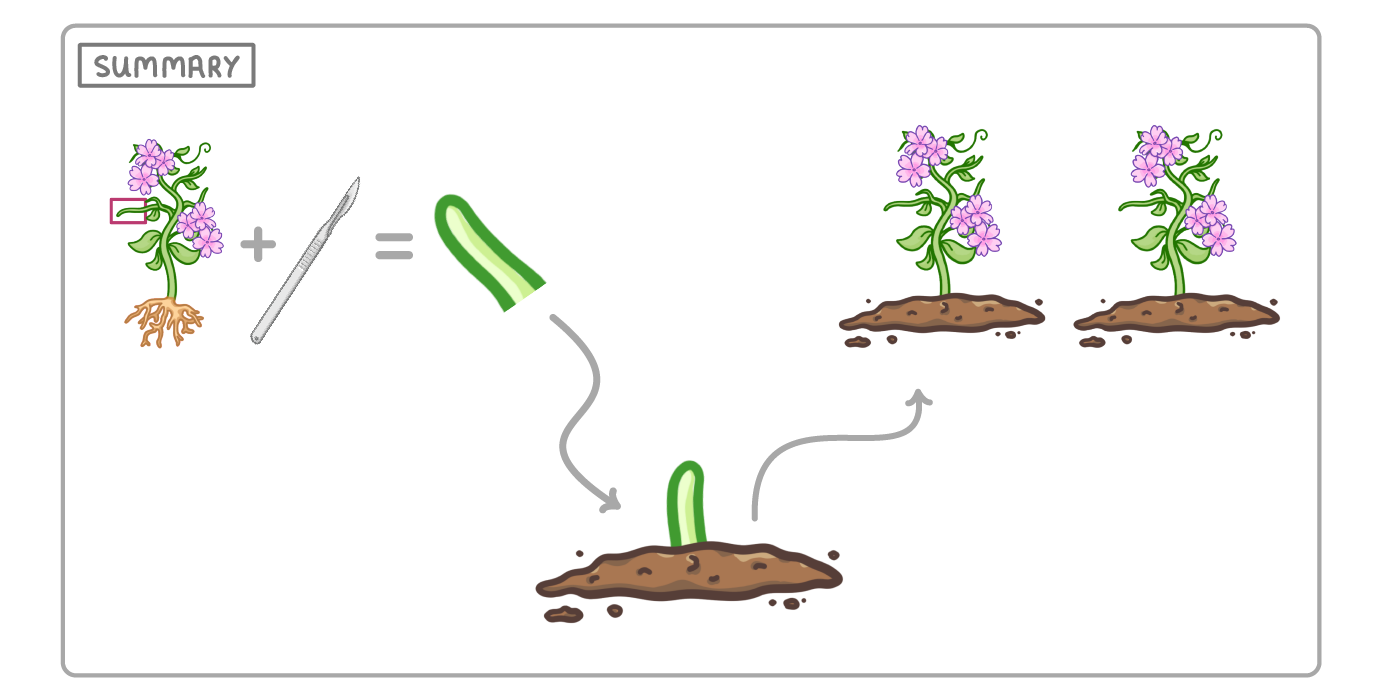
Cuttings
Cuttings can be used to quickly and cheaply clone a desirable plant:

Micropropagation (using tissue cultures) |
An alternative to using cuttings is to use cell cultures to clone a plant (this is also known as 'micropropagation'). Although it requires more expertise than using cuttings, it can produce many more clones. |
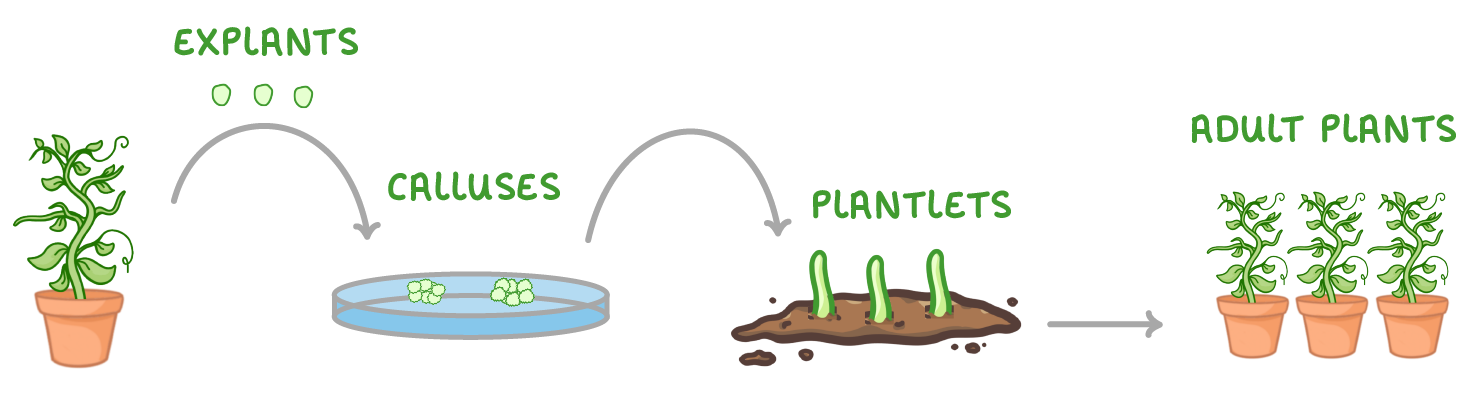 |
|
What is an explant?
A fertilised egg cell
A piece of DNA that codes for a protein
A small piece of plant that can develop into a clone
|
Give two benefits of cloning via cuttings rather than micropropagation.
|
Plants can be cloned by micropropagation.
Suggest how the tissue samples are removed and transferred to the agar medium.
|
Plants can be cloned by micropropagation. Nutrients are added to the agar medium to help plant growth.
Give two nutrients that should be added to the agar medium. Explain how each nutrient helps plant growth.
|
Plants can be cloned by micropropagation.
Suggest three precautions/conditions needed to ensure healthy growth of the small plants.
|
Some species of flowering plant are rare due to deforestation. To solve this problem scientists hope to use micropropagation to produce clones of these plants which can then be reintroduced into the wild.
Describe the process of micropropagation to clone plants.
|