Cell Structure
This lesson covers:
- The structure of animal, plant, and bacterial cells
- The function of each sub-cellular structure (organelle), such as ribosomes and mitochondria
Which of the following are Eukaryotes?
(Select all that apply)
Plants
Bacteria
Animals
|
The _________ contains the cell's genetic material (in the form of DNA), and so controls the cell's activities.
Mitochondria
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Cell membrane
|
mitochondria / nuclei / ribosomes
The are where proteins are made. We sometimes call them the site of protein synthesis.
|
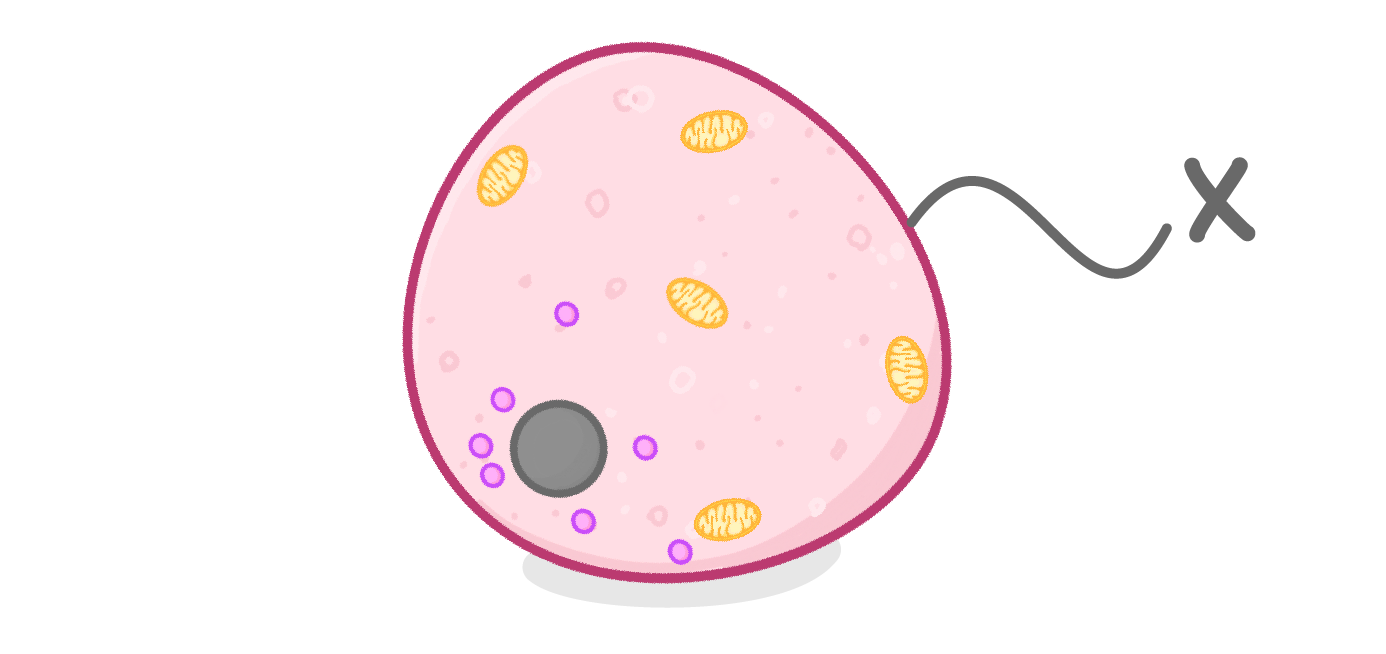
The diagram above shows an animal cell.
What is the structure labelled X?
Cell membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosome
Nucleus
|
What is 'cytoplasm'?
An organelle that controls what passes in and out of the cell
An organelle that makes proteins
The site of photosynthesis
A jelly-like material containing nutrients and salts, where chemical reactions take place
|
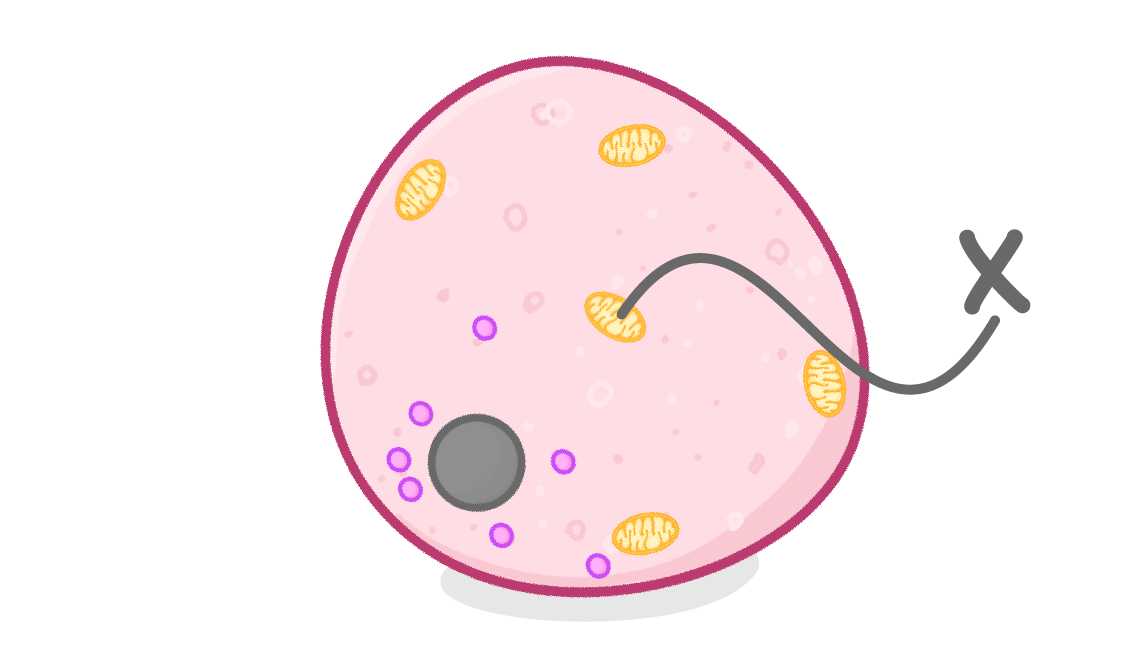
The diagram above shows an animal cell.
What is the structure labelled X?
Ribosome
Cell membrane
Nucleus
Mitochondria
|
What is the role of the mitochondria?
|
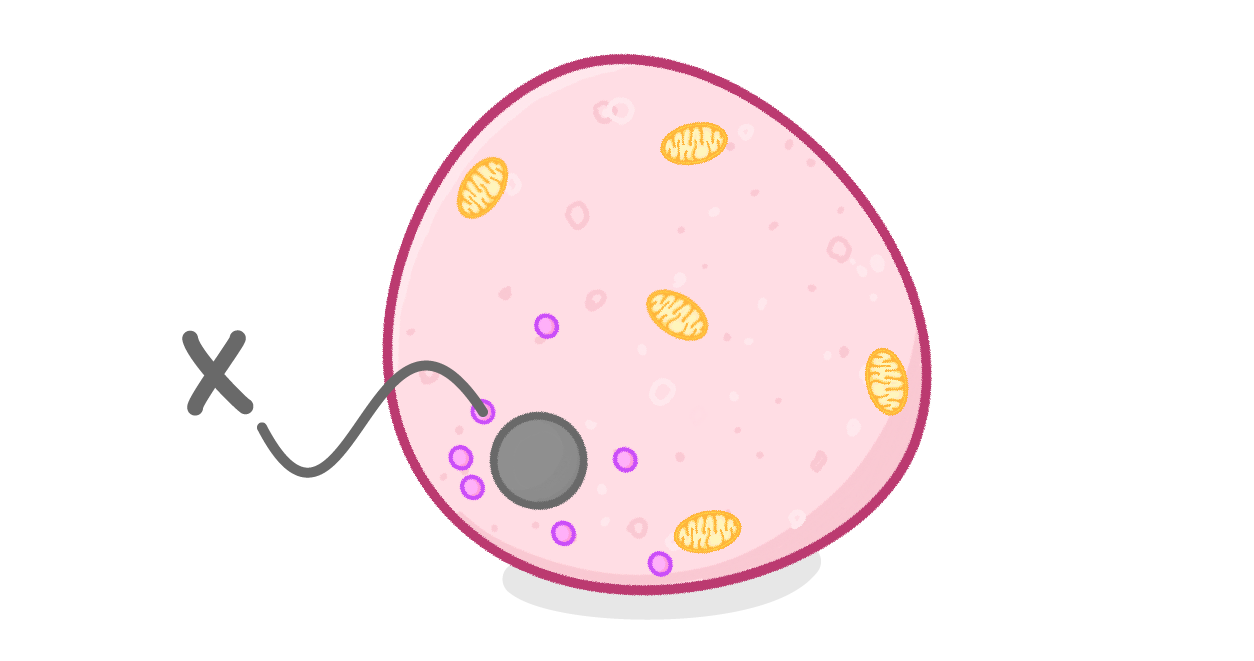
The diagram above shows an animal cell.
What is the structure labelled X?
Ribosome
Mitochondria
Cell membrane
Nucleus
|

Which of the following are found in plant cells, but not in animals cells?
(Select all that apply)
Nucleus
Cell wall
Permanent Vacuole
Cell membrane
Chloroplast
Ribosomes
|
sun / wind / photosynthesis / phagocytosis / chlorophyll / auxin
Chloroplasts carry out the process of , which involves using light energy from the to make glucose.
The green pigment that absorbs the light energy is called . This is what makes plants green.
|
The is a large sac in the middle of the cell that contains a watery solution of sugars and salts (cell sap). It helps maintain the structure and shape of the cell.
|
The ___________ is made of cellulose. This makes it strong and allows it to maintain the shape of the cell.
Nucleus
Cell membrane
Chloroplast
Cell wall
|
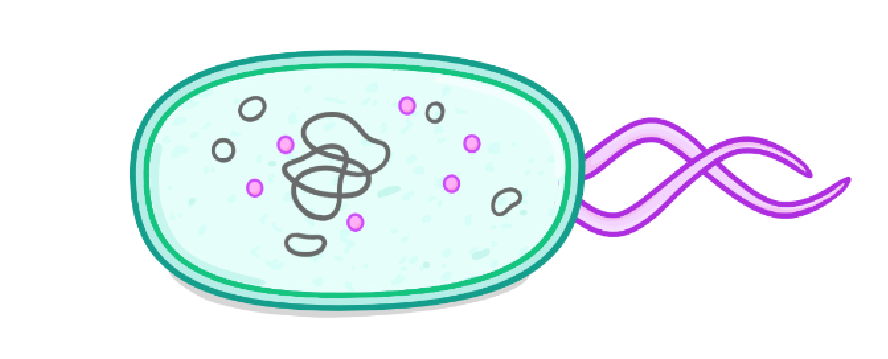
Bacteria are classed as ___________ organisms.
prokaryotic
eukaryotic
|
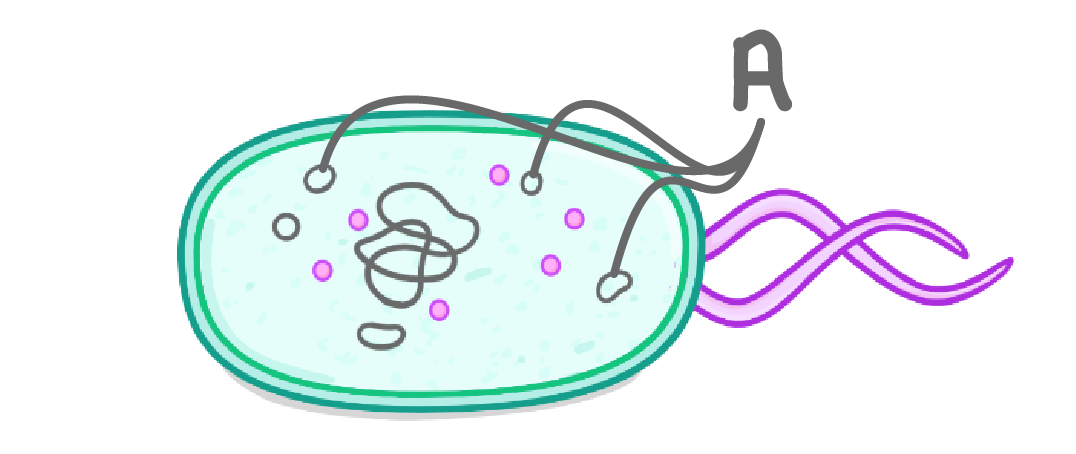
In the image above, which structure is labelled A?
|
True or false? Bacteria have both a cell membrane and a cell wall.
True
False
|
Are bacterial cells larger or smaller than animal cells?
Larger
Smaller
|
multicellular / unicellular
Bacteria are (only consist of a single cell).
|
Which of the following are not found in bacteria?
Cell wall
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Nucleus
|