Osmosis
This lesson covers:
- What 'osmosis' is
- What 'water concentration' means
- How osmosis applies to cells
Osmosis is the n movement of water molecules across a permeable membrane, from a region of water concentration, to a region of water concentration.
|
True or false? Osmosis is a special form of diffusion.
True
False
|
In living organisms, the partially permeable membrane is usually the ___________
Chloroplast
Cell wall
Nucleus
Cell membrane
|
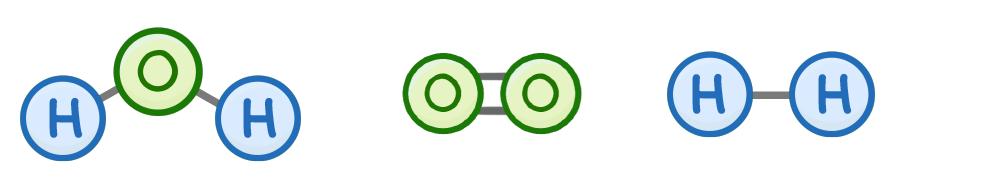
Osmosis is the movement of which molecules?
Any molecule
Water
Oxygen
Hydrogen
|
True or false? During osmosis, water moves against the concentration gradient.
True
False
|
What would happen to red blood cells if they were placed in pure water?
There would be no movement of water, so their size and shape would not change
They would lose water and shrink, becoming wrinkled
They would gain water and swell
|
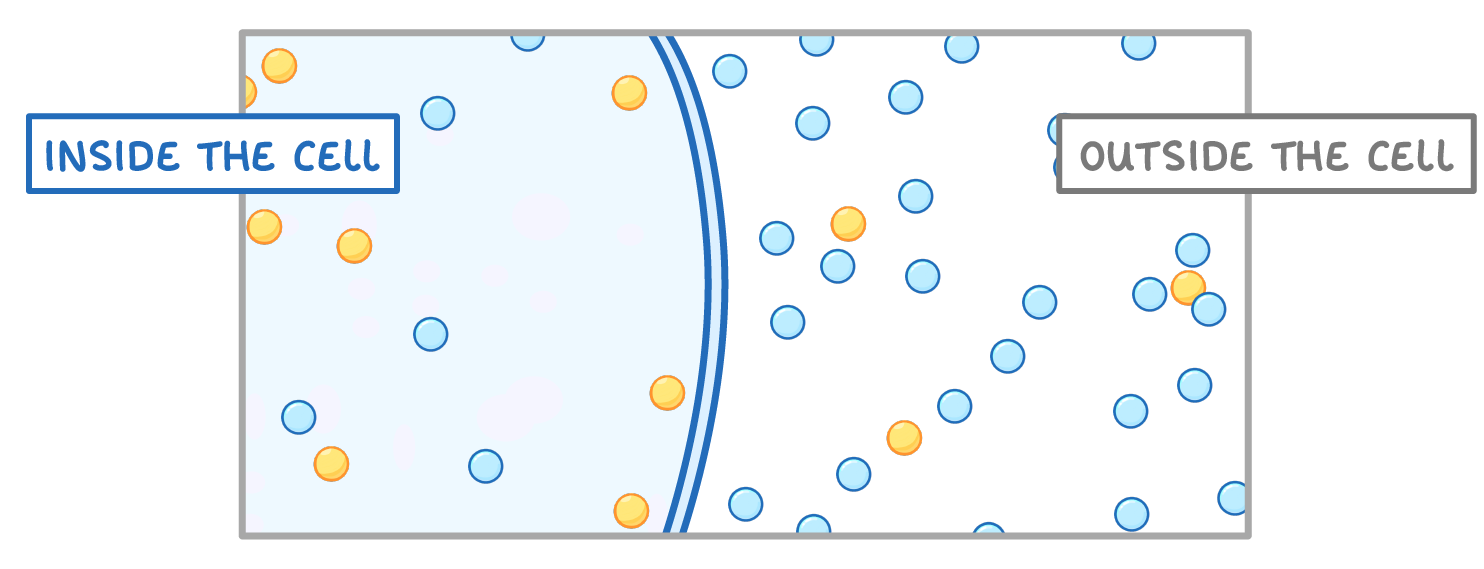
Looking at the diagram above, in which direction would you expect the water to move?
Inside the cell ➔ outside the cell
Outside the cell ➔ inside the cell
|