Eutrophication
This lesson covers:
- Why fertilisers are needed in agriculture
- Some negative environmental impacts of fertilisers
- What 'eutrophication' is
Fertilisers  A fertiliser is a substance that is applied to soil, in order to supply plants with nutrients. |
Why do we need fertilisers? In agriculture, fertilisers are added to soils to replace lost nutrients. Crops take nutrients from the soil in order to grow. When crops are harvested, these nutrients are removed and do not return to the soil, as they would in a natural ecosystem. Nutrients are also lost when livestock or animal products are removed, because animals absorb nutrients from the plants that they eat. If livestock are removed for slaughter, these nutrients aren't replaced through their urine, faeces or their remains when they die as they would be in a natural ecosystem. |
NPK fertilisers  Most fertilisers are made up of a mixture of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) compounds. This is because these are the three main elements plants require from soil. |
Fertilisers can have negative impacts on the environment Fertilisers can negatively impact waterways due to two related processes: leaching and eutrophication. |
Leaching  Fertilisers don't always stay in agricultural fields. Leaching occurs when nutrients in fertilisers are washed out of the soil by water. For example, by rain or irrigation systems. |
When fertilisers provide plants with more nutrients than they can use, leaching becomes more likely because the excess inorganic ions are washed away. Leached nutrients often wash into waterways such as rivers and ponds, and this can result in eutrophication. |
Eutrophication Eutrophication is a process - it's caused by excess nutrients that have leached into waterways. |
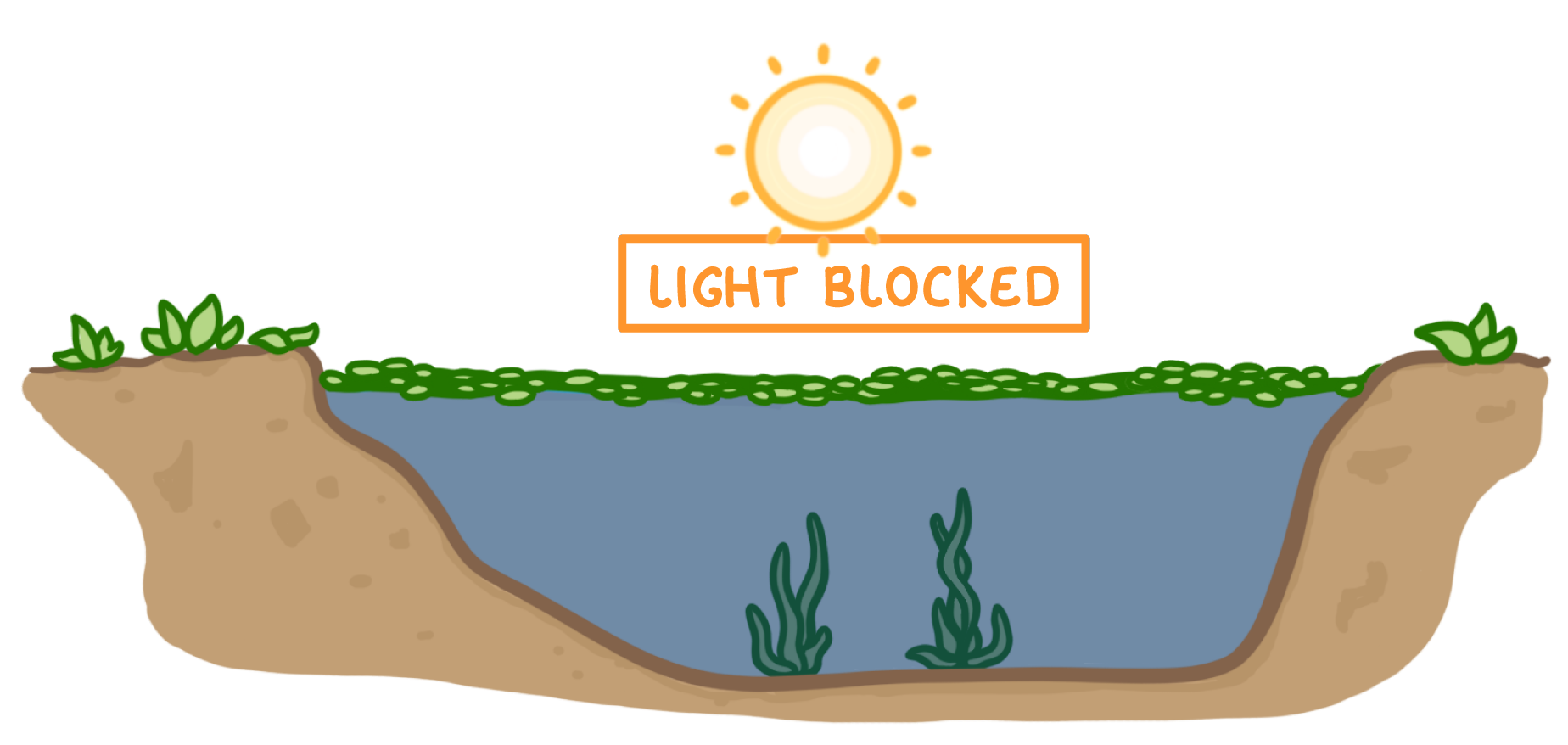
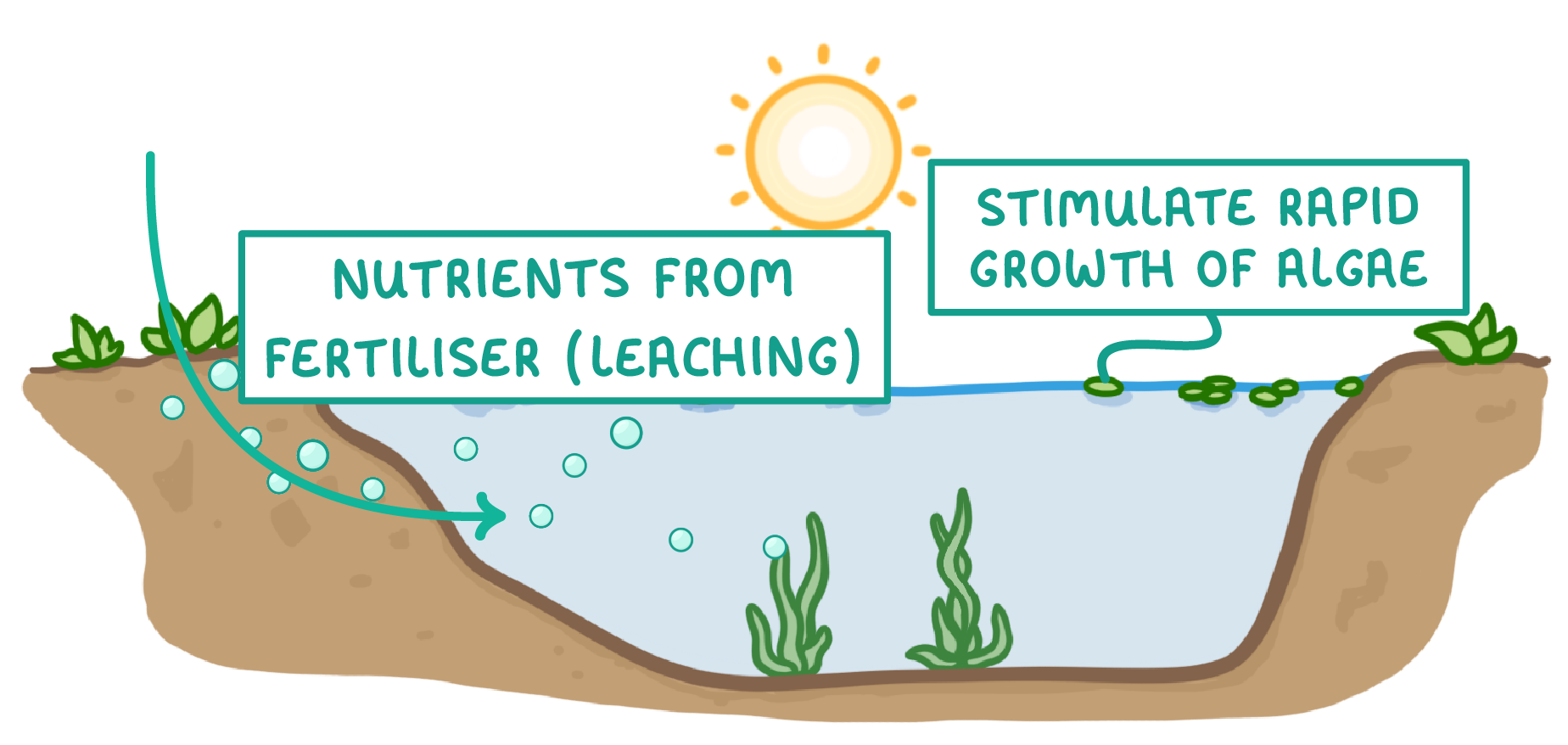 Mineral ions (e.g. nitrates) leach into lakes and rivers where they stimulate rapid growth of algae. |
What is the process by which fertilisers get into waterways?
Absorption
Leaching
Succession
|
1In the process of eutrophication, leaching of mineral ions into lakes from fertilised fields can cause the rapid growth of .
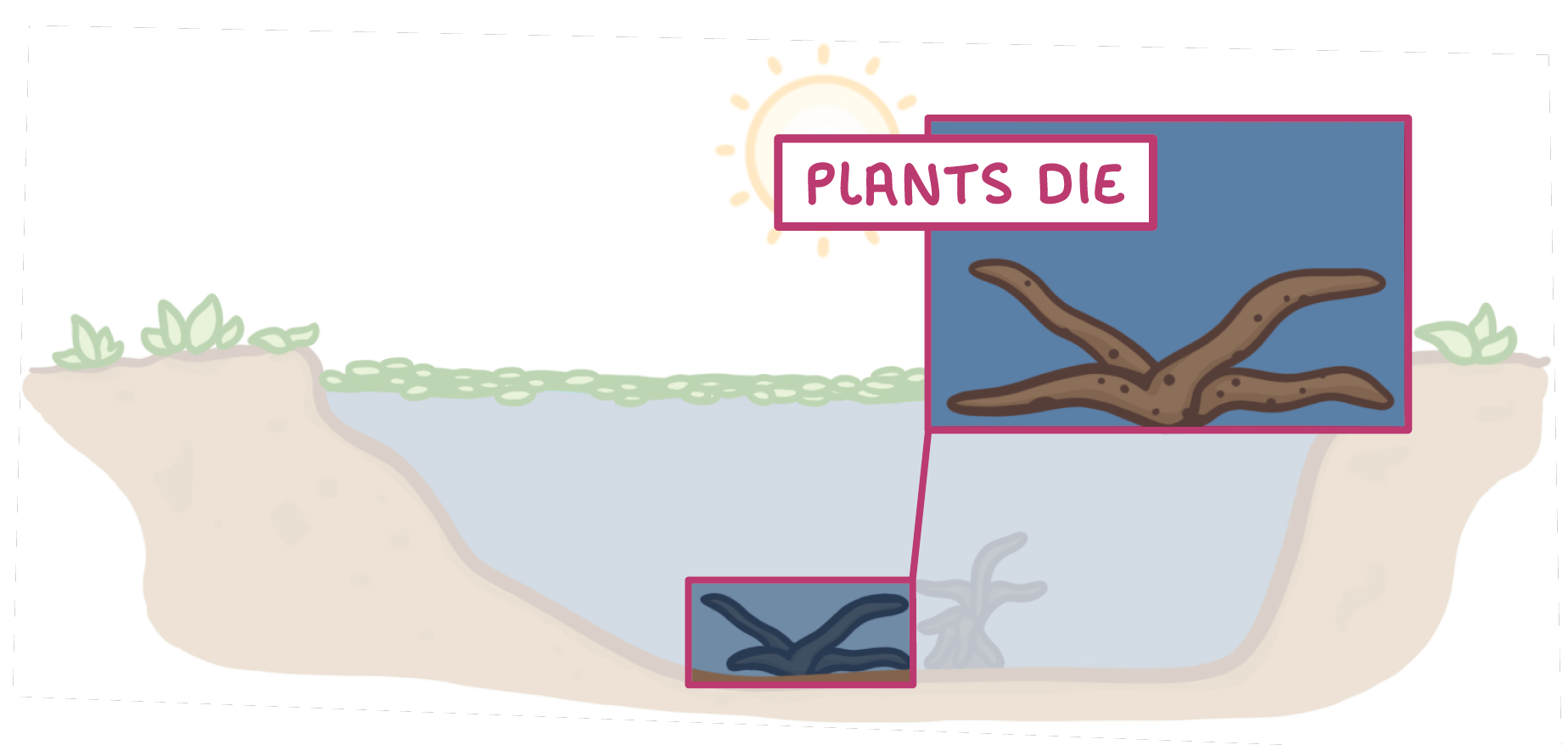
2This blocks light from reaching plants growing below the surface, and prevents them from performing .
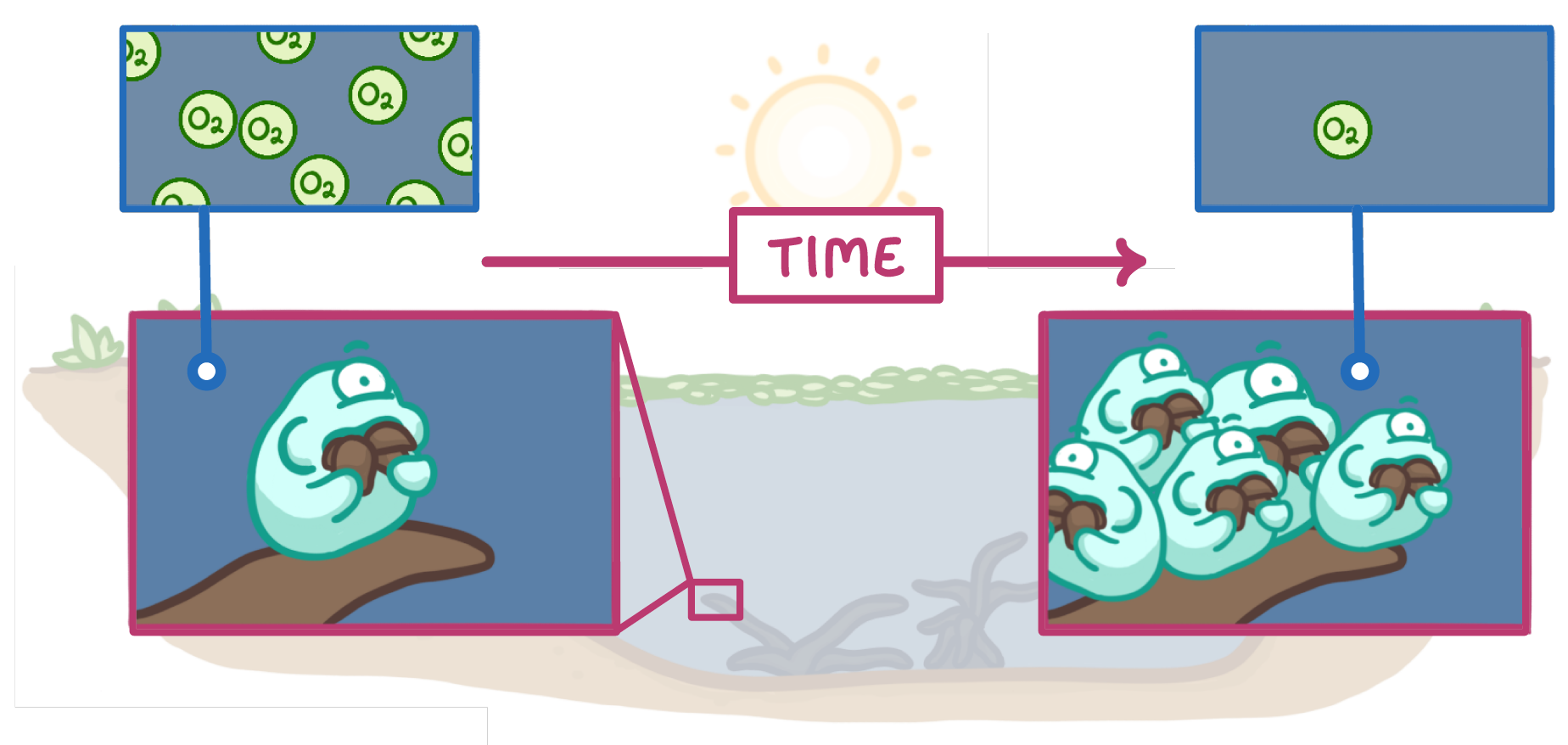
3This causes the plants to die, and the bacteria that feed on the dead plant matter are called bacteria.
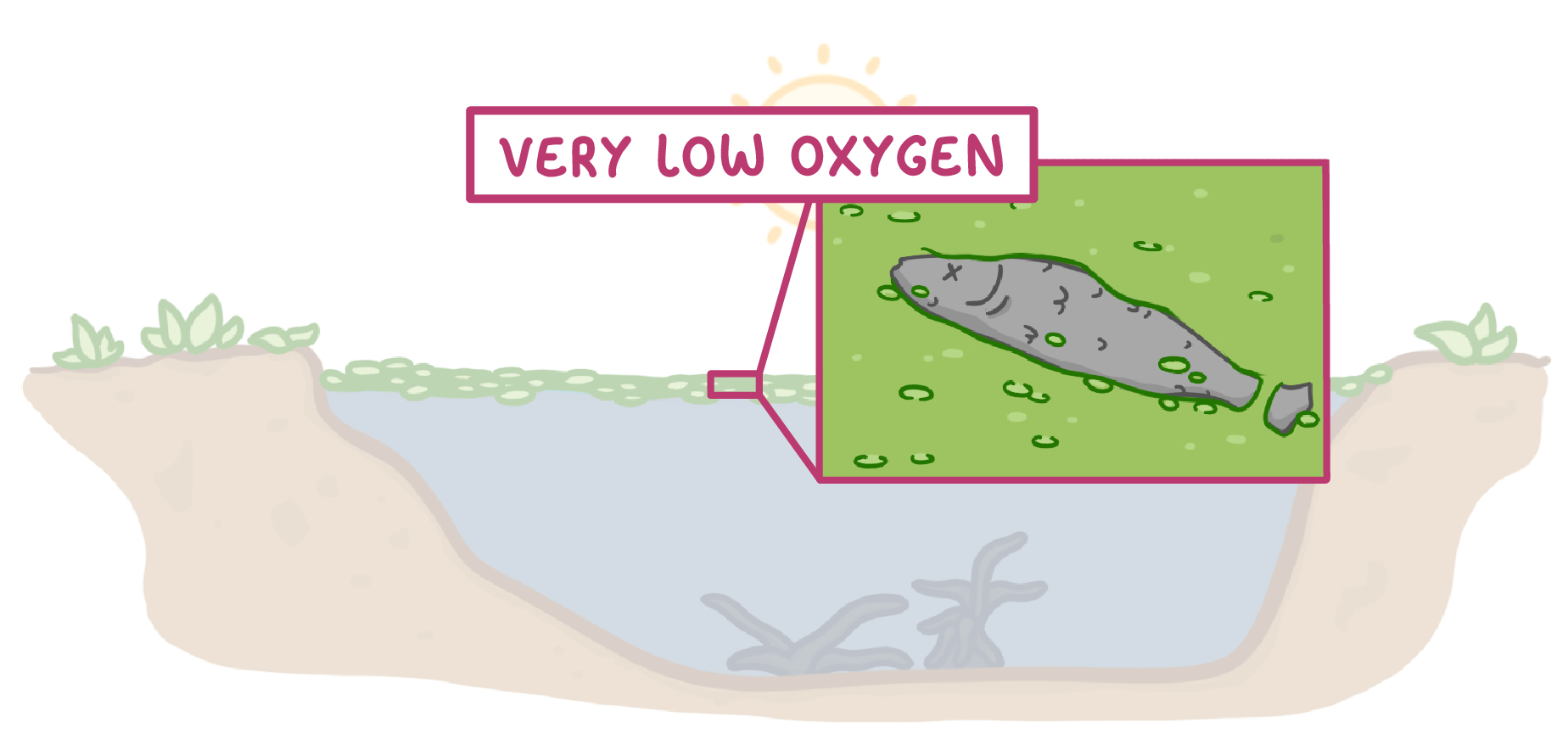
4As these bacteria increase in numbers, they use up the in the water through aerobic respiration.
5Low levels of can kill the fish and other aerobic organisms in the lake.
|
In biology, what is the cause of eutrophication?
Excess nutrients in waterways
Excess oxygen in waterways
|
During the process of eutrophication, what causes the algae in waterways to grow rapidly?
High levels of nutrients such as nitrates
Dead matter from dead plants and fish
Rapidly growing aquatic plants below the water's surface
|
What is leaching?
Anaerobic respiration by bacteria
Population growth of algae
Dissolved ions flowing through the soil into bodies of water
|
What is the order of events in eutrophication?
- Sunlight is blocked so plants start to die
- Bacteria digest the dead plants, using up the oxygen
- Excess nutrients get washed into rivers and lakes
- Animals in the water die due to lack of oxygen
- Algae grow and reproduce more quickly
3 ➔ 2 ➔ 1 ➔ 5 ➔ 4
1 ➔ 2 ➔ 3 ➔ 4 ➔ 5
3 ➔ 5 ➔ 1 ➔ 2 ➔ 4
5 ➔ 3 ➔ 2 ➔ 1 ➔ 4
|
Why do we use fertilisers in agriculture?
To feed livestock
To kill crop pests
To replace the nutrients lost through crop and livestock harvesting
|
A new golf course is built next to a river. Over the past several months, the nitrate levels of the water in the river have been increasing. Which of the following is a likely cause of the increasing nitrate levels?
Increased growth of bacteria
Decreased biodiversity
Fertiliser runoff from the golf course
|
Which of the following can reduce eutrophication?
Irrigating the fields more so the soil becomes waterlogged
Using larger quantities of fertiliser when growing crops
Controlling the use of fertiliser and storing manure and slurry more securely
|