Fertilisation, Dispersal & Germination
This lesson covers:
- How fertilisation works in plants
- How the pollen passes down the pollen tube to reach the egg cell
The process of fertilisation: |
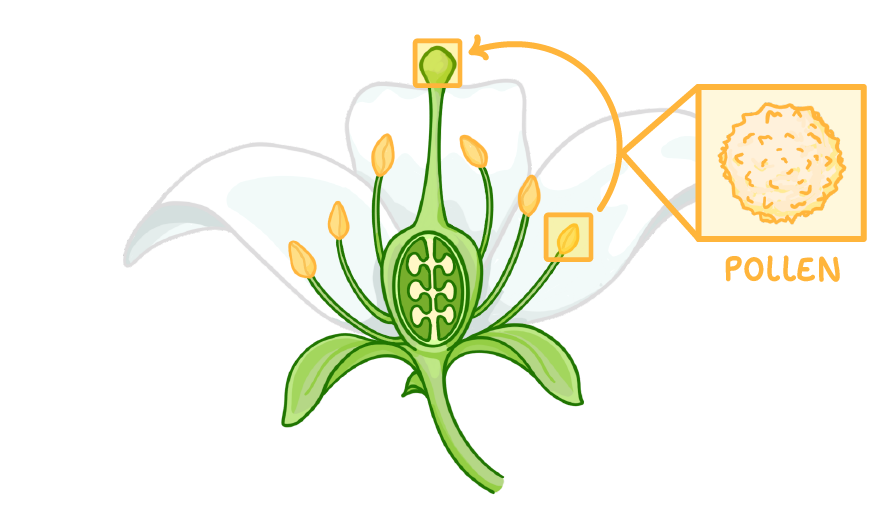 |
1The first step is pollination, where a pollen grain must land on the stigma. This could happen with the help of insects or the wind as we covered in the previous lesson. |
 |
2Next, a pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain and down through the stigma and the style. |
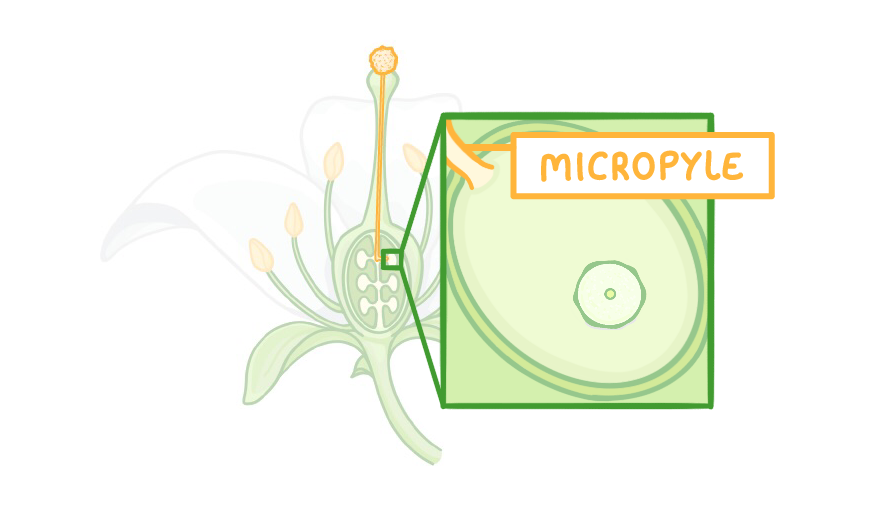 |
3The pollen tube enters the ovary via a micropyle. |
 4The male gamete then passes down the pollen tube and enters the ovary. This is when it fertilises the female gamete cell (egg cell). |
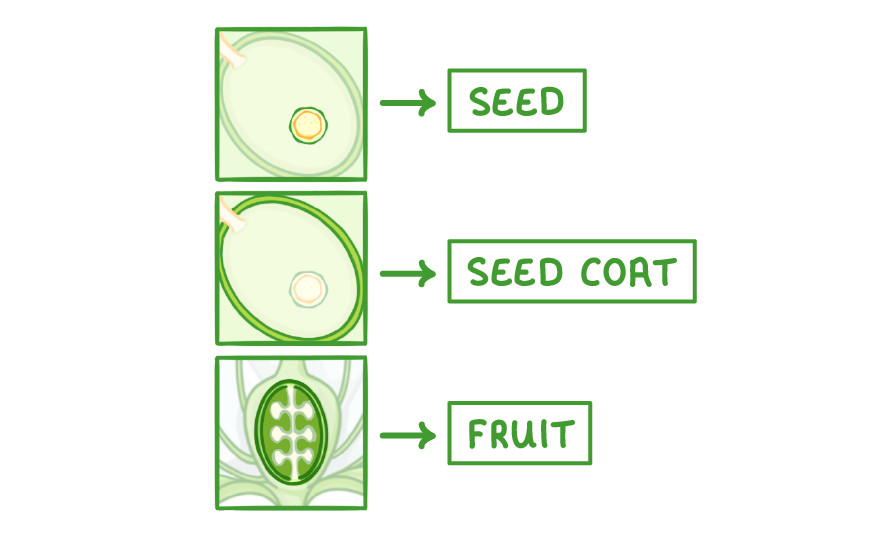 5Once fertilised, the zygote (fertilised egg cell) develops into a seed, while the ovule wall becomes the seed coat, and the ovary becomes the fruit. |
What is the transfer of pollen from the anther to stigma called?
|
The fusion of the female reproductive nucleus with the male reproductive nucleus is known as:
Pollination
Adoption
Fertilisation
Germination
|
A pollen nucleus fertilises an egg nucleus. Is this an example of sexual or asexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction
|
What is the order of the structures through which the pollen tube grows?
Ovary ➔ stigma ➔ style
Style ➔ stigma ➔ ovary
Stigma ➔ style ➔ ovary
|
Following fertilisation, which structure becomes the the seed?
Ovule wall
Ovary
Zygote
|
Following fertilisation, which structure becomes the the fruit?
Ovule wall
Zygote
Ovary
|