Genetic Diagrams & Punnet Squares
This lesson covers:
- How to draw Punnett squares
- How to use Punnett squares to find the probability of a child having a certain trait
How would you describe the genotype 'AA'?
Homozygous dominant
Heterozygous
Homozygous recessive
|
How would you describe the genotype 'Hh'?
Homozygous recessive
Homozygous dominant
Heterozygous
|
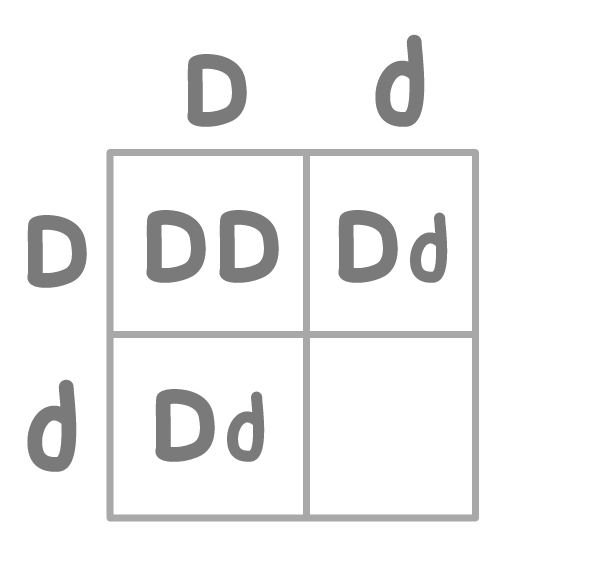
Which genotype completes the empty section of the Punnett square?
DD
Dd
dd
|
How would you describe the genotype 'dd'?
Homozygous recessive
Homozygous dominant
Heterozygous
|
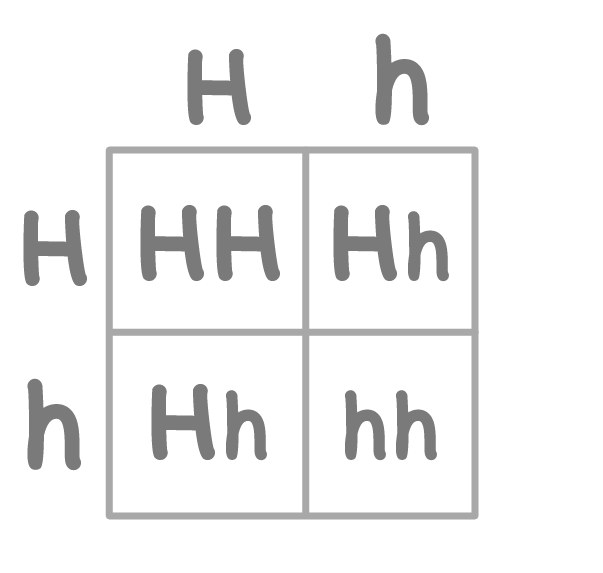
Looking at the genetic cross diagram above, what is the percentage probability that the offspring will have a heterozygous genotype?
%
|
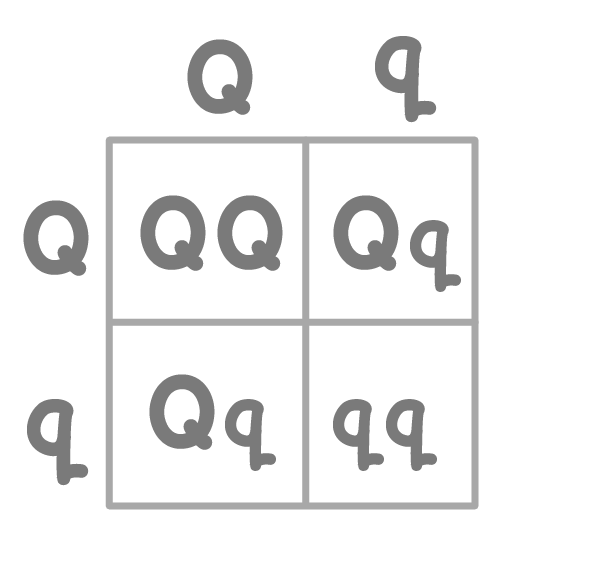
In the genetic cross shown, what is the ratio of brown-eyed : green-eyed phenotypes in the offspring?
Q = dominant allele for having brown eyes
q = recessive allele for having green eyes
1:3
2:1
1:1
3:1
|
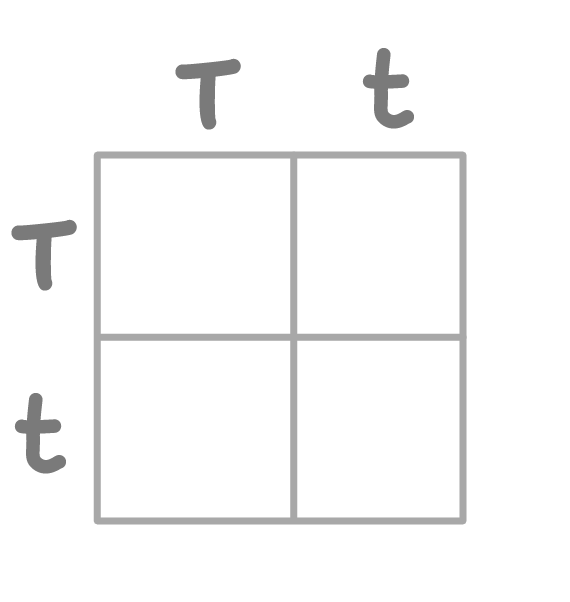
Use pen and paper to complete the Punnett square above.
Press 'Continue' when you're ready to check your answer.
|
Use pen and paper to complete a Punnett square between a homozygous dominant individual GG, and a heterozygous individual Gg.
Press 'Continue' when you're ready to check your answer.
|
In mice, fur length can be short or long. Draw a Punnett square for the cross between a homozygous dominant individual and a homozygous recessive individual.
H = dominant allele for short hair
h = recessive allele for long hair
Press 'Continue' when you're ready to check your answer.
|