Transpiration & Translocation
This lesson covers:
- How sugars are transported around the plant ('translocation')
- How water and mineral ions are transported from the roots to the leaves
- The factors that affect the rate of transpiration
Sources and sinks 1Sources - parts of the plant that create or release sucrose and amino acids. |
2Sinks - parts of the plant that use or store sucrose and amino acids. |
The concentration of sucrose and amino acids is higher at sources than at sinks. |
Translocation Translocation is the movement of sucrose and amino acids through the phloem, from sources to sinks. |
Different parts of a plant act as sources and sinks at different times: As a plant grows and develops, the direction of translocation changes. In reality, this means that a single part of a plant may act as both a source and a sink at different times of the year. |
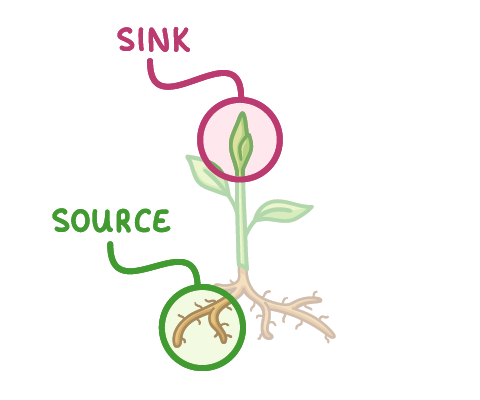 1When leaves sprout in the spring:
|
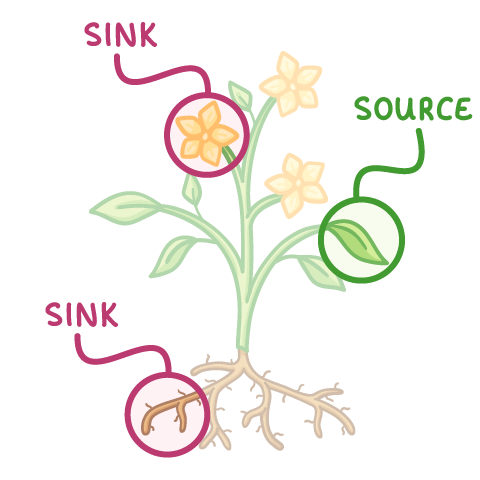 2When plants are growing in the summer:
|
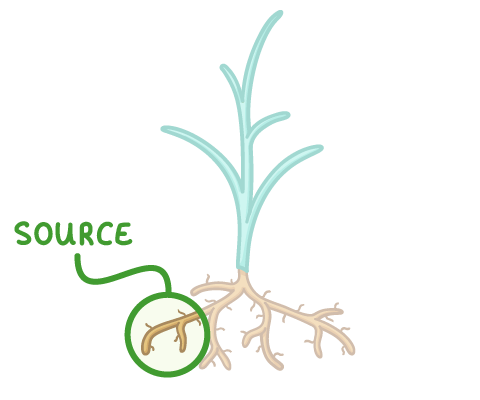 3When plants shed their leaves in the winter:
|
Which part of the plant is glucose produced in?
Stem
Roots
Leaves
|
What do we call the movement of cell sap (a mixture of sugar and water) up and down the plant?
|
Phloem cells have _________ in their end walls to allow cell sap to pass along the phloem tube.
stomata
starch
pores
lignin
|
What does the xylem transport in a plant?
Water and dissolved mineral ions
Water and dissolved sugars
Water only
|

How do root hair cells absorb water from the soil?
Osmosis
Active transport
Diffusion
|
How do root hair cells absorb mineral ions from the soil?
Mass transport
Diffusion
Active transport
Osmosis
|
Which substance are xylem cells reinforced with to make them stronger?
|
What is transpiration?
The release of energy in plant cells
The movement of water into the root hair cells
The evaporation of water from the leaves
|
What happens to the transpiration rate as the temperature increases?
It decreases
It increases
It stays the same
|

Are stomata normally open or closed during the night?
Open
Closed
|
Why does the rate of transpiration increase if the light intensity is increased?
The stomata open wider to let more carbon dioxide into the leaf for photosynthesis.
The root hair cells become more permeable to water, letting more water into the plant.
The humidity increases, which makes the rate of transpiration increase.
|
What happens to the rate of transpiration if wind speed increases?
It decreases
It increases
It stays the same
|
Why does water loss slow down if a plant is put into a plastic bag?
The humidity increases
The temperature increases
The light intensity increases
|
During the summer, where does the primary production of sugars through photosynthesis occur in a plant?
Leaves
Flowers
Stems
Roots
|
Which of the following best describes the role of roots in a plant during the winter season?
Sources, actively photosynthesising
Sinks, using nutrients for growth
Sinks, storing excess sugars
Sources, releasing stored nutrients
|