Puberty, Menstrual Cycle & Reproductive Hormones
This lesson covers:
- What 'puberty' is and which hormones are responsible for it
- The stages and hormones involved in the menstrual cycle
is the period in which adolescents start to develop secondary sexual characteristics.
|
The term 'secondary sexual characteristics' refers to the bodily changes that take place during puberty.
Which of the following are secondary sexual characteristics?
(Select all that apply)
Less body hair
Increase in height
Breast development
Deepening voice
Darker skin
More muscle mass
|
Which organ is testosterone released from?
Ovaries
Testes
Pituitary gland
Adrenal gland
|
Is oestrogen the main sex hormone in males or females?
Males
Females
|
Which organ is oestrogen released from?
Testes
Adrenal gland
Pituitary gland
Ovaries
|
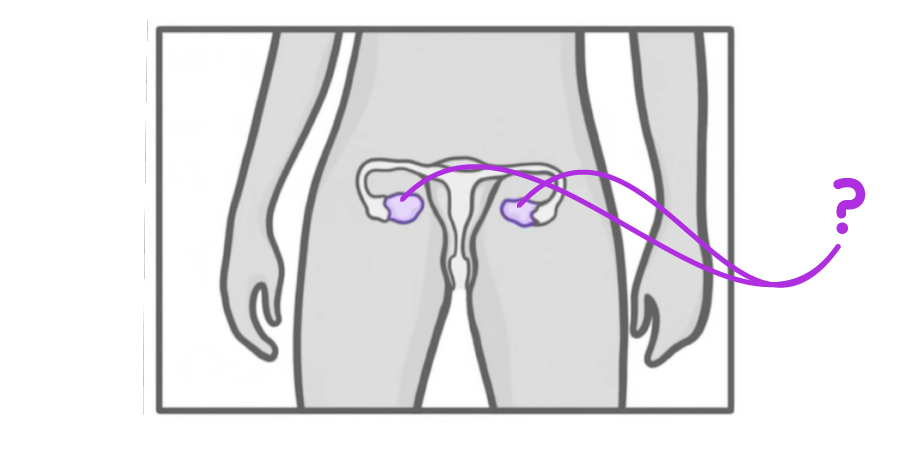
What is the structure indicated on the diagram above?
Fallopian tube
Uterus lining
Uterus
Ovaries
|
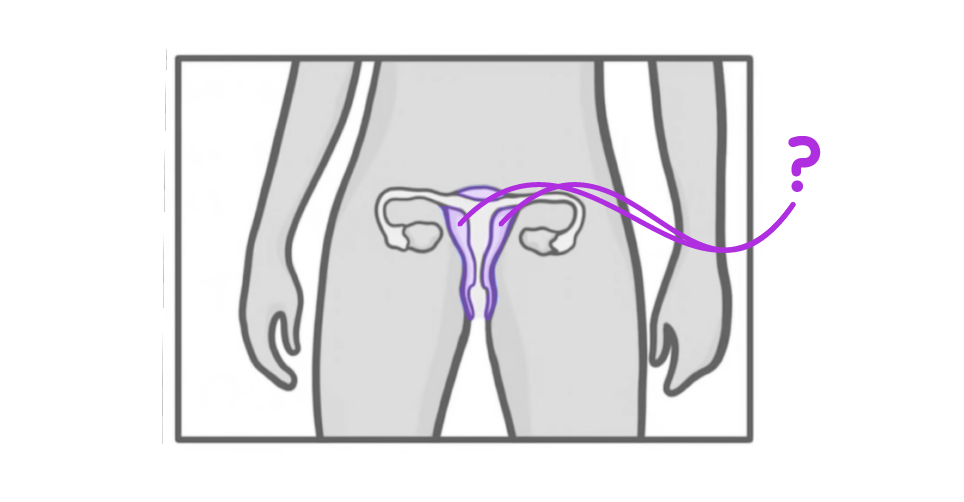
What is the structure indicated on the diagram above?
Uterus
Fallopian tube
Uterus lining
Ovaries
|
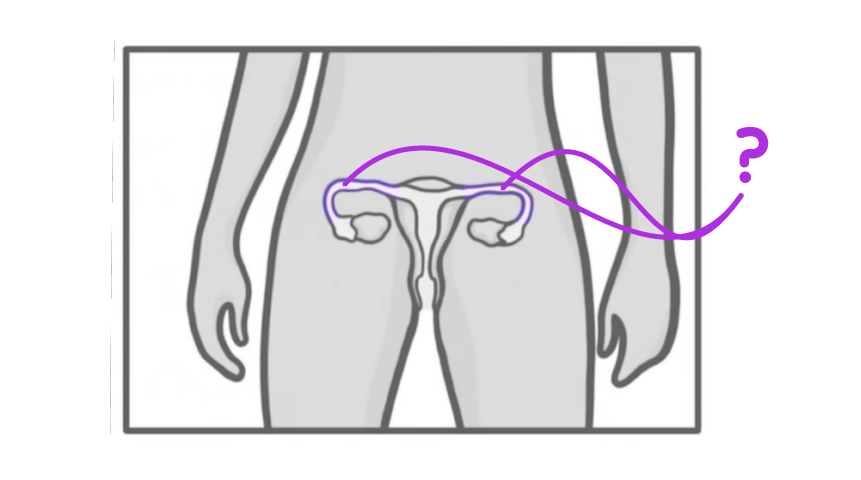
What is the structure indicated on the diagram above?
Ovaries
Uterus
Uterus lining
Fallopian tubes
|
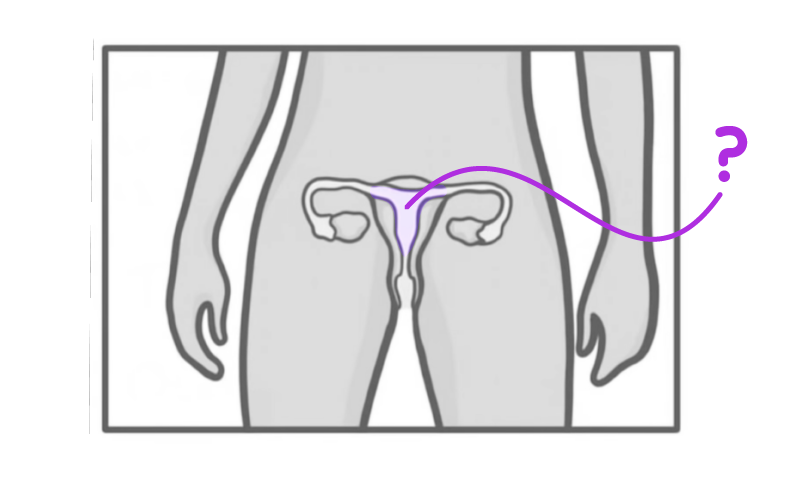
What is the structure indicated on the diagram above?
Fallopian tube
Ovaries
Uterus lining
Uterus
|
How long does the average menstrual cycle last?
24 days
28 days
32 days
36 days
|
The menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of steps that prepares the uterus for the implantation of a fertilised egg.
If there is no fertilised egg, then the cycle repeats.
But if there is a fertilised egg, then the cycle will stop and the egg will implant into the uterus lining, where it can develop into a foetus.
What happens in stage one of the menstrual cycle?
Release of the egg from the ovaries
Maintenance of uterus lining
Building up of the uterus lining
Period of bleeding as the uterus lining breaks down
|
What is the name of stage one of the menstrual cycle?
|
What happens in stage two of the menstrual cycle?
Building up of the uterus lining
Release of the egg from the ovaries
Maintenance of uterus lining
Period of bleeding as the uterus lining breaks down
|
What happens in stage three of the menstrual cycle?
Maintenance of uterus lining
Building up of the uterus lining
Period of bleeding as the uterus lining breaks down
Release of the egg from the ovaries
|
What is the name of stage three of the menstrual cycle?
|
What happens in stage four of the menstrual cycle?
Release of the egg from the ovaries
Period of bleeding as the uterus lining breaks down
Maintenance of uterus lining
Building up of the uterus lining
|
What happens after stage four if there is no fertilised egg?
The cycle stops
The lining gets thicker
The cycle starts again
|
If a fertilised egg implants into the uterus lining then the menstrual cycle stops and the lining is maintained.
True
False
|
Which hormone stimulates the uterus lining to develop?
Luteinising hormone (LH)
Progesterone
Oestrogen
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
|
Which organ are both luteinising hormone and follicle stimulating hormone released from?
Testes
Adrenal gland
Ovaries
Pituitary gland
|
Which hormone stimulates the egg to be released around day 14 (ovulation)?
Luteinising hormone (LH)
Oestrogen
Progesterone
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
|
Which hormone stimulates the egg follicle to mature?
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinising hormone (LH)
Progesterone
Oestrogen
|
Which hormone maintains the lining of the uterus?
Progesterone
Oestrogen
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinising hormone (LH)
|