DNA 3 - Structure & How it Codes
This lesson covers:
- The structure of DNA
- The structure of nucleotides
- What 'complementary base pairing' is
- How DNA can code for a protein
DNA consists of two strands wrapped around each other in a double .
|
DNA is considered to be a polymer because it is made up of multiple monomers.
What are the monomers of DNA called?
|
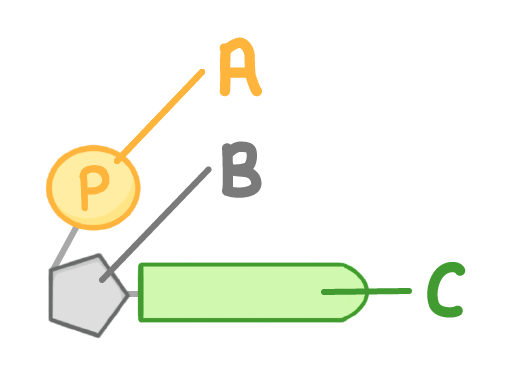
The diagram above shows a single nucleotide.
Which part is the base (sometimes called an organic base or nitrogenous base)?
A
B
C
|
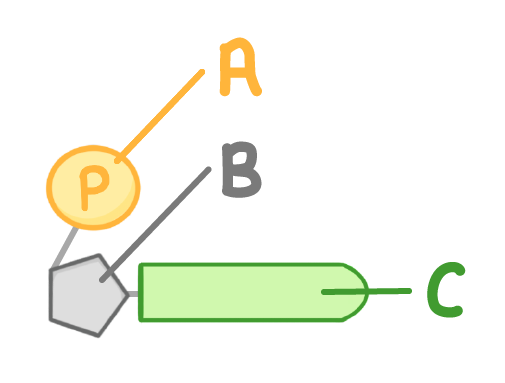
The diagram above shows a single nucleotide.
What is the part labelled A?
|
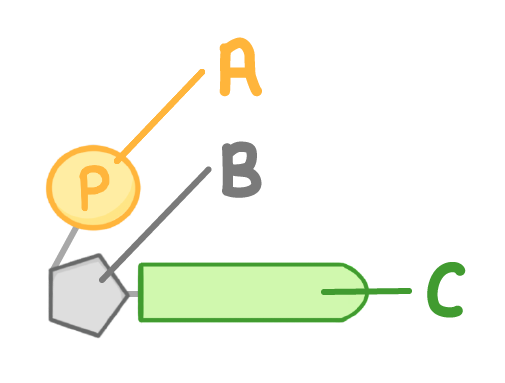
The diagram above shows a single nucleotide.
What is the part labelled B?
|
There are four types of bases in DNA. What are their names?
|
Complementary base pairing is the phenomenon whereby the same pairs of bases always bond to each other.
Which two options below describe correct pairing?
Adenine pairs with guanine
Cytosine pairs with guanine
Cytosine pairs with thymine
Adenine pairs with thymine
|
The image above show a section of DNA.
What would the sequence of DNA on the complementary strand be (reading from left to right).
|
A is section of DNA, with a particular sequence of bases, that codes for a protein.
|

Each set of three bases (known as a codon or triplet) codes for a single _________.
gene
amino acid
protein
|
DNA and proteins
sequence / bases / protein / shapes
- The sequence of in DNA determines the of amino acids in the chain.
- The chain of amino acids (a 'polypeptide'), then folds up to form a .
- Different sequences of amino acids lead to proteins with different .
- This allows different proteins to carry out different functions.
|

One function of proteins is as to act as enzymes.
What is the role of enzymes?
To let molecules move into and out of cells
To speed up the rate of chemical reactions
To provide strength to cells and tissues
|
One of the uses of proteins is to carry messages around the body.
What do we call these proteins?
Hormones
Antibodies
Structural proteins
|