Lungs & Gas Exchange
This lesson covers:
- Why gas exchange is so important
- The structure of the lungs, including trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli
- How alveoli are adapted for gas exchange
- How to calculate breathing rate

Which organ system are the lungs part of?
Respiratory system
Immune system
Reproductive system
Circulatory system
|
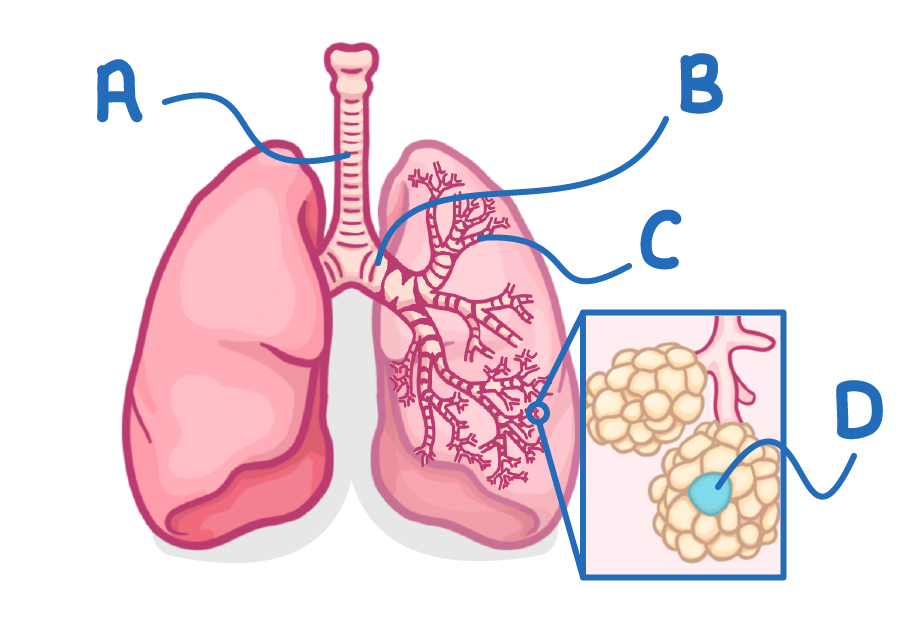
Which letter indicates a single bronchus?
(The plural of bronchus is 'bronchi')
A
B
C
D
|
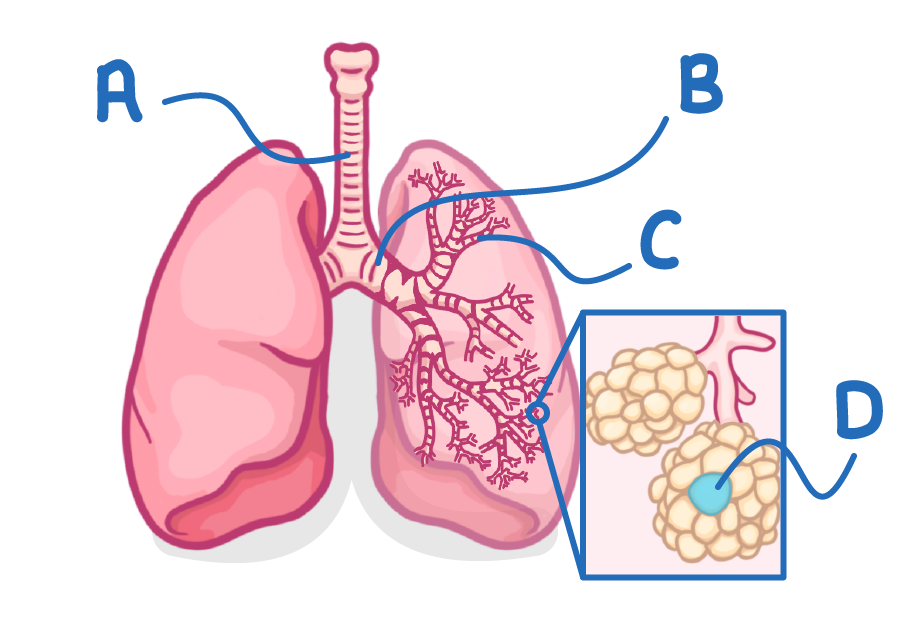
Which letter indicates a single alveolus?
(The plural of alveolus is 'alveoli')
A
B
C
D
|
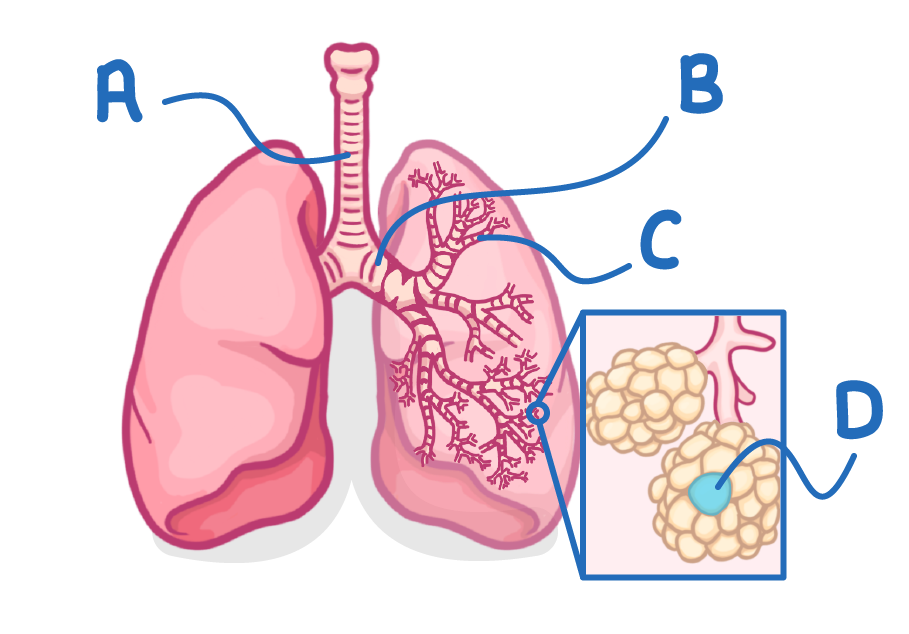
Which letter indicates a single bronchiole?
(The plural of bronchiole is 'bronchioles')
A
B
C
D
|
Which structures connect the bronchi to the alveoli?
Diaphragm
Oesophagus
Trachea
Bronchioles
|
What are the tiny air sacs in the lungs called?
|
What is the name of the process by which oxygen moves through the wall of the alveoli, into the blood?
Mass transport
Osmosis
Diffusion
Active transport
|
How are alveoli adapted for efficient gas exchange?
|
Which gas diffuses from the blood in the capillaries, into the air in the alveoli?
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
|
oxygen / carbon dioxide / hydrogen
passes down its concentration gradient from the alveoli, into the bloodstream.
|

Which substance inside red blood cells does oxygen bind to?
Haemoglobin
Insulin
Antibodies
Urea
|
True or false? Carbon dioxide is transported around the body dissolved in the blood plasma.
True
False
|
A boy has a breathing rate of 14 breaths per minute. How many breaths will he take in 30 seconds?
breaths
|
While running for 5 minutes, a woman takes 115 breaths.
What is her breathing rate for the 5 minute period?
breaths/min
|