Family Trees
This lesson covers:
- What 'family trees' are and how they work
- How to use the 'key' of a genetic diagram
- The example of cystic fibrosis
- How to use family trees to predict the chance of a disease being inherited
Is cystic fibrosis a dominant or recessive condition?
Dominant
Recessive
|
Cystic fibrosis is a recessive condition.
Which of the genotypes below would result in an individual having cystic fibrosis?
Heterozygous
Homozygous dominant
Homozygous recessive
|
Cystic fibrosis is a recessive condition.
Which of the genotypes below would result in an individual being a carrier for cystic fibrosis?
Homozygous dominant
Heterozygous
Homozygous recessive
|
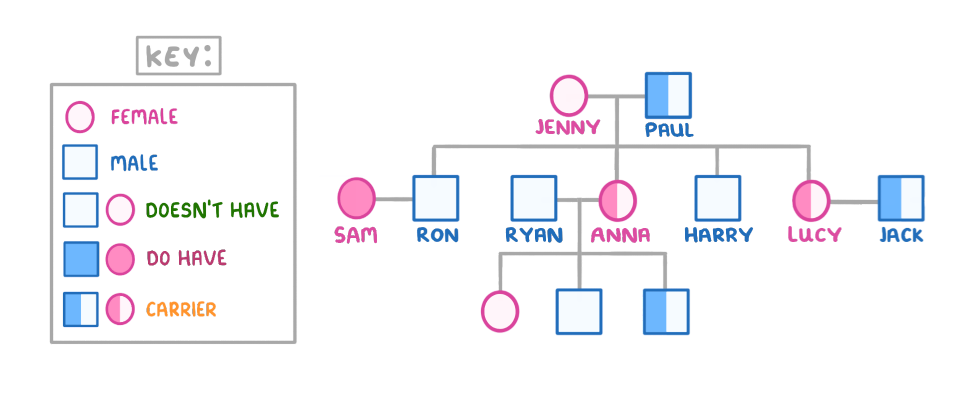
The diagram above shows a family tree for the inheritance of cystic fibrosis.
What is the genotype of Harry in the family tree above?
Ff
FF
ff
|
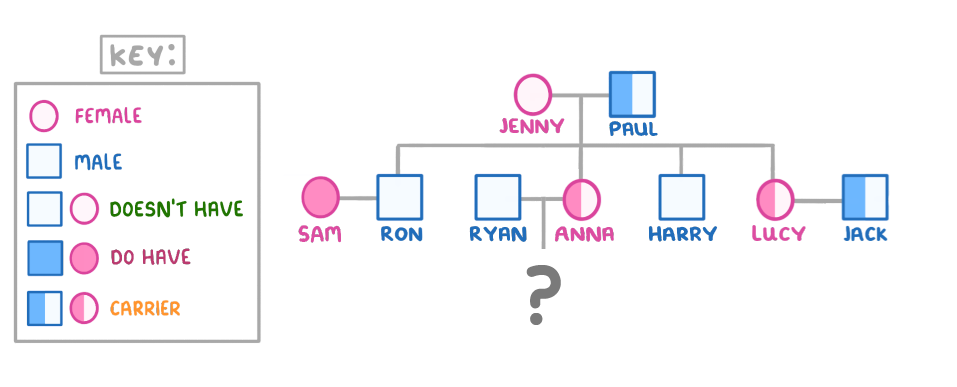
The diagram above shows a family tree for the inheritance of cystic fibrosis.
Is it possible for Ryan and Anna to have a child with cystic fibrosis?
Yes
No
|
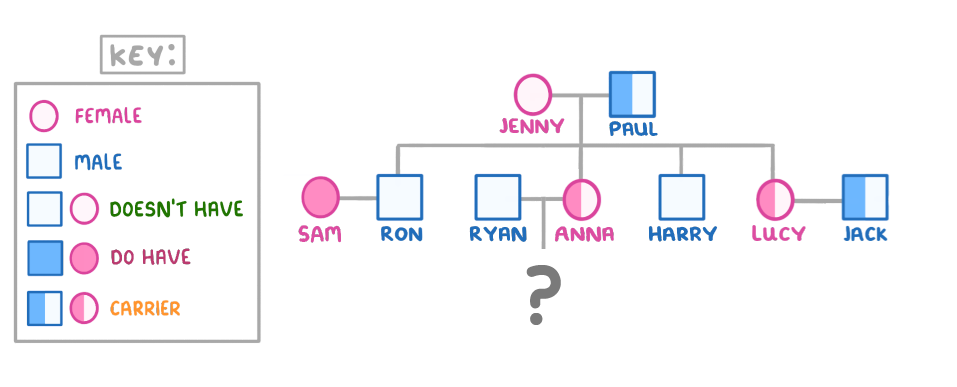
The diagram above shows a family tree for the inheritance of cystic fibrosis.
Draw a Punnett square for the cross between Sam and Ron, and then use it to calculate the percentage chance that their child will be a carrier.
Press 'Continue' when you're ready to check your answer.
|