Surface Area to Volume Ratio
This lesson covers:
- What surface area (SA) to volume (V) ratio means
- How SA : V changes as organisms get larger
- Why large organisms need specialised exchange surfaces

Which organisms have a larger surface area to volume ratio?
Small organisms
Large organisms
|
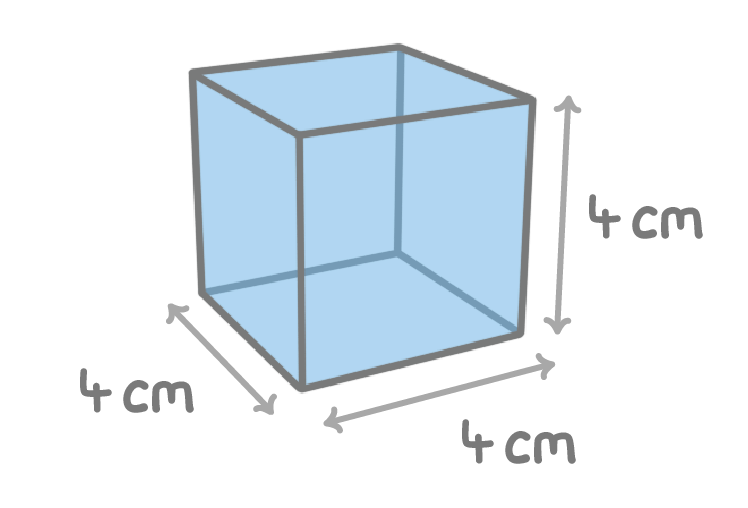 |
The above cube is 4 cm x 4 cm x 4 cm. What is the total surface area of the cube? cm2
|
Calculate the volume of the cube. cm3
|
Calculate the surface area : volume ratio of the cube. 3 : 2 5 : 2 2 : 3 3 : 1
|
|
Which type of organism can rely on diffusion to exchange all of the nutrients and waste products it needs?
Bacteria
Grasshopper
Leopard
Oak tree
|
Give two examples of exchange surfaces in humans and describe their function.
|