Specialised Cells & Differentiation
This lesson covers:
- What 'specialised' cells are
- The process of 'differentiation'
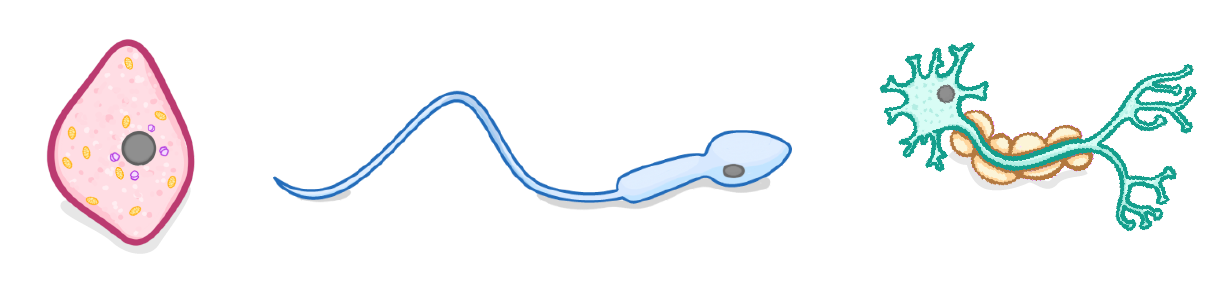
Which of the following specialised cells is adapted for transmitting messages from one part of the body, to another?
Muscle cells
Sperm cells
Nerve cells
|
Explain how a sperm cell is adapted for its role.
|
What is 'differentiation'?
The maintenance of internal body temperature
The process by which cells become specialised
The movement of a cell around the body
|
Which two of the following cells are adapted to their roles by having a large surface area?
Root hair cells
Red blood cells
Xylem cells
Nerve cells
|
Cells that are adapted to perform a particular function are called cells.
|
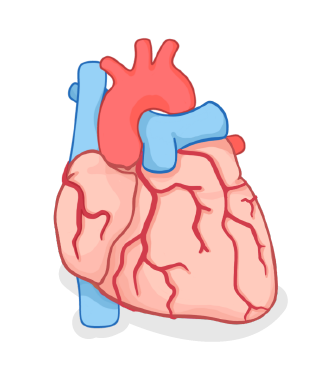
Heart muscle tissue has to be able to beat continually without stopping. What adaptation would you expect heart cells to have?
A large vacuole
A large number of mitochondria
A thick cell membrane
A large nucleus
|
Which of the following specialised cells is adapted to their role by having lots of mitochondria?
Skin cells
Sperm cells
Guard cells
Palisade mesophyll cells
|