The Nervous System, Synapses & Reflexes
This lesson covers:
- The structure of the nervous system
- How synapses work
- How reflex arcs work
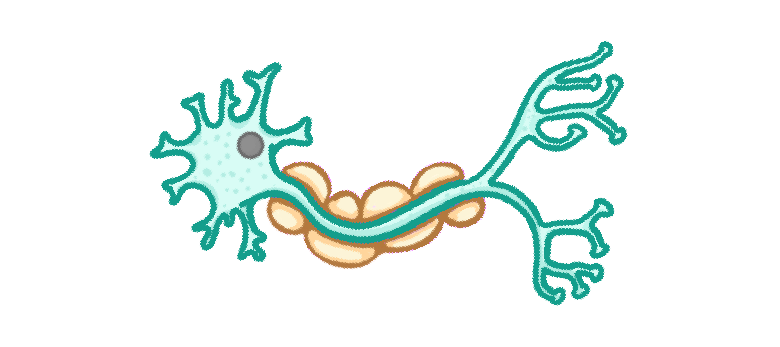
What passes along nerve cells?
Light pulses
Electrical impulses
Heat
|
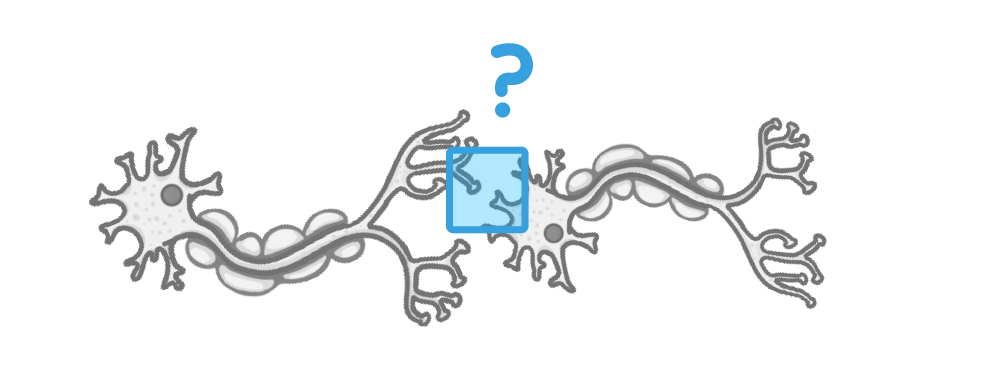
What is the gap between two neurones called?
|
What is released across a synapse?
Blood
Electricity
Chemicals
|
Which of these is part of the central nervous system (CNS)?
(Select all that apply)
Skin
Spinal cord
Liver
Brain
|
What is the role of a receptor?
To detect a stimulus
To transfer a signal from a sensory neurone to a motor neurone
To transfer a signal from a receptor to the CNS
To transfer a signal from the CNS to an effector
|
What is the role of a sensory neurone?
To detect a stimulus
To transfer a signal from the CNS to an effector
To transfer a signal from a receptor to the CNS
To transfer a signal from a sensory neurone to a motor neurone
|
What is the role of a motor neurone?
To transfer a signal from the CNS to an effector
To transfer a signal from a receptor to the CNS
To detect a stimulus
To transfer a signal from a sensory neurone to a motor neurone
|
What is the role of a relay neurone?
To transfer a signal from a sensory neurone to a motor neurone
To transfer a signal from the CNS to an effector
To transfer a signal from a receptor to the CNS
To detect a stimulus
|
What is a reflex?
A voluntary response to a stimulus
An automatic response to a stimulus
|
The pathway of a reflex arc
automatic / response / sensory neurone / stimulus / motor neurone / reflex
➔ receptor ➔ ➔ relay neurone ➔ ➔ effector ➔
|
What are the two main types of effectors?
Muscles
Glands
Sense organs
Brain
|
Reflexes are: Fast Slow
|
Conscious Automatic
|
|
Which of the following are reflexes?
(Select all that apply)
Blinking when you get dust in your eye
Sitting down
Sneezing
Picking up a pen
|
Why are reflexes important?
They protect us from harm
They are controlled by hormones
They last a long time
|
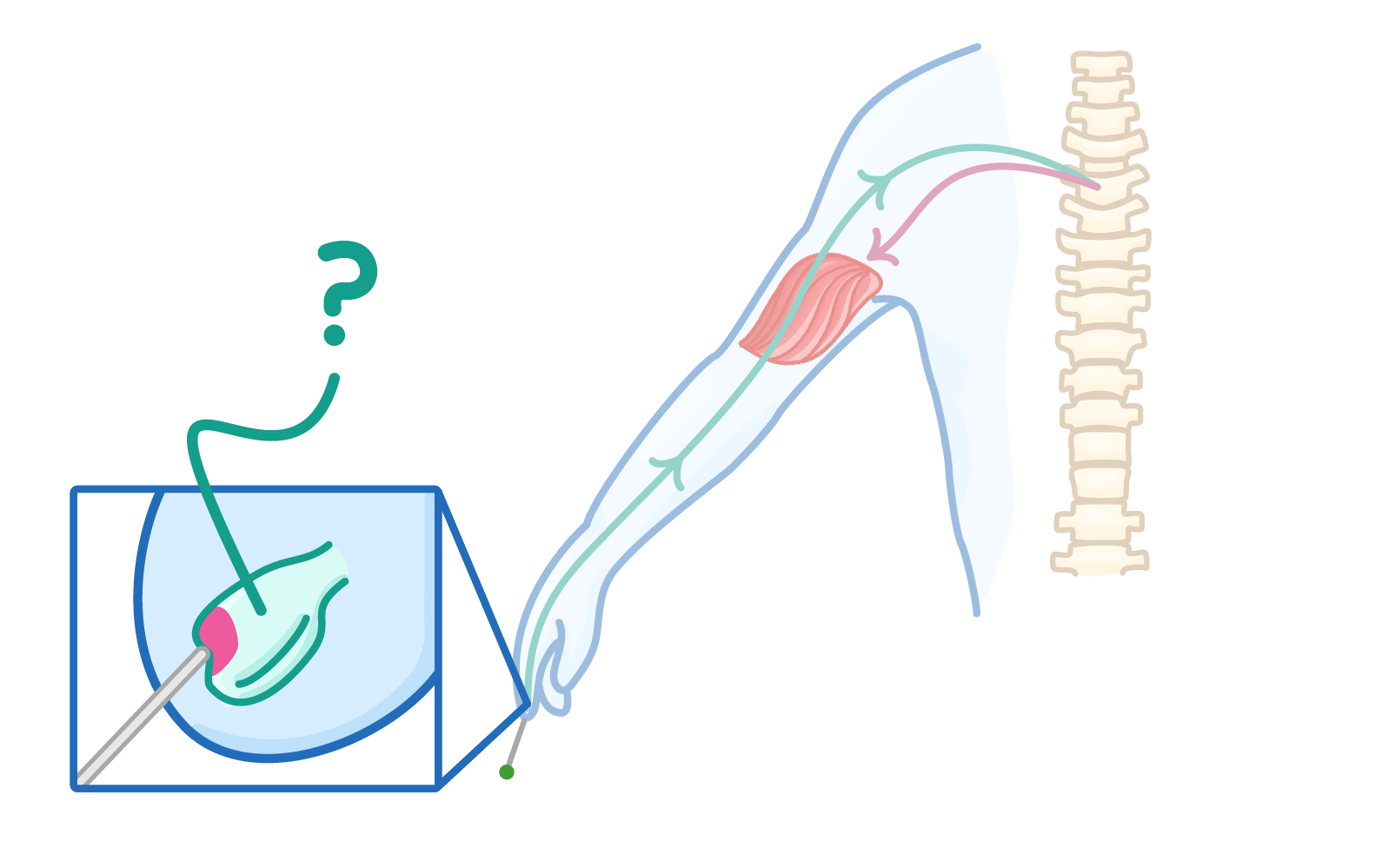
The diagram above shows part of a reflex arc. Which structure is being indicated?
Relay neurone
Sensory neurone
Receptor
Effector
Motor neurone
|
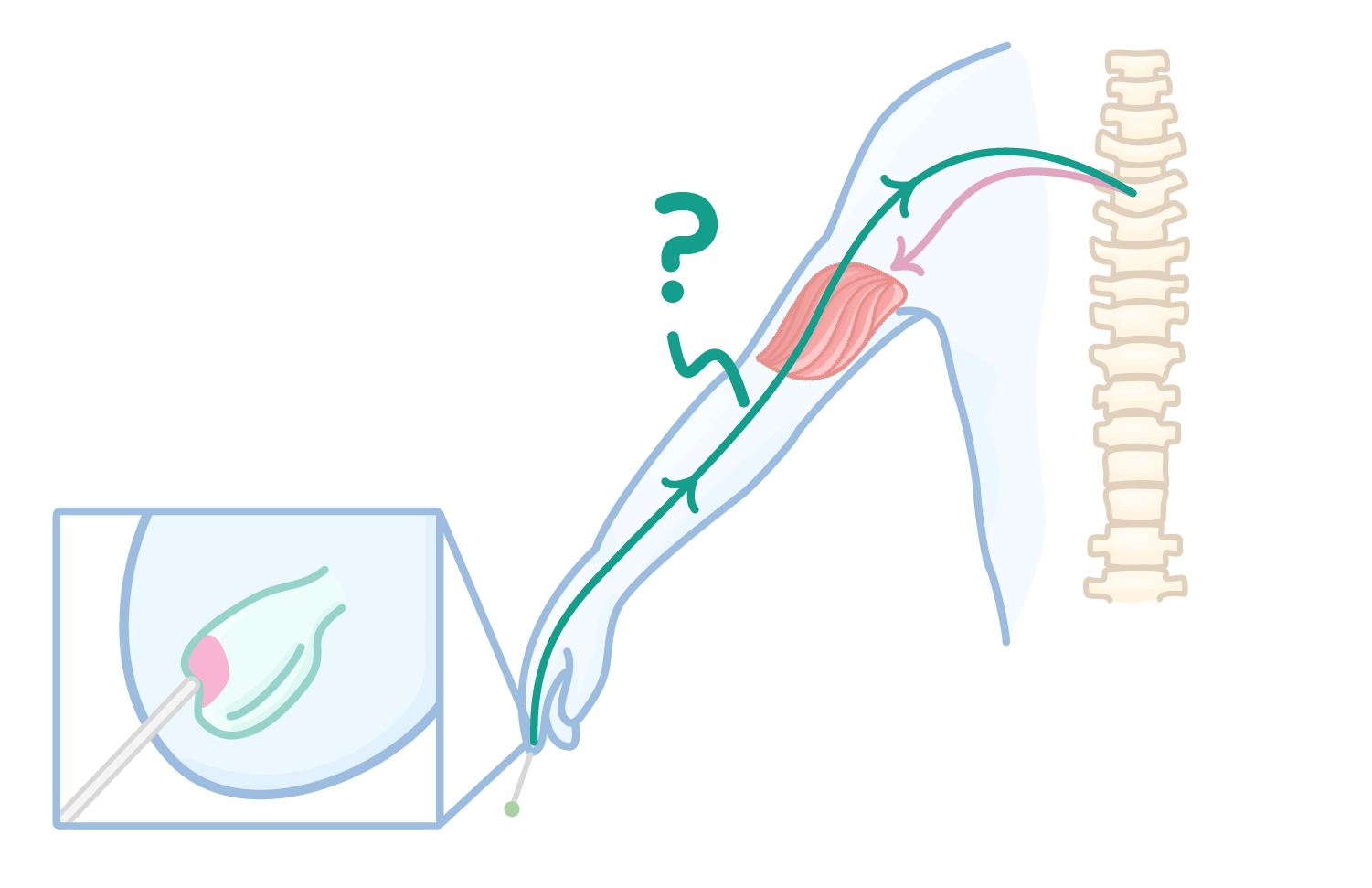
The diagram above shows the part of a reflex arc. Which structure is being indicated?
Effector
Receptor
Sensory neurone
Motor neurone
Relay neurone
|
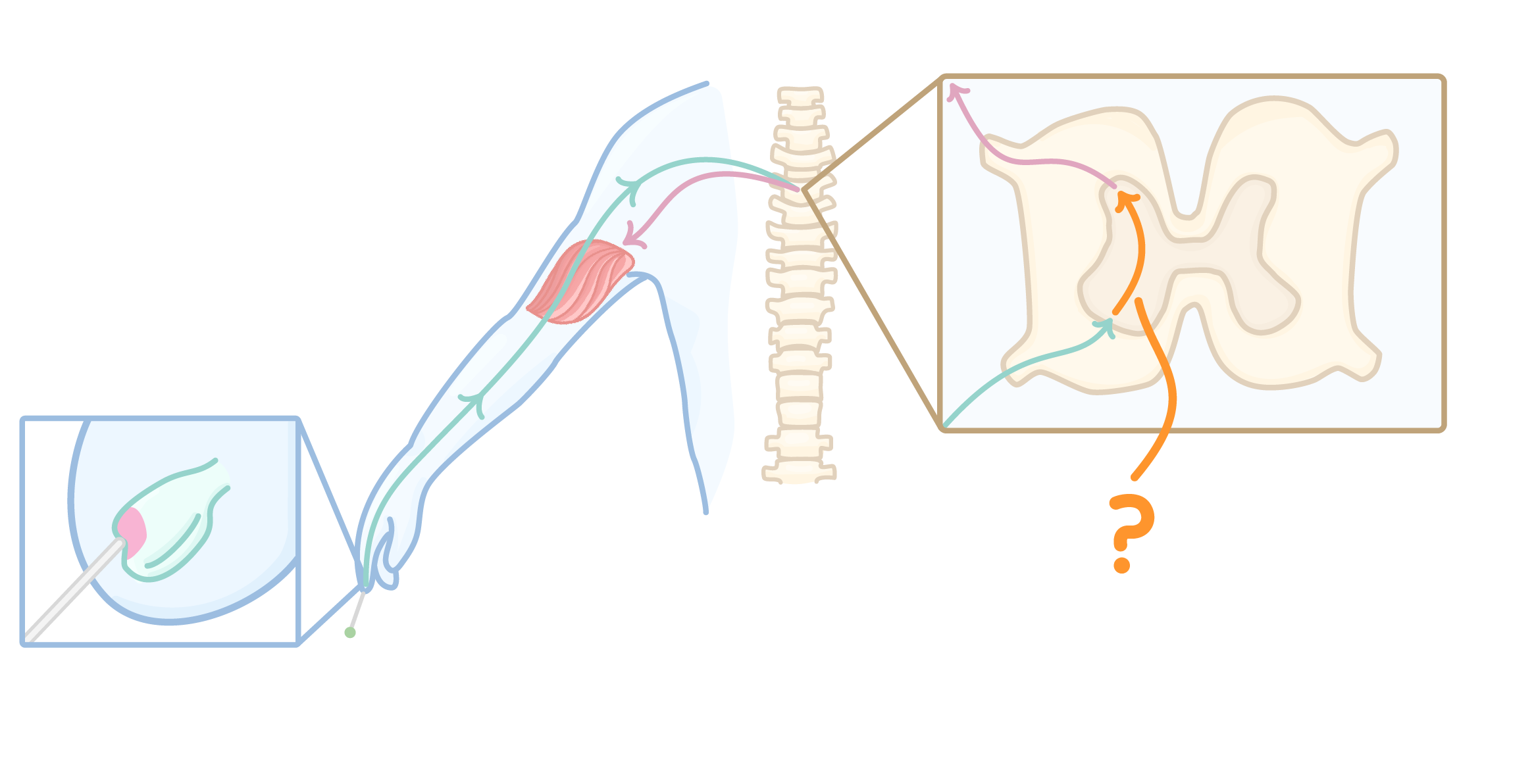
The diagram above shows the part of a reflex arc. Which structure is being indicated?
Relay neurone
Receptor
Effector
Sensory neurone
Motor neurone
|
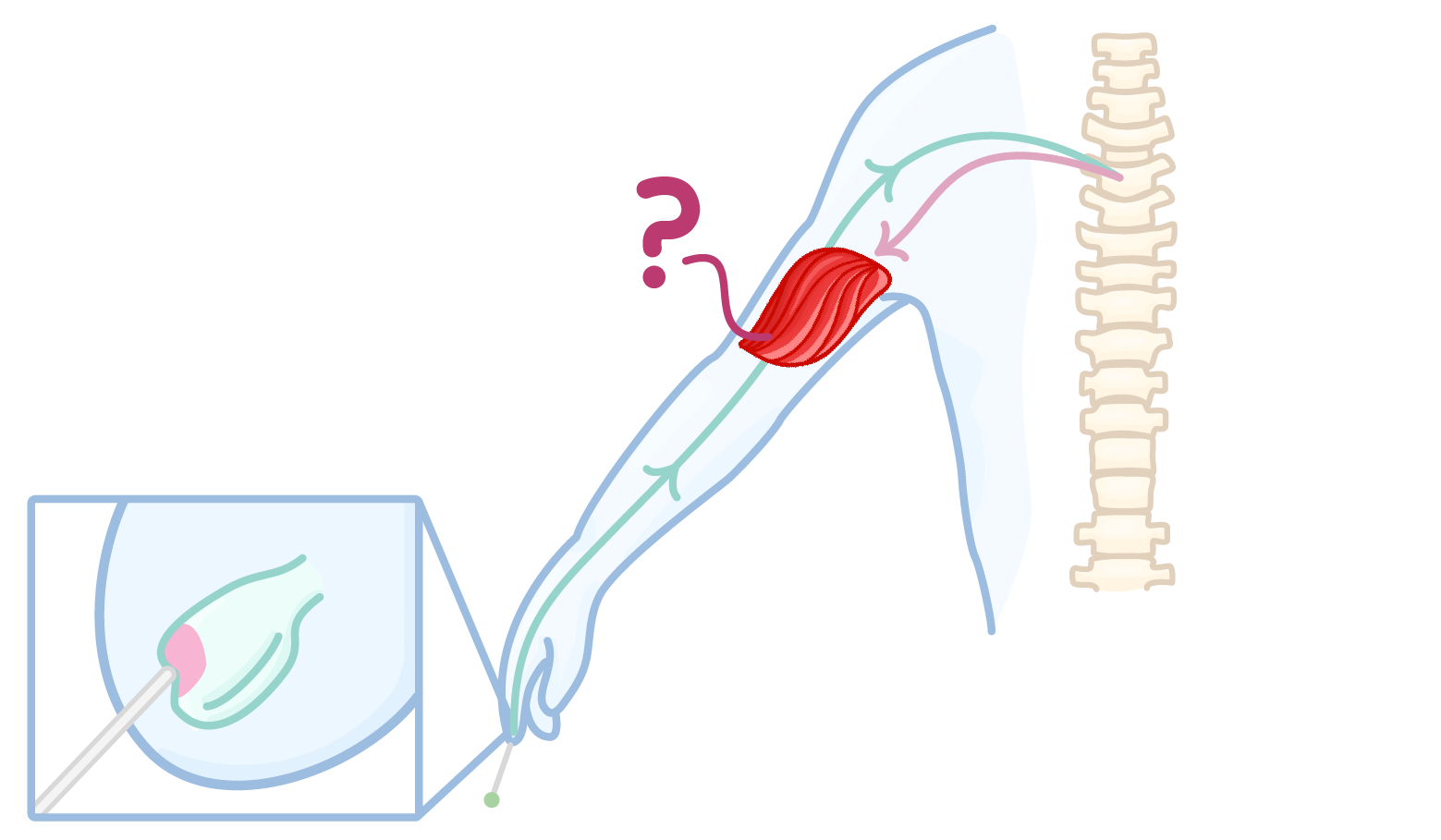
The diagram above shows the part of a reflex arc. Which structure is being indicated?
Motor neurone
Effector
Receptor
Sensory neurone
Relay neurone
|