Adrenaline & Thyroxine
This lesson covers:
- Where adrenaline is released from, and what it does in the body
- Where thyroxine is released from, and what it does in the body
Adrenaline  Adrenaline is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands (which sit just on top of the kidneys). |
When is adrenaline produced?  Adrenaline is produced during the 'fight or flight' response, when you get scared, stressed, or need to exercise. It prepares the body for activity. |
What does adrenaline do?  1Increases heart rate  2Increases blood pressure  3Increases blood flow to muscles  4Increases blood sugar (glucose) levels by stimulating the liver to break glycogen down into glucose |
Which organ is adrenaline released from?
Liver
Pancreas
Thyroid gland
Adrenal gland
|
What effect does adrenaline have on heart rate?
It decreaes heart rate
It increases heart rate
It has no effect on heart rate
|
When is adrenaline released?
When you're sad
When you're happy
When you're resting
When you're scared
|
Adrenaline causes changes in the body to prepare for a ‘fight or flight’ response.
Describe 3 of these changes.
|
Adrenaline causes the conversion of which substances?
Glucose ➔ glycogen
Glucagon ➔ glucose
Glycogen ➔ glucose
Glucose ➔ glucagon
|
Thyroxine  Thyroxine is produced by the thyroid gland, which is found in the neck. |
What does thyroxine do? Thyroxine has lots of roles in the body, including growth and development, but the main role is to increase your metabolic rate (the rate at which chemical reactions are taking place). |
How is the production of thyroxine regulated? 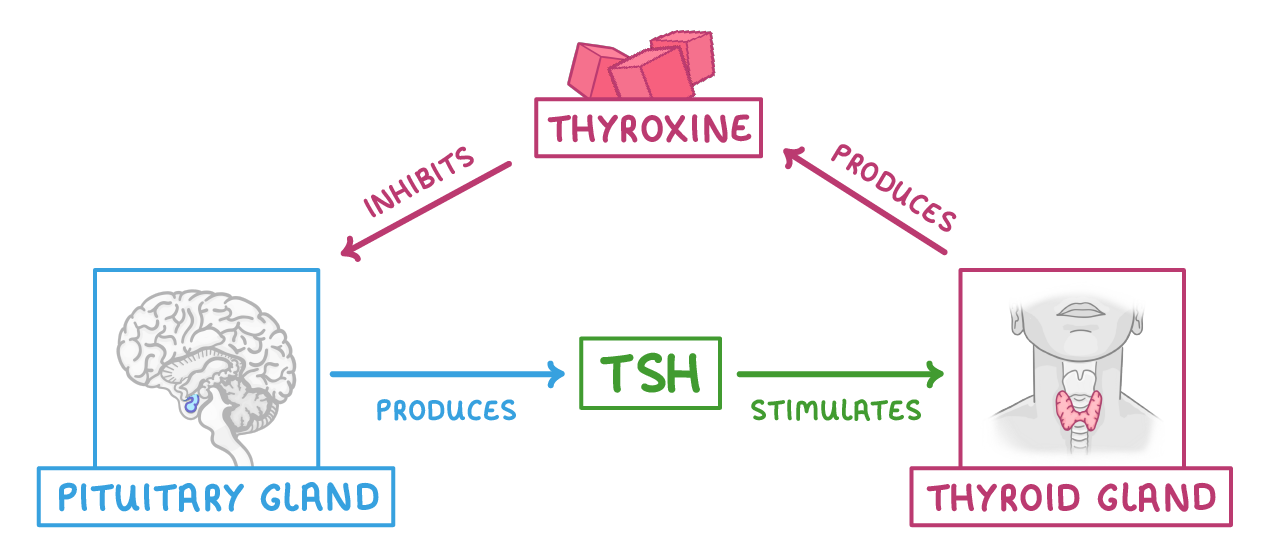 The pituitary gland produces Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine. Thyroxine then inhibits the production of TSH from the pituitary gland. |
 |
The exact steps are as follows: |
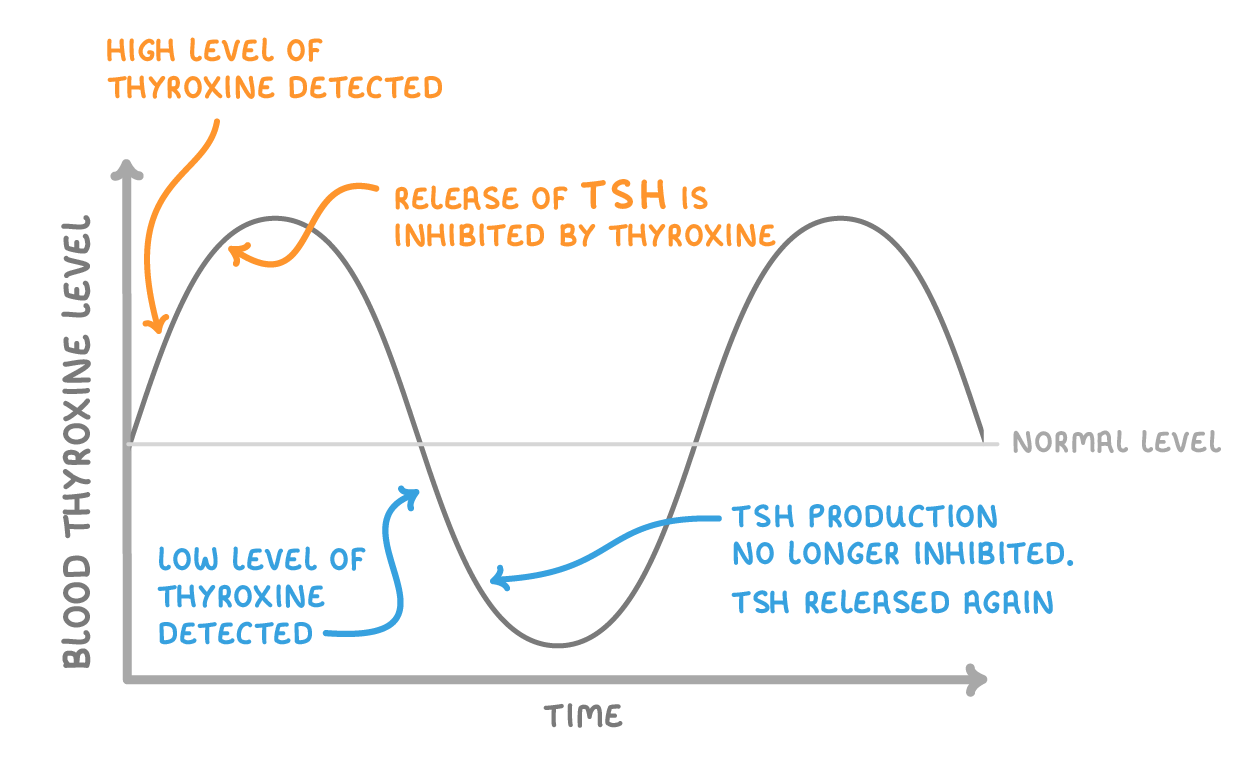
1If thyroxine levels are too low - the pituitary gland will release TSH. This then stimulates the thyroid gland to release more thyroxine. So thyroxine levels in the blood increase back up to normal. |
2If thyroxine levels are too high - the thyroxine will inhibit the pituitary gland from producing TSH. Less TSH means that the thyroid gland won't release as much thyroxine. So thyroxine levels in the blood fall back to normal. |
 |
The control of thyroxine levels by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland is an example of negative feedback. If levels of thyroxine rise too high, it will bring about changes to lower the levels, and if they fall too low, it brings about changes to raise them back up. |
 |
Which organ is thyroxine released from?
Liver
Thyroid gland
Adrenal gland
Pancreas
|
What is the main role of thyroxine?
|
Which organ is TSH released from?
Testes
Pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Kidneys
|
The hormone TSH is involved in the regulation of thyroxine levels.
What does TSH stand for?
|
Does thyroxine stimulate or inhibit the pituitary gland from releasing TSH?
Stimulate
Inhibit
|
Does TSH stimulate or inhibit the thyroid gland from releasing thyroxine?
Stimulate
Inhibit
|
Which type of feedback is involved in the regulation of thyroxine levels?
Positive feedback
Negative feedback
Recursive feedback
|
Describe what will happen when thyroxine levels are too high.
|