Circulatory System 2 - Blood Vessels
This lesson covers:
1The structure and function of arteries
2The structure and function of capillaries
3The structure and function of veins
4How to calculate the rate of blood flow
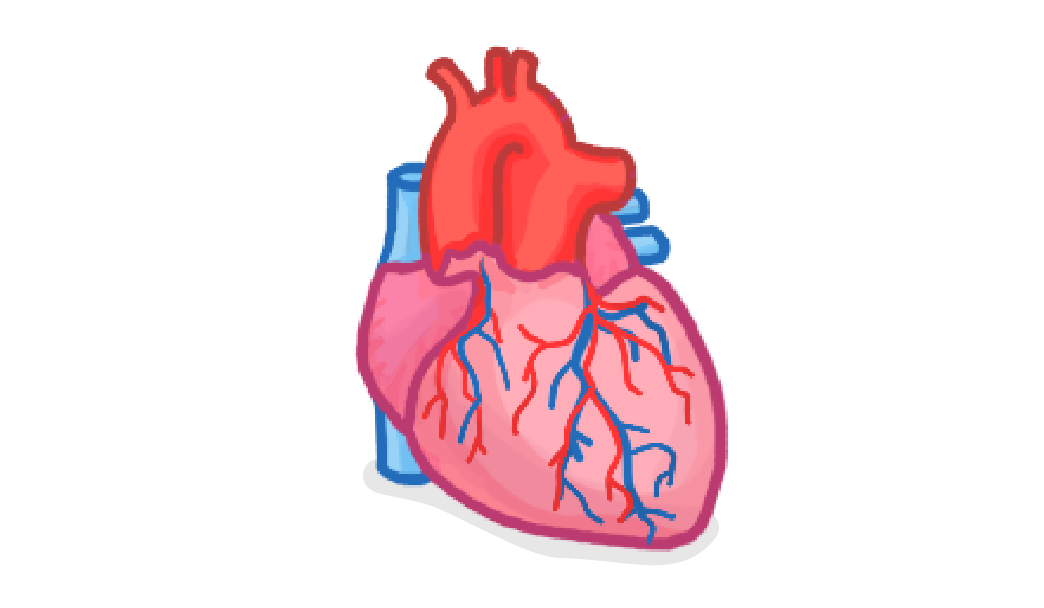
Arteries carry blood ___________ the heart.
away from
towards
|
nerves / arteries / capillaries / veins
carry blood through the body tissues, allowing oxygen, nutrients, and waste products, to be exchanged between tissues and the blood.
|
Veins carry blood ___________ the heart.
towards
away from
|
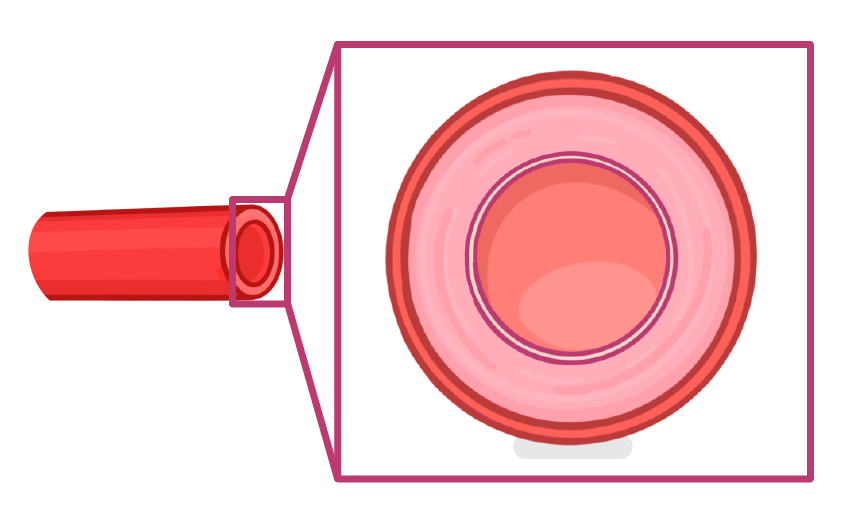
Structure and function of arteries
high / low / elastic / plastic / muscle / nerve / narrow / wide
- Arteries are large and carry blood at a very pressure.
- Artery walls have a thick middle layer, containing both muscle and tissue.
- The tissue provides strength, and allows the arteries to direct blood flow.
- The tissue allows the arteries to stretch and recoil.
- Compared to their walls, arteries have a relatively lumen, which keeps the blood pressure high.
|
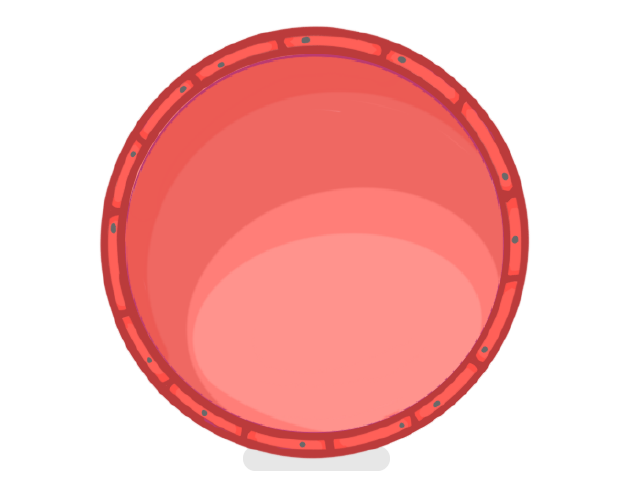
Structure and function of capillaries
high / low / waste / one / exchange / diffusion / permeable / wide
- Capillaries are the smallest of the three blood vessels.
- The role of capillaries is to nutrients and products with the tissues.
- Capillary walls are , meaning substances are able to move through them.
- Their walls are also only cell thick which means a short distance for .
- Capillaries carry blood at a pressure and have a lower rate of flow than arteries.
|
Which of the following substances are nutrients that are exchanged between the blood in the capillaries and the body tissues?
(Select all that apply)
Glucose
Carbon dioxide
Urea
Amino acids
Proteins
|
Which of the following substances are waste products that are exchanged between the blood in the capillaries, and the body tissues?
(Select all that apply)
Carbon dioxide
Glucose
Amino acids
Oxygen
Proteins
Urea
|
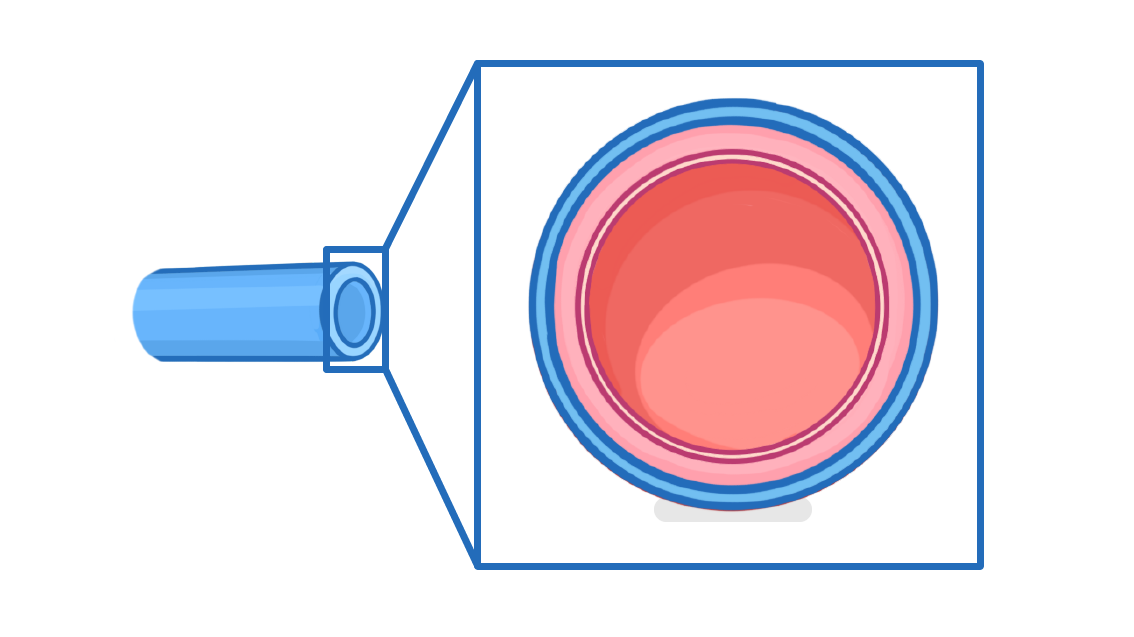
Structure and function of veins
higher / lower / thin / thick / heart / wide / small / valves
- The role of veins is to carry blood from the body (or lungs) back to the .
- Veins are a similar size to arteries, but they have relatively walls and a relatively lumen
- This is because they carry blood at a much pressure.
- Veins also contain to prevent the blood from flowing backwards.
|
Which of the following substances are exchanged between the blood in the capillaries, and the body tissues?
(Select all that apply)
Urea
Oxygen
Proteins
Glucose
Carbon dioxide
|
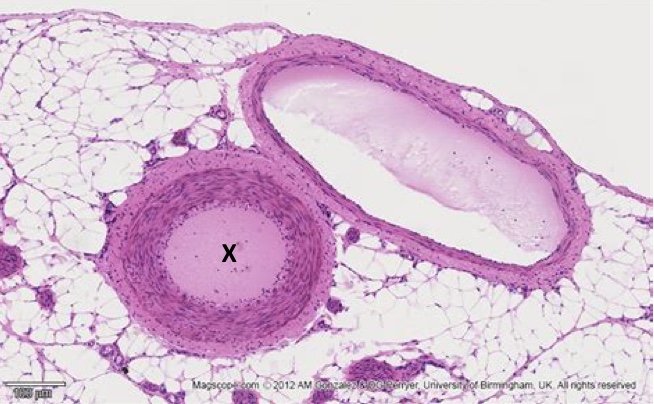
Which type of blood vessel is marked with an X?
Capillary
Artery
Vein
|
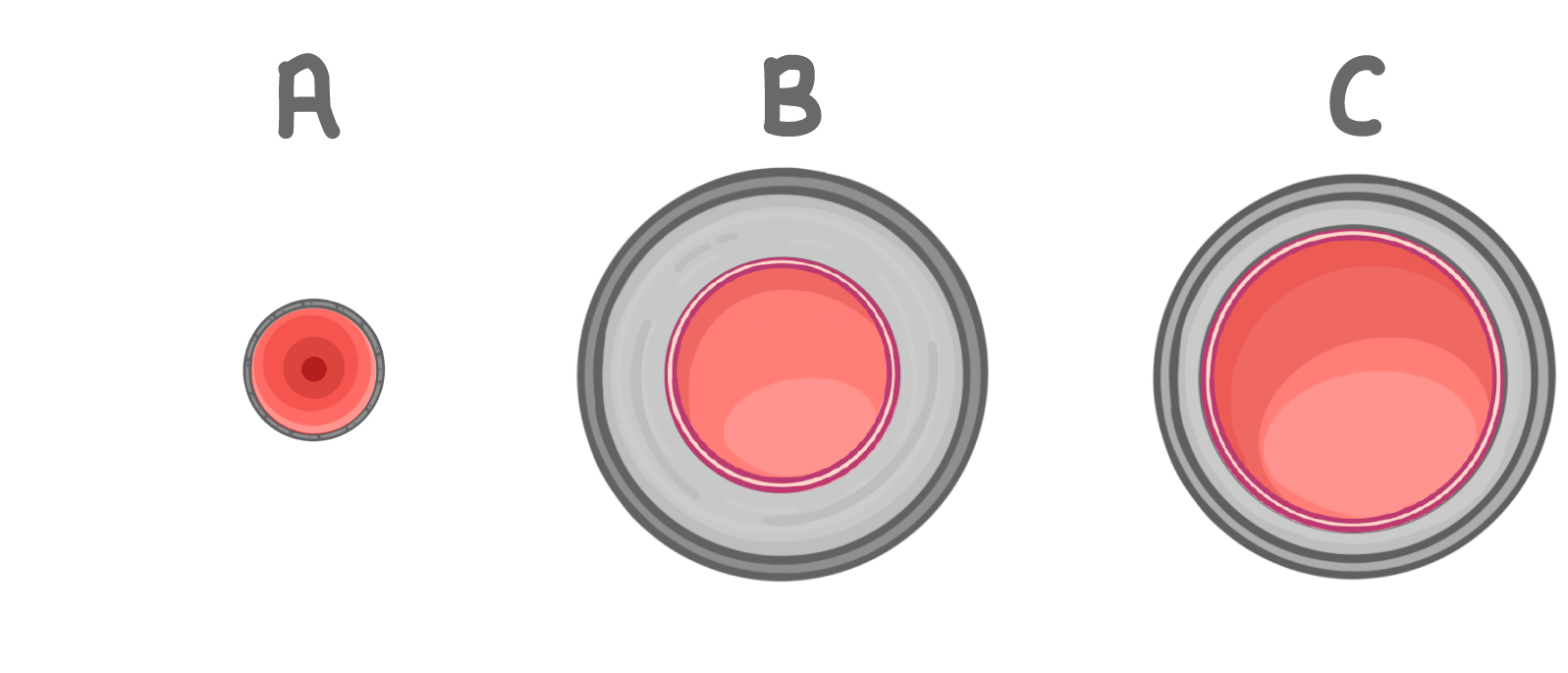
Based on the size of the lumen relative to the whole vessel, which of these blood vessels must be an artery?
A
B
C
|
1.4 litres of blood passes through an artery in 7 minutes.
What is the rate of blood flow in millilitres per minute?
ml/min
|
Blood is flowing through a vein at a rate of 37 ml/min.
How long will it take for 407 ml of blood flow through the vessel? Give your answer in minutes.
minutes
|
If you consider all the blood vessels inside of a human body, which type of blood vessel accounts for the majority of the cross-sectional area?
Veins
Capillaries
Arteries
|
In which order does blood flow through the three types of blood vessels?
Heart ➔ ➔ ➔ ➔ heart
|