Making Use of Enzymes
This lesson covers:
- How enzymes are used in important commercial processes
Enzymes can be used to speed up many processes As you have learned, enzymes are biological molecules that catalyse chemical reactions in living organisms. However, enzymes can also be extracted from cells, and used to catalyse a wide range of commercially important processes. This makes the process faster or easier to carry out, and therefore cheaper. |
Pectinase - used in the production of fruit juice 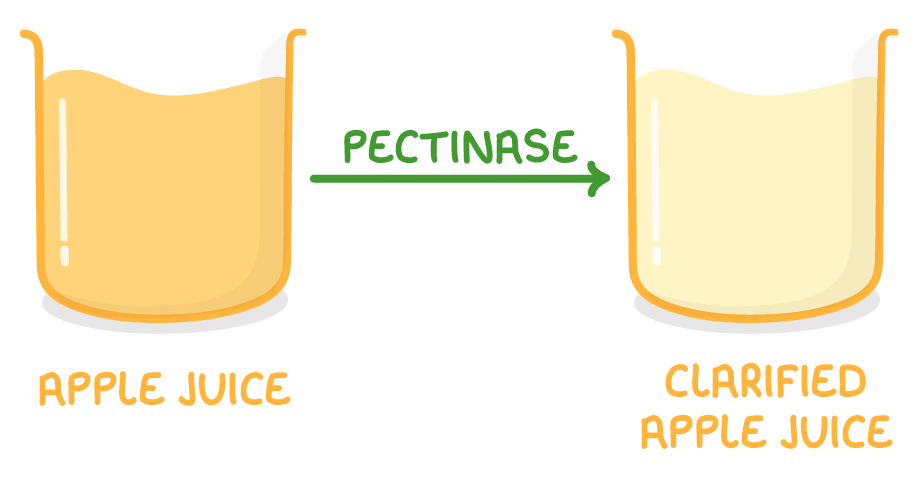 Pectinase breaks down pectin, a complex polysaccharide present in the cell walls of fruit cells. This improves the process in a few different ways:
|
Enzymes used in biological washing powders |
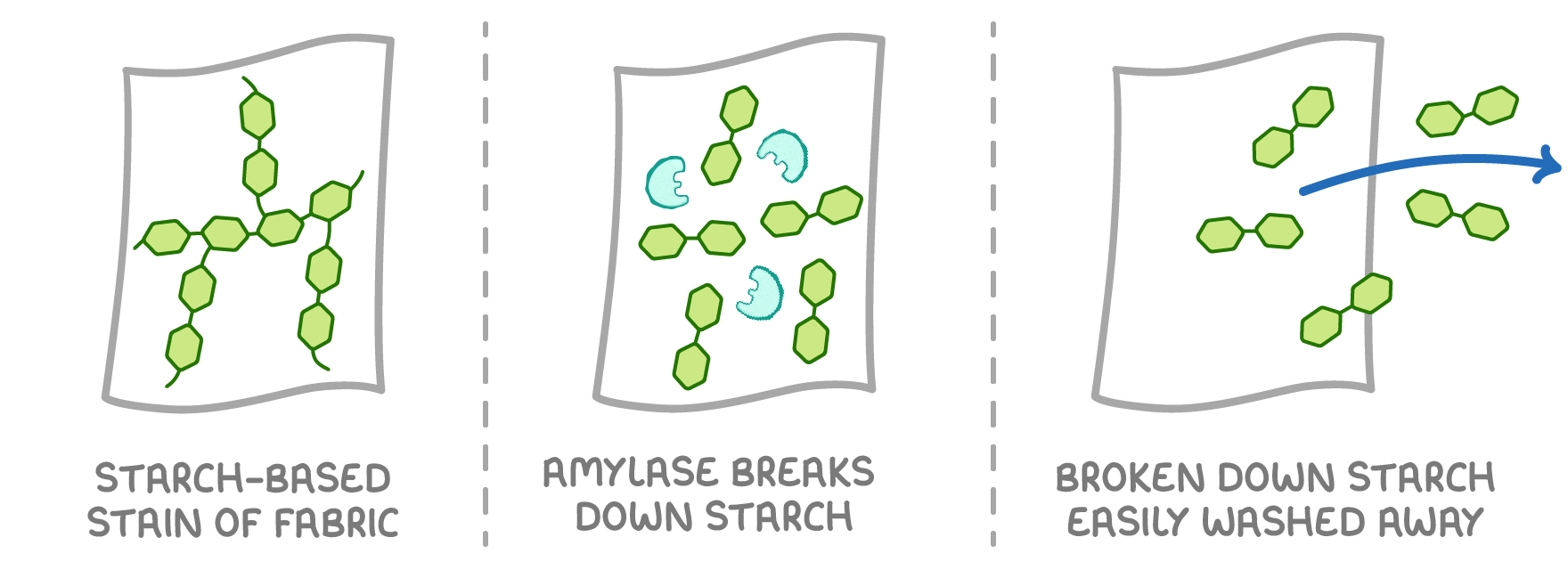 Enzymes are also used in the washing powders we use to clean our clothes. The enzymes break down the substances that are staining the fabric, and multiple types of enzymes are combined together in order to remove a range of substances:
Pros and cons of biological washing powders: PRO - Biological detergents are more effective than non-biological detergents at cleaning at lower temperatures, thereby reducing energy consumption and environmental impact. CON - However, some people find that the enzymes in bio washing powder can irritate their skin. |
Lactase in lactose-free milk  Lactase is used to break down lactose, a sugar present in milk, into its component simple sugars, glucose and galactose. The breakdown of lactose makes milk lactose-free, suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance. Lactose-free milk provides an alternative for those who cannot digest regular milk. |
What is the primary function of pectinase in food processing?
Increasing sugar content in fruits
Enhancing the sweetness of fruits
Stimulating fruit growth
Breaking down pectin in cell walls
|
Lactase is an enzyme used for:
Fermenting yoghurt
Preserving milk freshness
Breaking down lactose in milk
Enhancing the flavour of cheese
|
In the context of laundry, what is the main purpose of enzymes in bio detergents?
Breaking down the staining substances
Adding fragrance to clothes
Softening fabric texture
Improving colour retention in clothes
|
How does lactase contribute to lactose-free milk production?
By enhancing milk's protein content
By preserving lactose in its original form
By increasing lactose concentration
By breaking down lactose into simpler sugars
|
Which of the following is a valid statement about biological detergents?
Biological detergents are more abrasive on fabrics
Biological detergents have stronger fragrances
Biological detergents contain enzymes
Biological detergents use more water
|