Immune System & Defences
This lesson covers:
- The physical and chemical barriers that prevent pathogens from entering our bodies.
- The immune system, which destroys pathogens that do mange to enter our bodies.
The difference between antigens and antibodies.
An antigen is any substance that your body sees as foreign, which then causes your immune system to produce antibodies against it. For example, the toxins and cell walls of pathogens would be considered antigens.
An antibody on the other hand is a protein produced by our white blood cells that binds to specific antigens. This acts as a signal to our immune system to destroy the antigen (or the pathogen it is part of).
What are memory cells?
The first time you're infected with a new pathogen, you normally get quite ill as it takes your body time to identify and destroy the pathogens.
However, in the process, you also develop memory cells, which are a special type of white blood cells that remember the pathogen for next time.
This means that if you're infected again your immune system can respond much more quickly and powerfully - and so you don't get as ill!
Which of the following act as barriers to reduce the entry of pathogens?
(Select all that apply)
White blood cells
Skin
Enzymes in tears
Phagocytes
Hairs in the nose
|
How does skin help to defend against disease?
(Select all that apply)
It secretes oils and antimicrobial substances that kill pathogens
It traps pathogens so that they can be removed
It covers the body, physically preventing pathogens from entering
|
Does skin act as a physical or chemical barrier to pathogens?
Physical barrier
Chemical barrier
|

The nose has hairs inside it that act as a physical barrier to pathogens. What are the hairs in the nose coated with to catch pathogens?
Enzymes
Phagocytes
Mucus
|
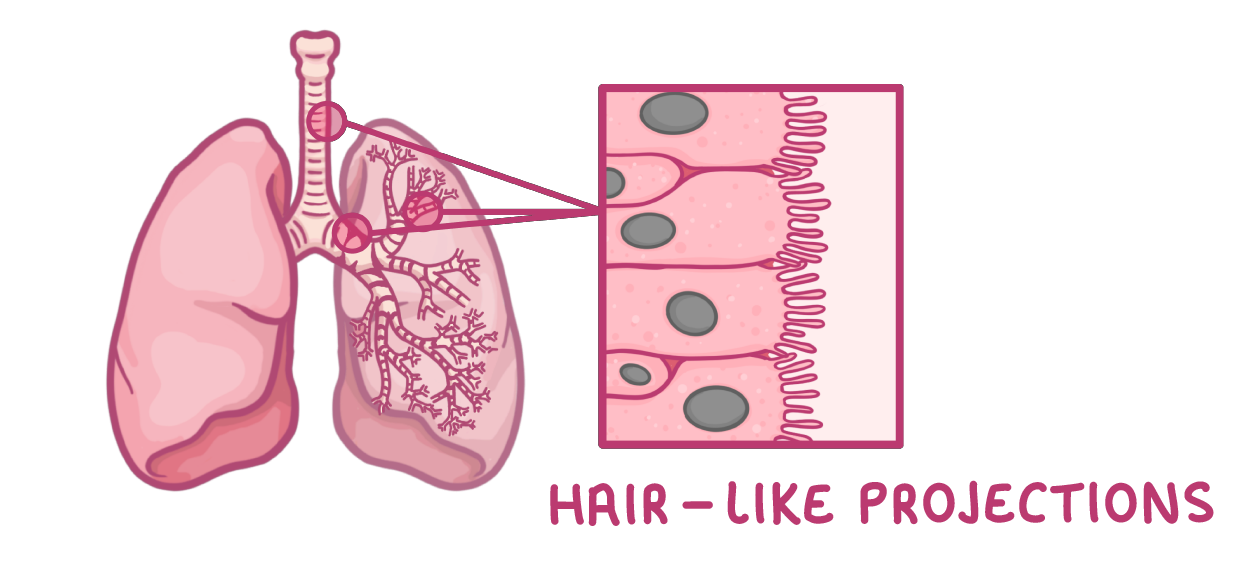
The cells that line the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles have tiny hair-like projections that waft the mucus and pathogens away from the lungs.
What are these structures called?
|
What substance does the stomach produce to kill pathogens?
Mucus
Enzymes
Nitric acid
Hydrochloric acid
|
Does the acid produced by the stomach act as a physical barrier, or a chemical barrier, to pathogens?
Physical barrier
Chemical barrier
|
What is the role of the immune system?
To locate and destroy pathogens that enter the body
The allow communication between different parts of the body
To regulate the level of water and ions in the blood
|
Which type of cells are part of the immune system?
Red blood cells
Skin cells
Nerve cells
White blood cells
|
Phagocytes are a special type of white blood cell.
Which of the following are functions of white blood cells?
(Select all that apply)
Produce antitoxins
Producing antibodies
Phagocytosis
Produce hormones
|
Stages of phagocytosis
cells / engulf / make / destroy / bind / phagocyte
- Phagocytosis is carried out by a special type of white blood cell called a .
- The first step is for the phagocyte to track down a pathogen, and then to it.
- The phagocyte's membrane will then surround the pathogen and it.
- Finally, enzymes inside the phagocyte break down the pathogen in order to it.
|
What do antitoxins do?
Stimulate the immune system
Bind and neutralise the toxins produced by bacteria
Kill pathogens
|