Communicable Disease 2 - Viruses
This lesson covers:
- What viruses are
- How viruses spread
- Examples of viral diseases
Ebola - key information
- Pathogen - Ebola virus
- Transmission - direct contact with bodily fluids of an infected person or through contaminated surfaces
- Symptoms - fever, bleeding, severe headache, muscle pain
- Treatment - supportive care, including rehydration
- Prevention - strict infection control measures, with isolation of patients and sterilisation of all contaminated surfaces, and public health education
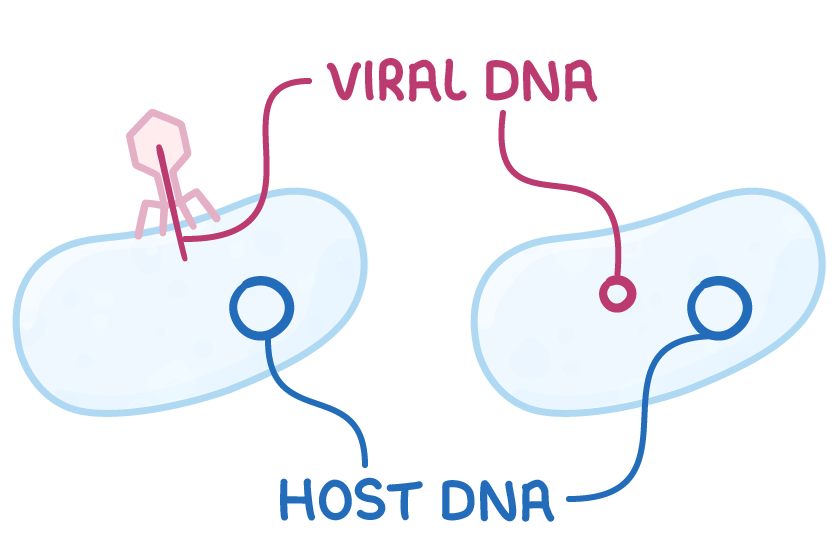
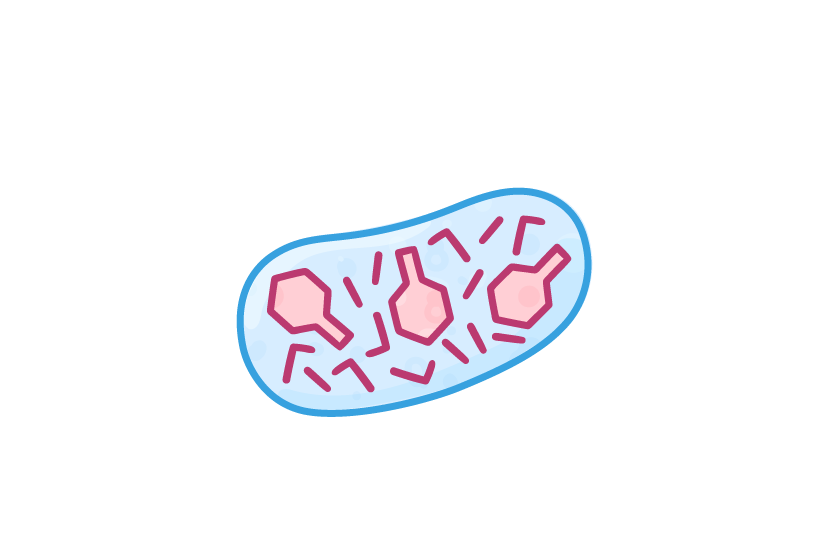
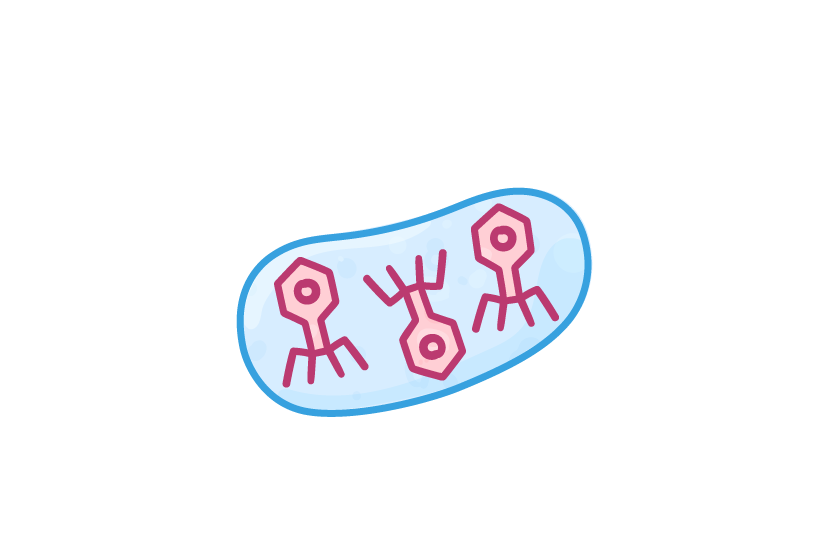
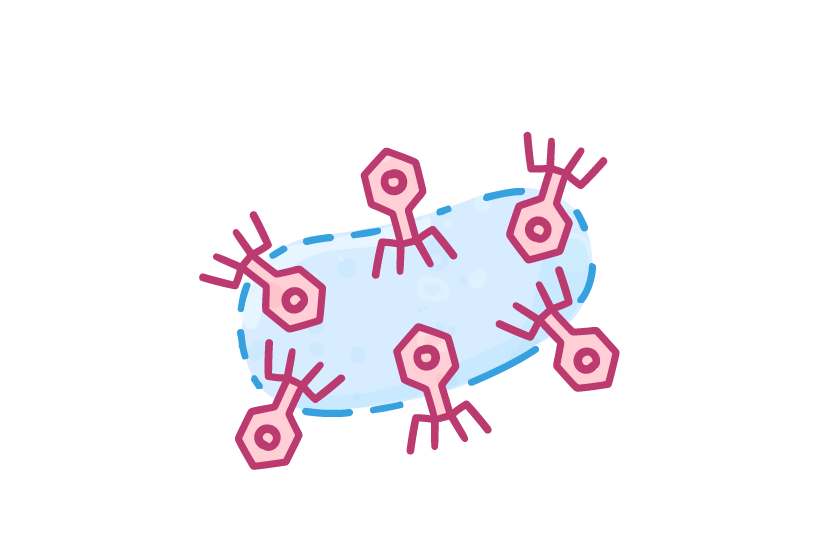
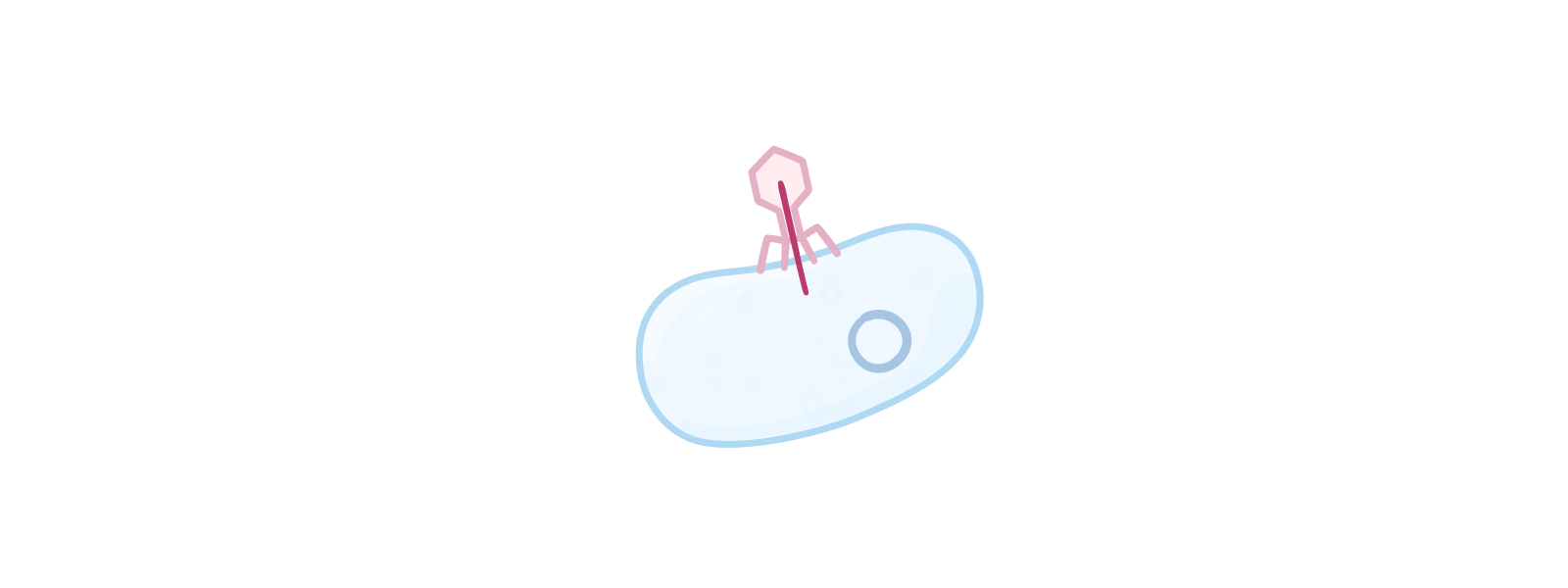
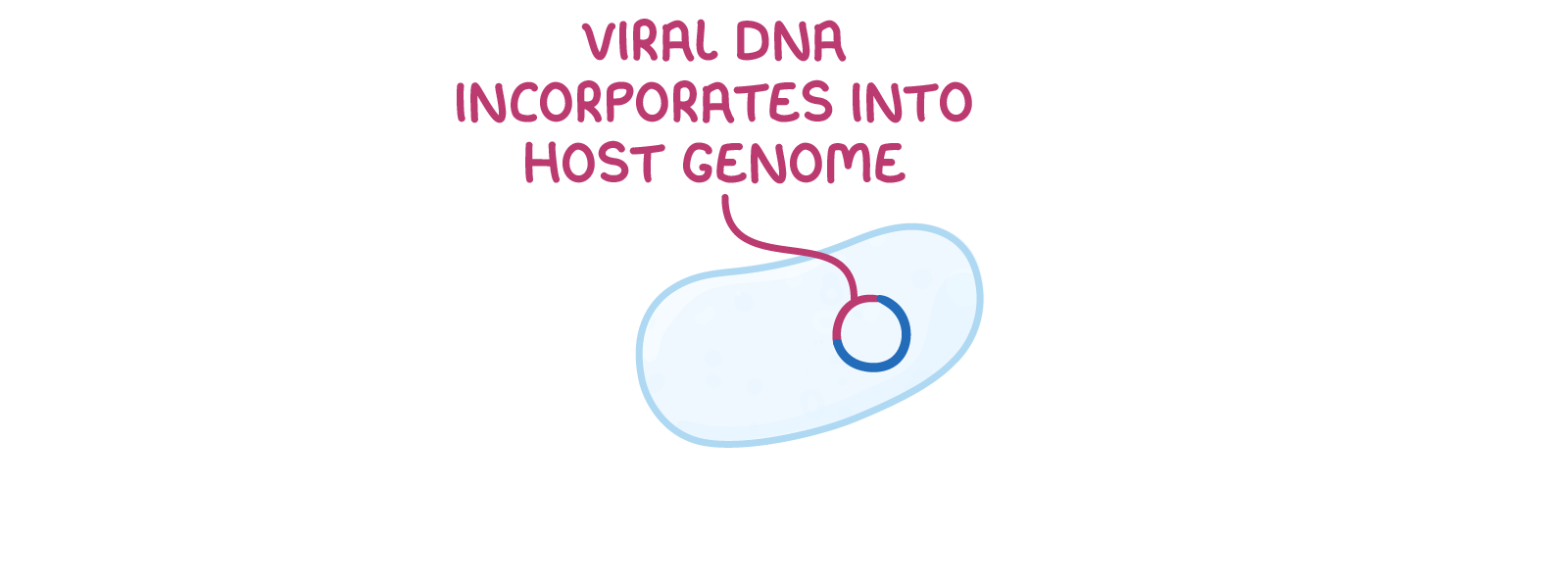
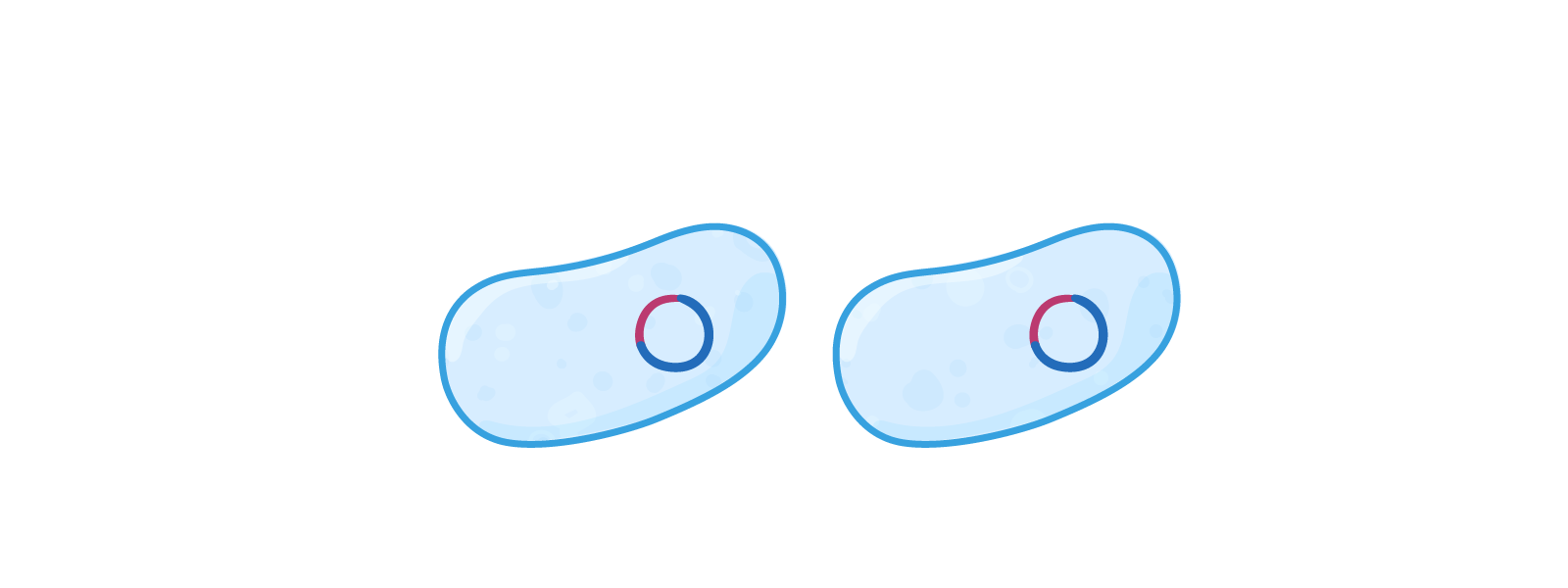
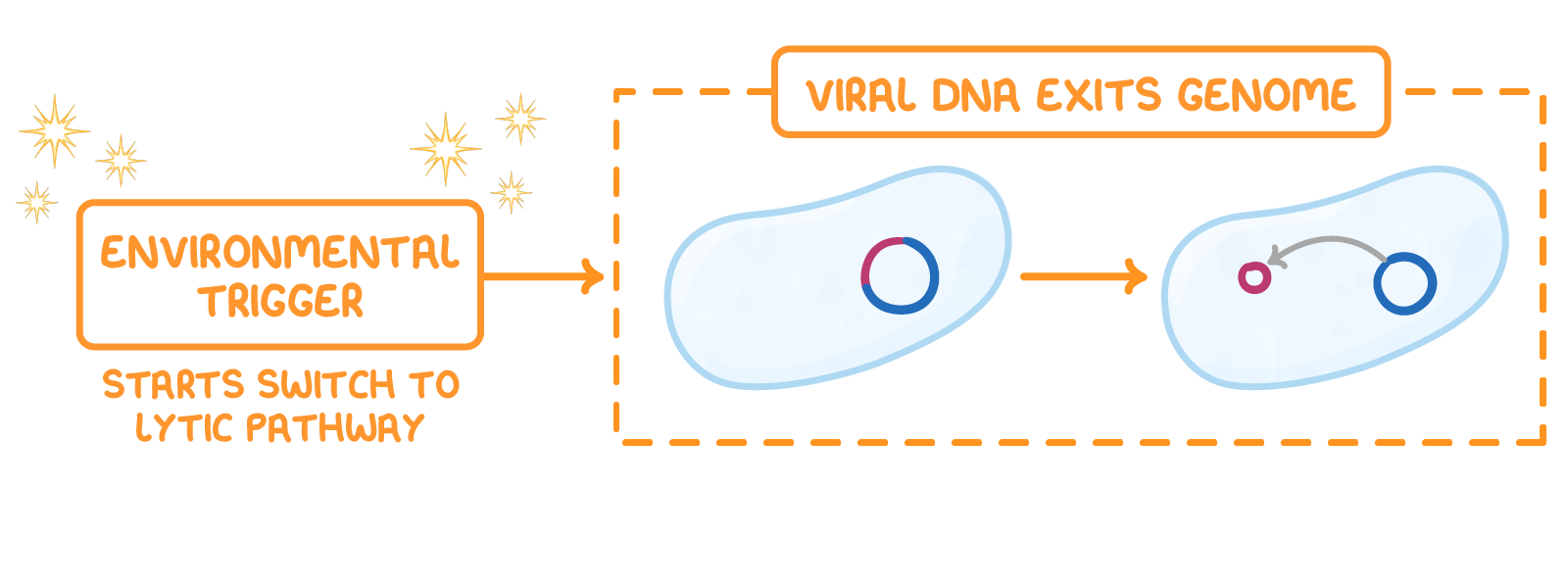
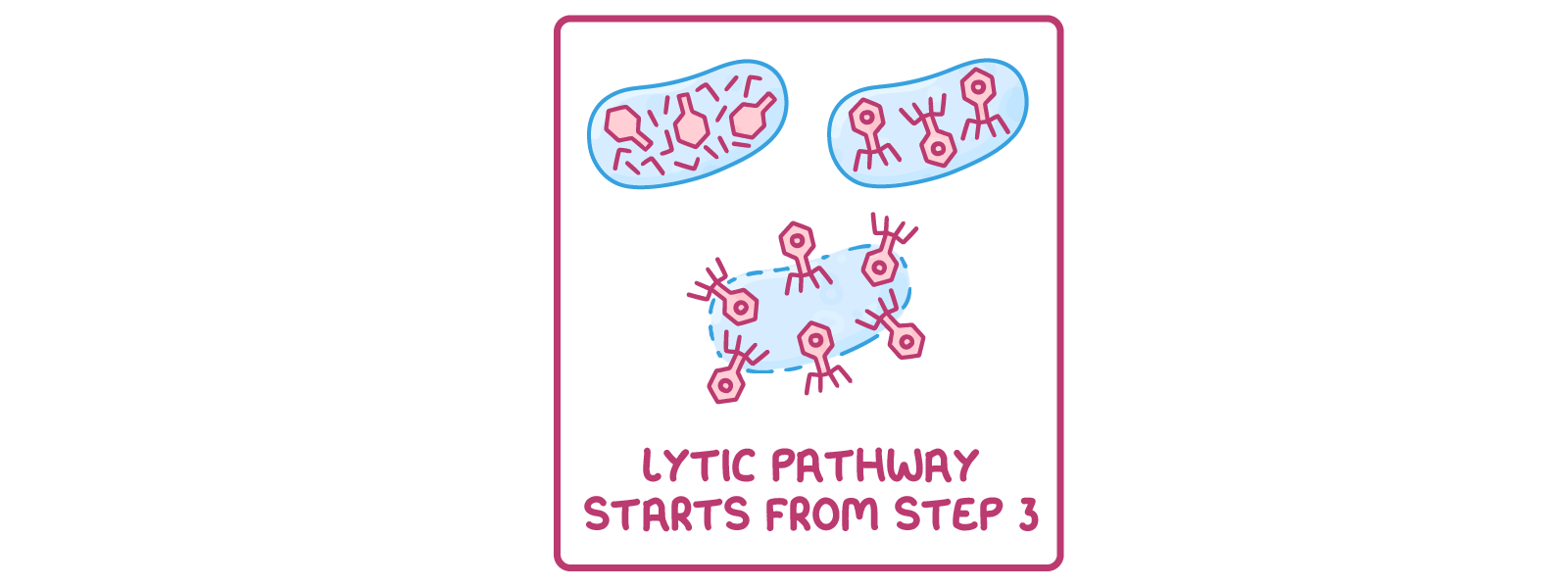
The lifecycle of a virus Viruses can only reproduce inside the cells of living organisms. Viruses can reproduce via two different pathways, depending on the environmental conditions and the type of virus:
|
Lytic pathway 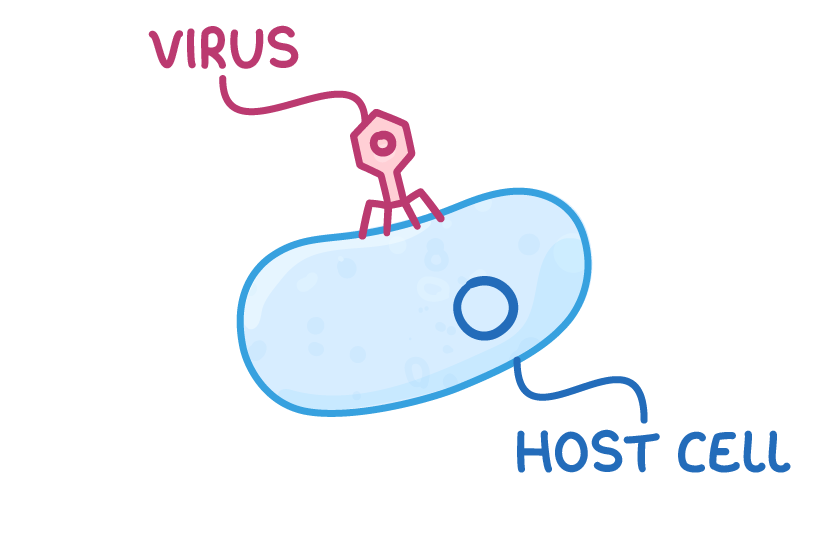 1Virus attaches to a host cell. |
Lysogenic pathway 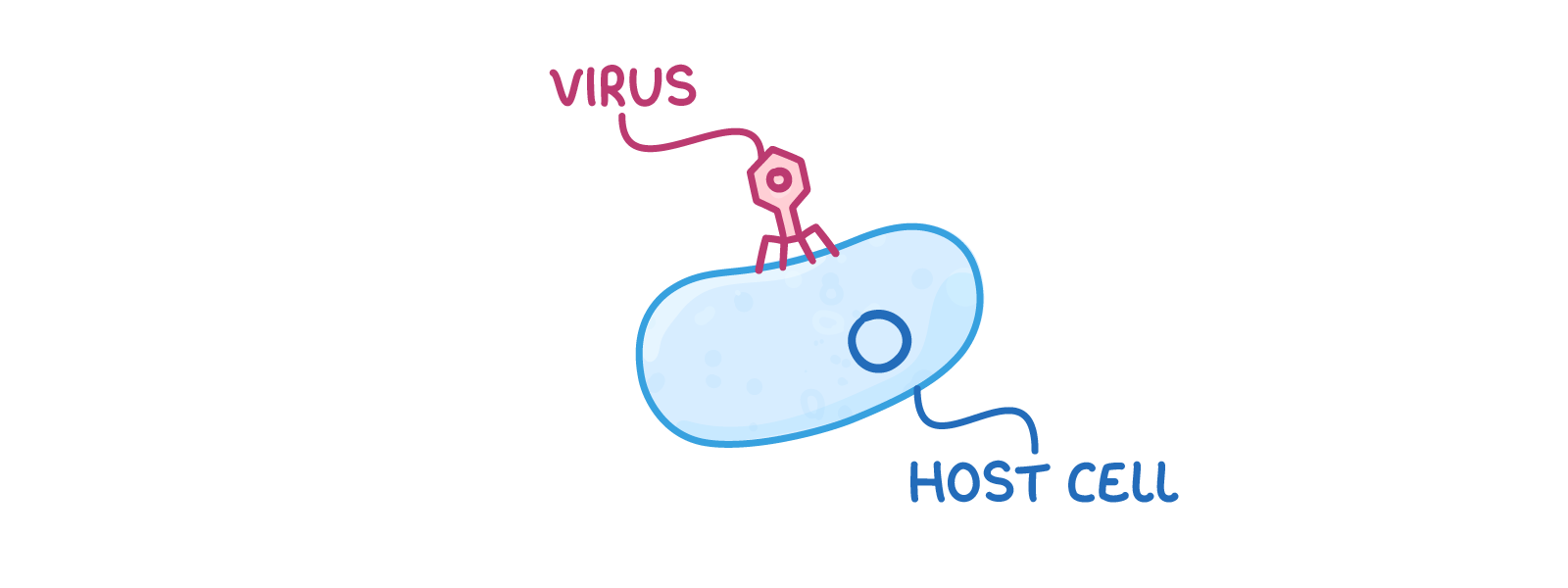 1Virus attaches to a host cell. |
Are viruses living organisms?
Yes
No
|
Are viruses made of cells?
Yes
No
|
Viruses are about 10,000 times __________ than animal or plant cells.
larger
smaller
|
How viruses spread and multiply
spread / food / infect / virus / cells
- Viruses can pass between humans via the air, contaminated or water, or by direct contact.
- As they can't reproduce themselves, viruses have to enter one of our , and then use it to create multiple copies of the virus itself.
- Once there are lots of copies, the viruses cause the cell to burst, and then go on to neighbouring cells.
|
How can measles be spread between people?
Via direct contact
Via droplets in air when an infected person coughs or sneezes
Via contaminated food
|
What are the symptoms of measles?
(Select all that apply)
Fever (feeling hot and cold)
Red skin rash
Compromised immune system
|
In the UK, are most people are vaccinated against measles?
Yes
No
|
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
This is because it affects humans, it weakens the immune system (immunodeficiency), and it is a virus.
Which two ways can HIV be spread between people?
Sexual contact
Exchange of bodily fluids
Coughing or sneezing
|
Infection with the HIV virus can lead to __________. This is where the immune system is so weak that the person can catch unusual infections.
SDIC
SIDS
AIDS
|
What is the treatment for HIV/AIDS?
Statins
Antiretroviral drugs
Kidney transplant
|

What type of organism does Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) infect?
Bacteria
Plants
Fungi
Animals
|
What is the main symptom of Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)?
Roots start to die
Leaves turn black
Patches of the leaves get discoloured
|
Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) reduces the amount of photosynthesis that a plant can do.
What are the consequences of this?
(Select all that apply)
The plants leaves will turn purple
The plant won't be able to grow as well
The plant won't be able to produce as many sugars
|
What is the main mode of transmission for the Ebola virus?
Airborne droplets from sneezing
Direct contact with infected bodily fluids
Mosquito bites
Contaminated food
|