Eyes 2 - Accommodation & Visual Defects
This lesson covers:
- How the 'accommodation reflex' allows us to see both near and distant object
- The roles of the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments
- How we can use glasses to fix near or far-sightedness
Which two structures refract (bend) light entering the eye?
Lens
Pupil
Cornea
Iris
|
When light passes into the eye, where on the retina should the light be focused?
The sclera
The optic nerve
The fovea
The vitreous fluid
|
When looking at a nearby object, the light from the object hits the eye at a wide angle. This means that the eye needs to refract the light strongly.
To achieve this, what should the shape of lens be?
Cuboidal
Short and fat
Long and thin
|
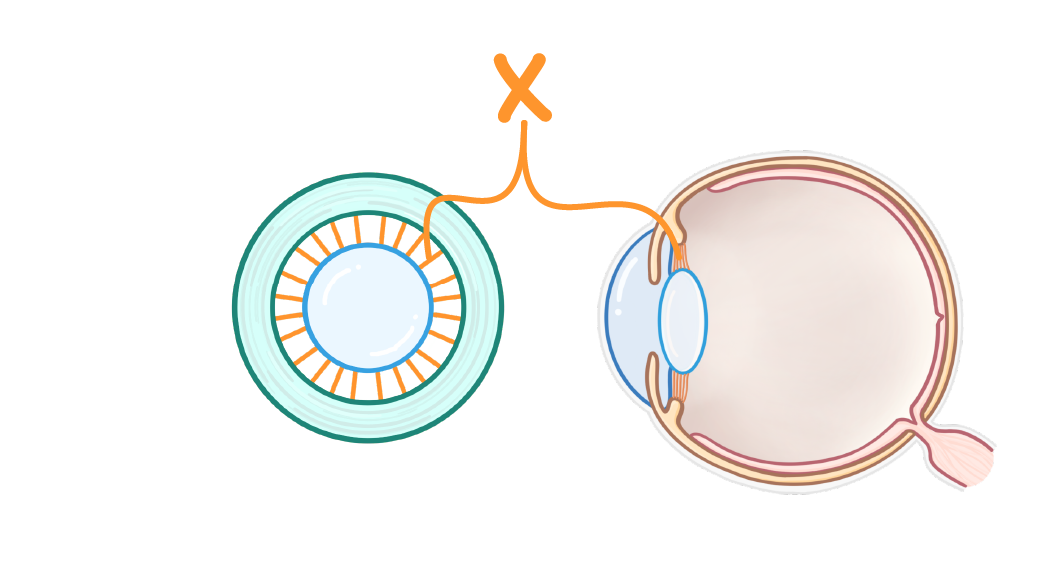
The diagram above shows a side-on and front-on view of the lens and it's surrounding structures.
What is the structure labelled X?
Suspensory ligament
Lens
Ciliary muscle
|
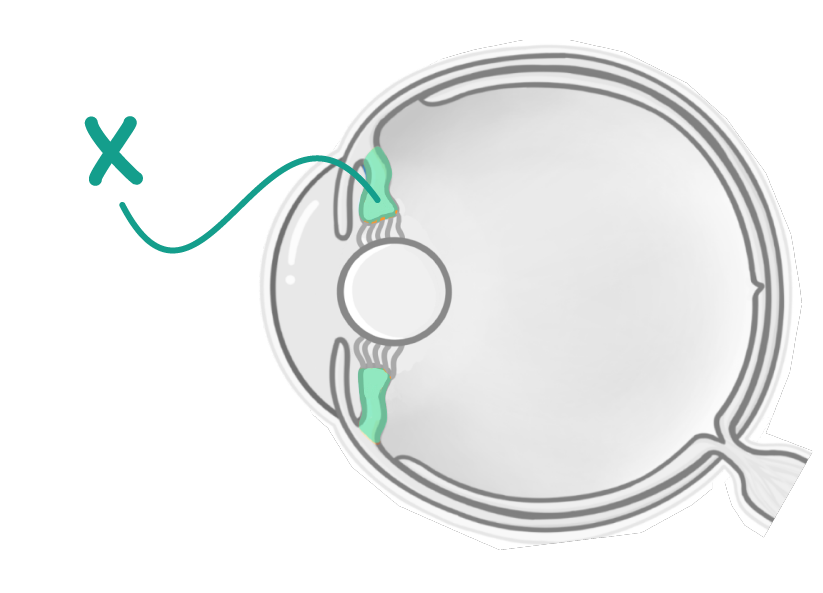
The diagram above shows a side-on cross-sectional view of the lens and it's surrounding structures.
What is the structure labelled X?
Lens
Ciliary muscle
Suspensory ligament
|
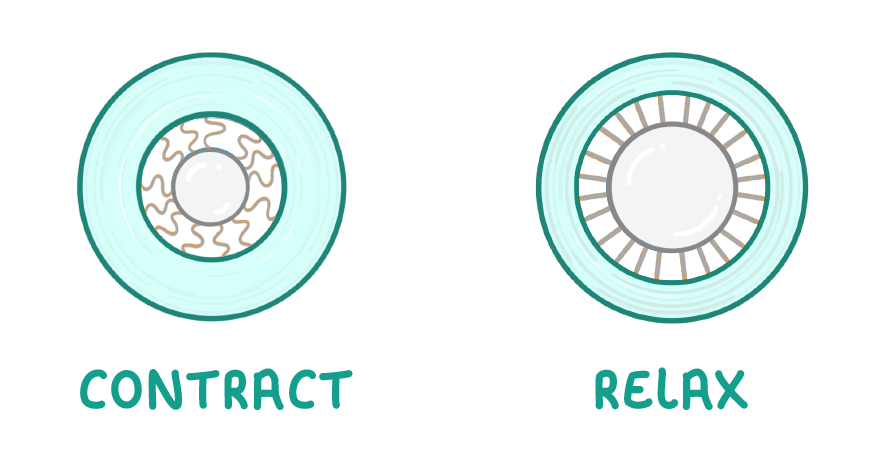
True or false? The ciliary muscle is just like any other muscle, so it can contract or relax.
True
False
|
The suspensory ligament is not a muscle, it is a ligament.
Can it contract and relax?
Yes
No
|
When looking at a nearby object, the lens must be short and wide to refract the light strongly and focus the light on the retina.
How do the ciliary muscle and suspensory ligaments achieve this?
(Select all that apply)
The ciliary muscle contracts
The suspensory ligaments are pulled taut
The ciliary muscle relaxes
The suspensory ligaments slacken
|
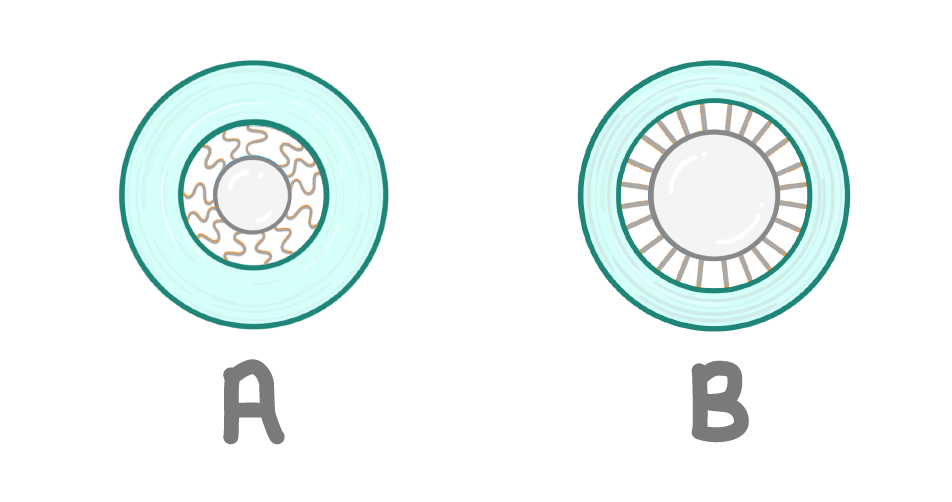
The ciliary muscle is a circle band of muscle that encircles the suspensory ligaments and the lens.
Which of the images above, A or B, show the ciliary muscle in its contracted state?
A
B
|
What happens to the ciliary muscle, suspensory ligaments, and the lens, when the eye focuses on a distant object?
(Select all that apply)
Lens is short and wide
Lens is pulled tall and thin
The suspensory ligaments are pulled taut
The ciliary muscle relaxes
The suspensory ligaments slacken
The ciliary muscle contracts
|
What does long-sighted mean?
The eye is unable to focus on distant objects
The eye is unable to focus on nearby objects
|
One solution to long-sightedness is to wear glasses.
Which type of lens would the glasses need to contain?
Concave lens
Convex lens
|
If somebody cannot focus on distant objects, are they long-sighted or short-sighted?
Long-sighted
Short-sighted
|