Mitosis
This lesson covers:
- Why multicellular organism require a continuous supply of new cells
- What the 'cell cycle' is
- What 'chromosomes' are
- How mitosis works
Names of the four stages of mitosis Mitosis is often described as a 4 stage process. 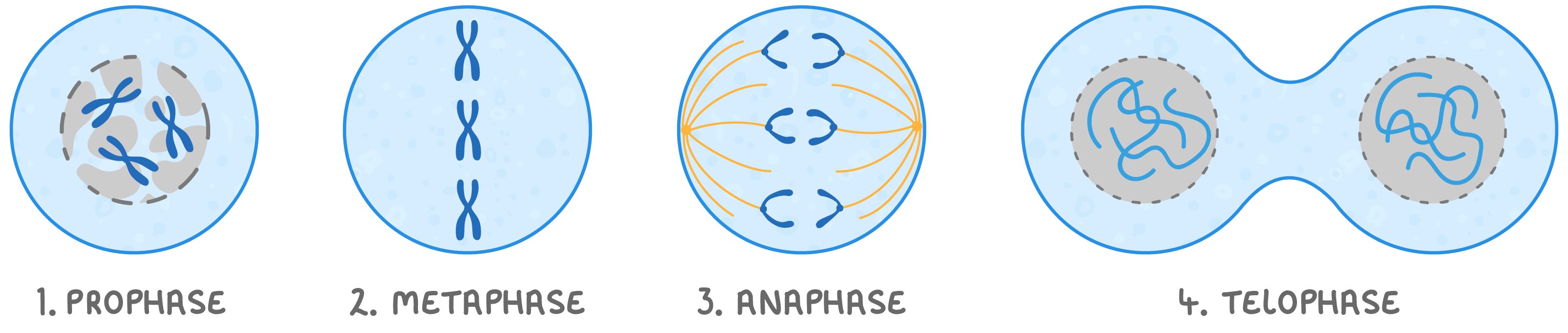 |
Remember that cells have already replicated their DNA before mitosis and each chromosome is X-shaped as it is now made up of two identical sister chromatids. |
Prophase 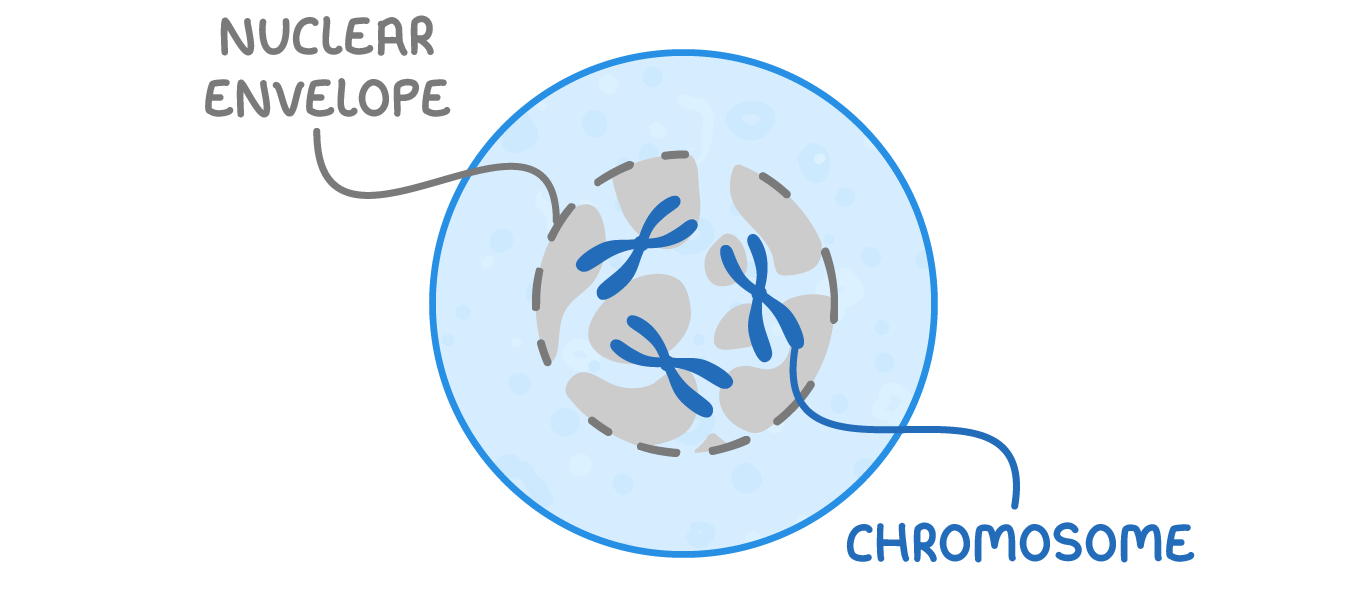 The chromosomes condense (become shorter and thicker) and are now visible under a microscope. The nuclear envelope starts to break down, leaving the chromosomes free in the cytoplasm.
|
Metaphase 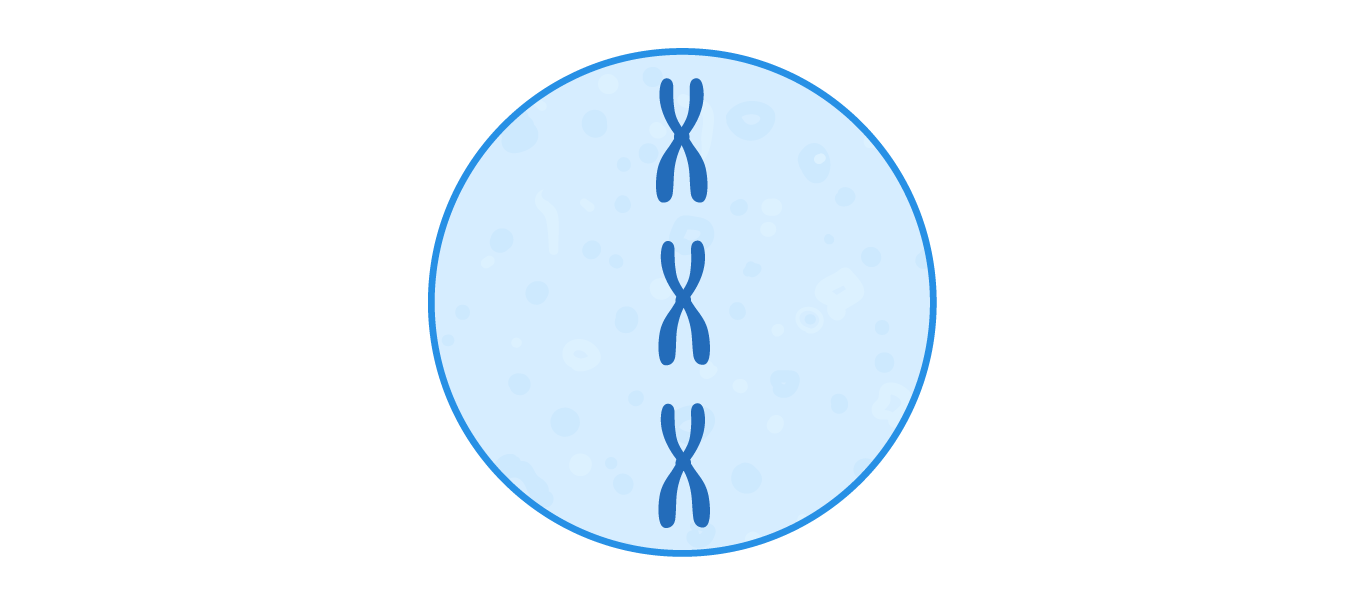 The chromosomes line up at the equator (middle) of the cell. |
Anaphase 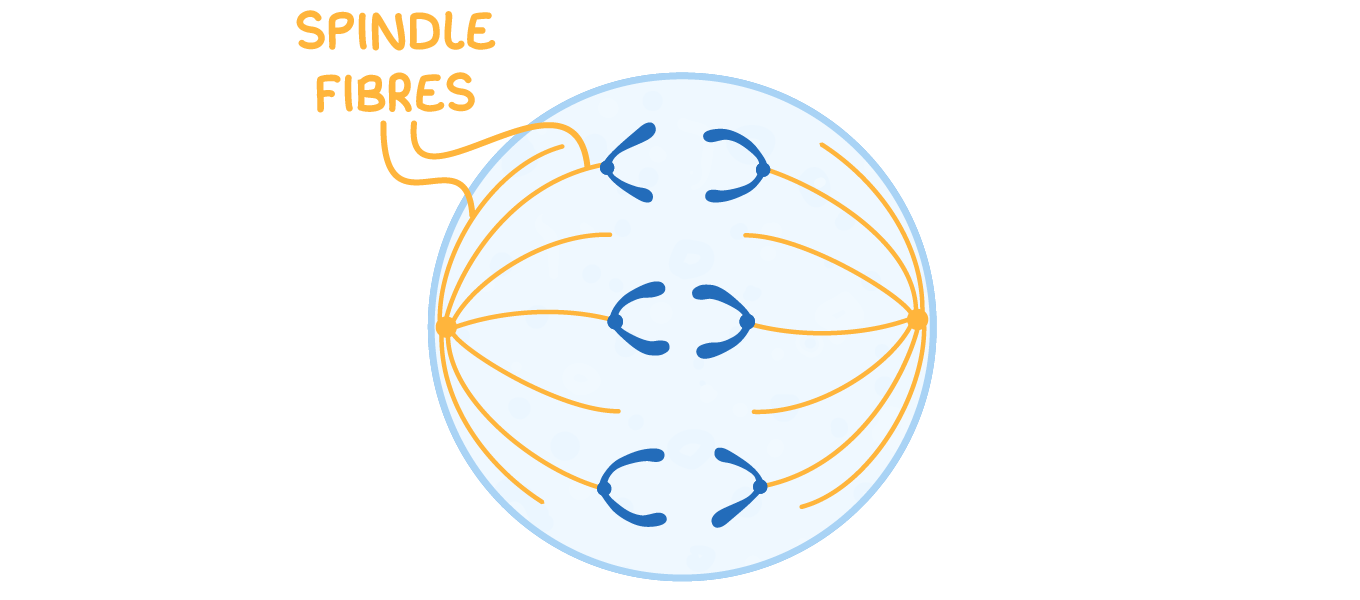 Spindle fibres contract and shorten to pull the chromatids to opposite poles of the cell. |
Telophase 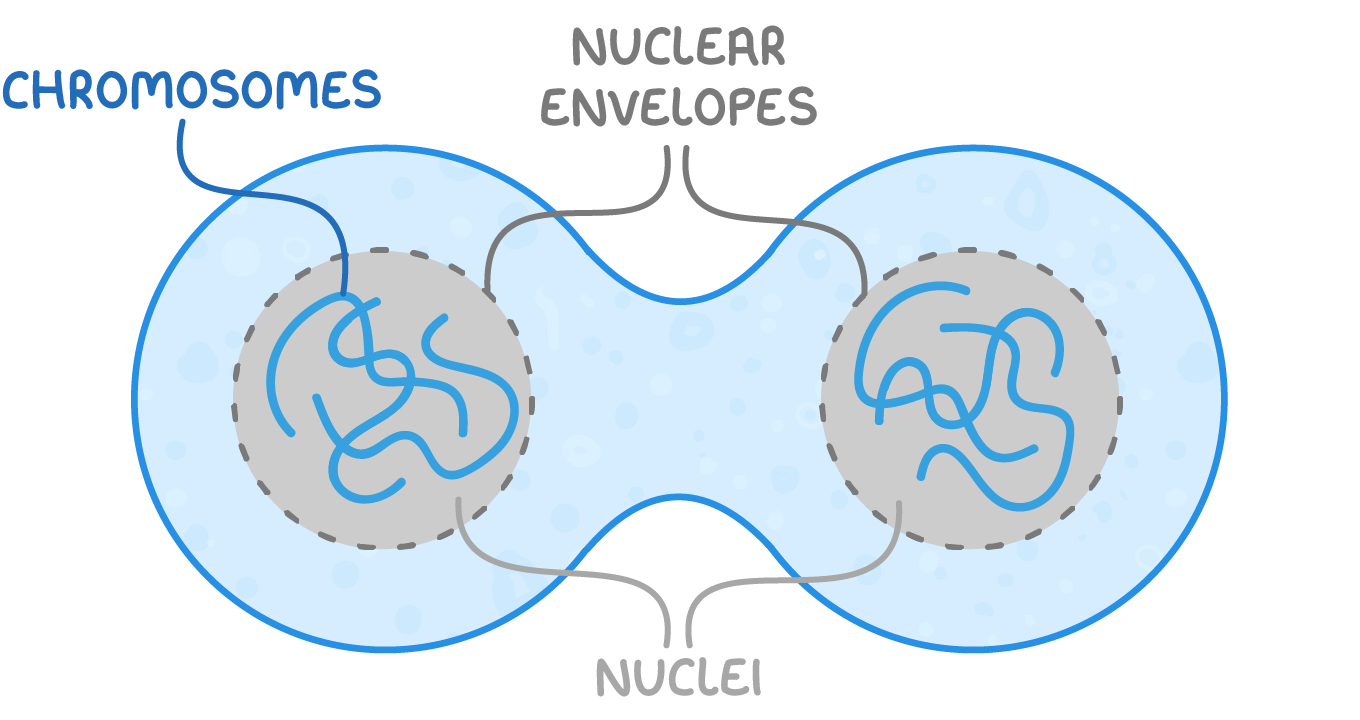 The chromatids reach the opposite poles of the cell where they uncoil to become long and thin chromosomes again. A nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes to form two nuclei. |
Cytokinesis 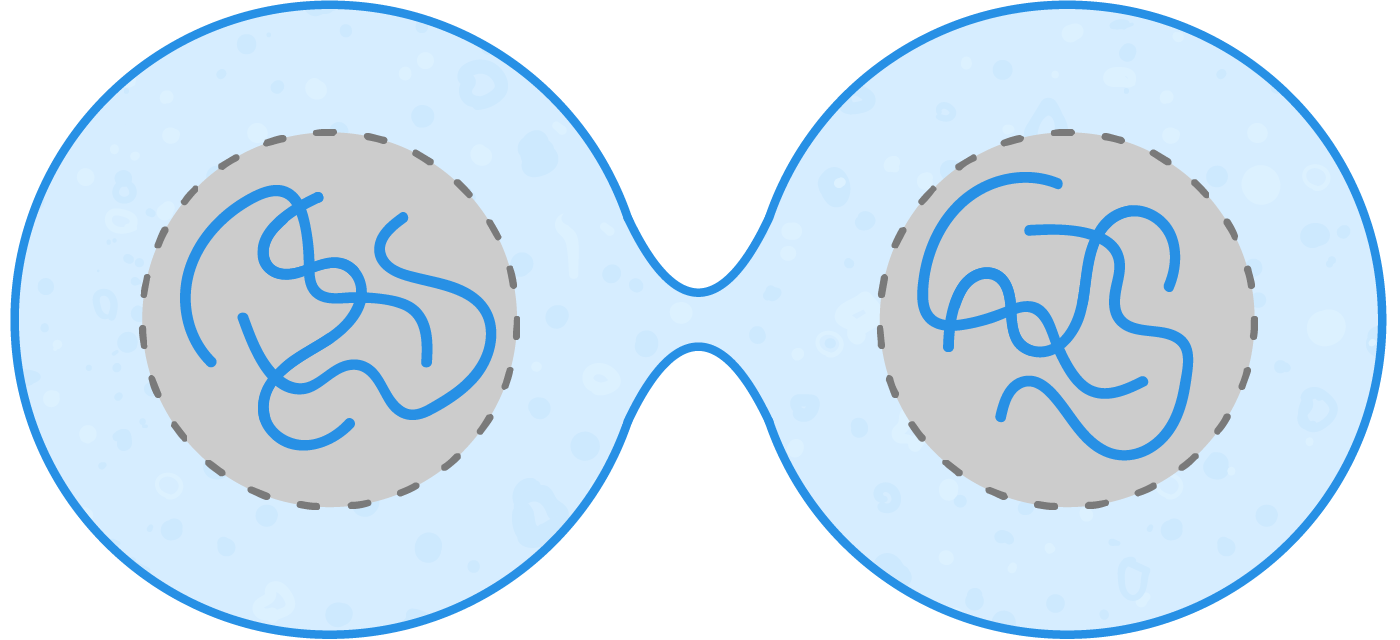 After the steps of mitosis, the cytoplasm divides in a process known as cytokinesis. This produces two daughter cells that are genetically identical to one another. |
Steps of mitosis & cytokinesis
centre / divides / daughter / chromosomes / fibres
- DNA condenses to form .
- Chromosomes line up along the of the cells.
- Cell pull the two arms of each chromosome to opposite sides (poles) of the cell.
- Cytokinesis - the entire cell to form two identical cells.
|
Multicellular organisms, like ourselves, require a continuous supply of new cells.
What are the three reasons why new cells are required?
|
What is the cell cycle?
The passage of cells around the body
The series of steps that take place as a cell grows and then divides
The process by which molecule move around the cell
|
Steps of the cell cycle
one / two / larger / chromosomes / cell / ribosomes / DNA
- Cellular growth - the cell gets and produces more sub-cellular structures, such as mitochondria and .
- DNA replication - duplicate, so that each consists of arms (copies).
- More cell growth.
- Mitosis - the divides into two.
- Cytokinesis - the divides into two.
|
How many pairs of chromosomes do most human cells have?
|
Are the cells created by mitosis genetically identical to each other, or genetically different?
Genetically identical
Genetically different
|
When a cell divides by mitosis, how many cells are produced?
|

What do we commonly call the cells produced by mitosis?
Daughter cells
Son cells
Offspring cells
|
Which stage of mitosis involves centromeres dividing to pull chromatids apart?
|
Name the four stages of mitosis in the correct order.
|