Obesity
This lesson covers:
- What obesity is
- What BMI is, and how it's used
- What wait-to-hip ratio is, and how it's used
Obesity Obesity is a non-communicable disease, characterised by large amount of excess body fat. People who eat a lot of sugary or fatty foods and who don't do much exercise are usually at risk of becoming obese. This is because body fat develops when an individual's diet provides them with more energy than they use. |
Measures of obesity Measuring obesity is important because obesity is associated with a number of serious health issues. Two common methods of measuring obesity: 1Body mass index (BMI) 2Waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) |
Body mass index (BMI) |
BMI is calculated using a person's mass and height. The formula for BMI is shown below. BMI = (height (m))2mass (kg) |
Once a BMI value has been calculated, it can be compared to a table of BMI values, and used to classify an individual's weight. 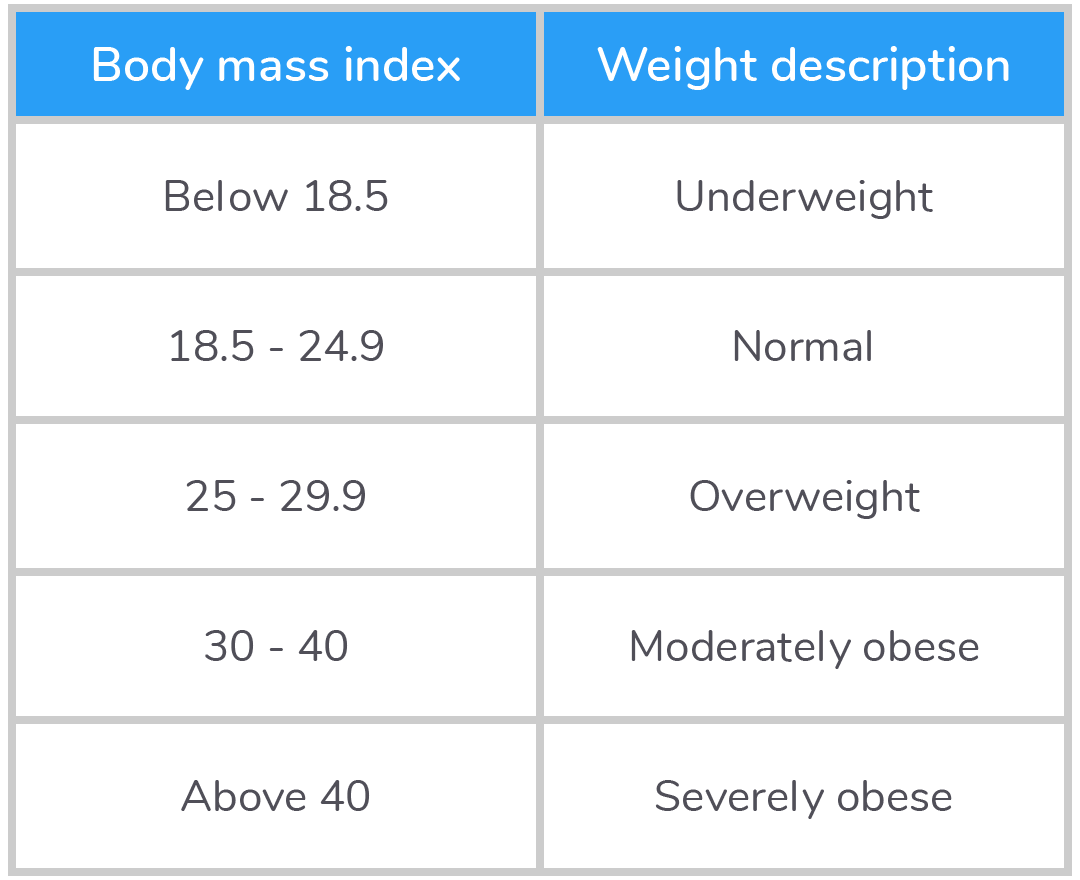 |
Worked example: calculating BMI An individual has a mass of 72 kg, and is 1.77 m tall. Calculate their body mass index (BMI), and identify their BMI classification using the table provided in the section above. |
BMI can be an unreliable measure of obesity Factors other than body fat affect a person's mass, and these other factors can make BMI measurements unreliable. For example, muscle tissue has a greater mass than fat tissue, and individuals with lots of muscle often have a high BMI, but are not overweight or obese. |
Waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) |
Waist-to-hip ratio (sometimes called 'WHR') is an another method of measuring obesity. To calculate someone's waist-to-hip ratio, measure the circumference of their waist and the circumference of their hips (usually in cm), and use the following formula to calculate the ratio. WHR = hip circumferencewaist circumference |
A higher waist-to-hip ratio usually indicates more abdominal fat. If a person has too much abdominal fat it is classified as abdominal obesity. |
The waist-to-hip ratio classified as abdominal obesity is different for men and women: For men - a waist-to-hip ratio greater than 1.0 is classified as abdominal obesity. For women - a waist-to-hip ratio greater than 0.85 is classified as abdominal obesity. |
Identifying abdominal obesity is useful because abdominal obesity increases the risk of developing other obesity-related health issues, such as heart attacks and strokes. |
Worked example: calculating waist-to-hip ratio An man has a waist circumference of 32 cm, and a hip circumference of 34 cm. State whether or not his waist-to-hip ratio indicates abdominal obesity. |
What is the definition of obesity?
a high metabolic rate
excessive muscle mass
low body mass
excessive body fat
|
How is someone's BMI calculated?
mass (lb) multiplied by height (m)
mass (kg) divided by height (m2)
mass (lb) divided by height (cm2)
height (cm) divided by mass (kg)
|
What does a high waist-to-hip ratio suggest about body fat distribution?
higher fat accumulation in the hips
low overall body fat
higher fat accumulation in the waist
even distribution of fat
|
Which waist-to-hip ratio is generally considered indicative of a higher risk for cardiovascular diseases in women?
1.0
0.85 or higher
1.2 or higher
0.8 or lower
|