Specialised Exchange Surfaces
This lesson covers:
- What 'specialised exchange surfaces' are
- What alveoli, villi, root hair cells, and leaves are
- How exchange surfaces are adapted to their role by having a large surface area, thin membranes, and being permeable
What is an exchange surface?
A part of an organism over which substances are exchanged with the environment
A part of an organism that transfers messages around the body
A part of an organism that transfers substances around the body
|
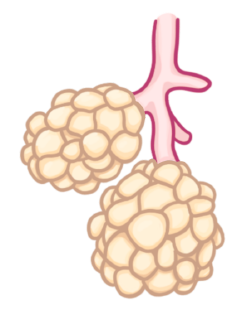
Where are alveoli found?
Lungs
Intestines
Plants roots
Plant stem
|
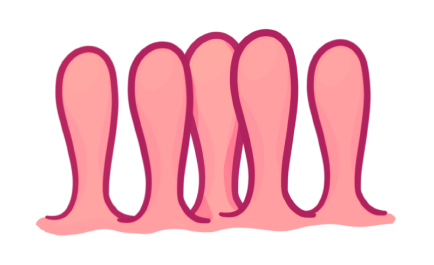
The small protrusions of the lining of the small intestines are called . These have a large area which increases the area over which we can absorb nutrient molecules.
|
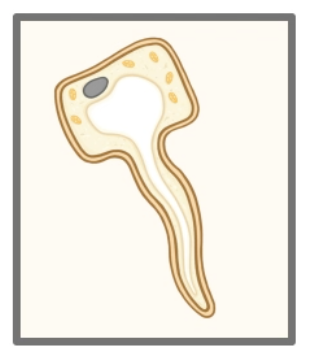
What type of cell is shown in the image above?
|
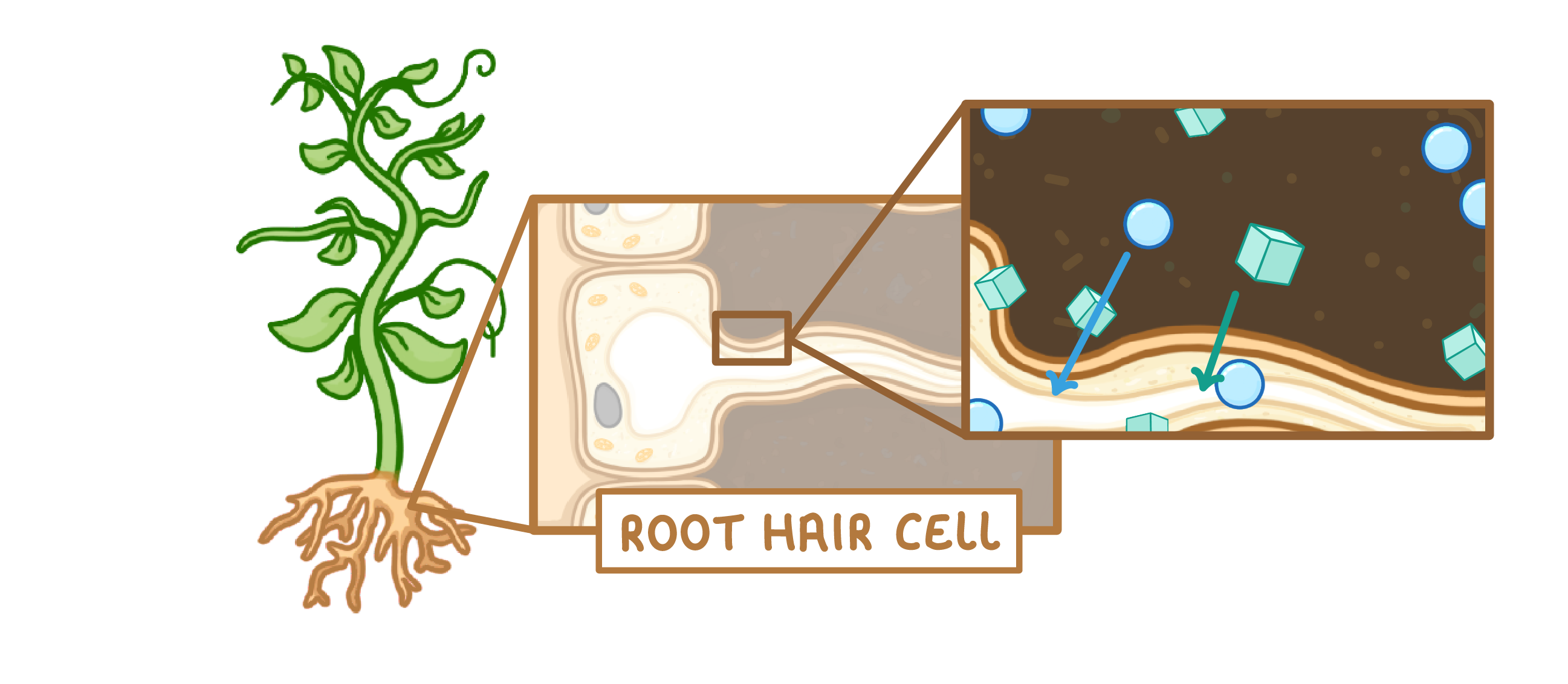
Root hair cells absorb and ions from the soil.
|
State and explain three features that most exchange surfaces have in common.
|
State and explain three features of alveoli that make them good exchange surfaces.
|
Which adaptation in plants contributes to the efficient exchange of gases?
Small leaves
They are able to ventilate their leaves
The flattened shape of their leaves
|