Circulatory System 1 - Heart
This lesson covers:
- How the heart, blood vessels, and blood, make up the circulatory system
- What we mean by 'single circulatory system' and 'double circulatory system'
- The structure of the heart
- The route of blood flow through the heart
- The role of the coronary arteries
Fish have a single circulatory system In single circulatory systems the blood travels in a single loop, passing through the heart once for each complete circuit of the body.
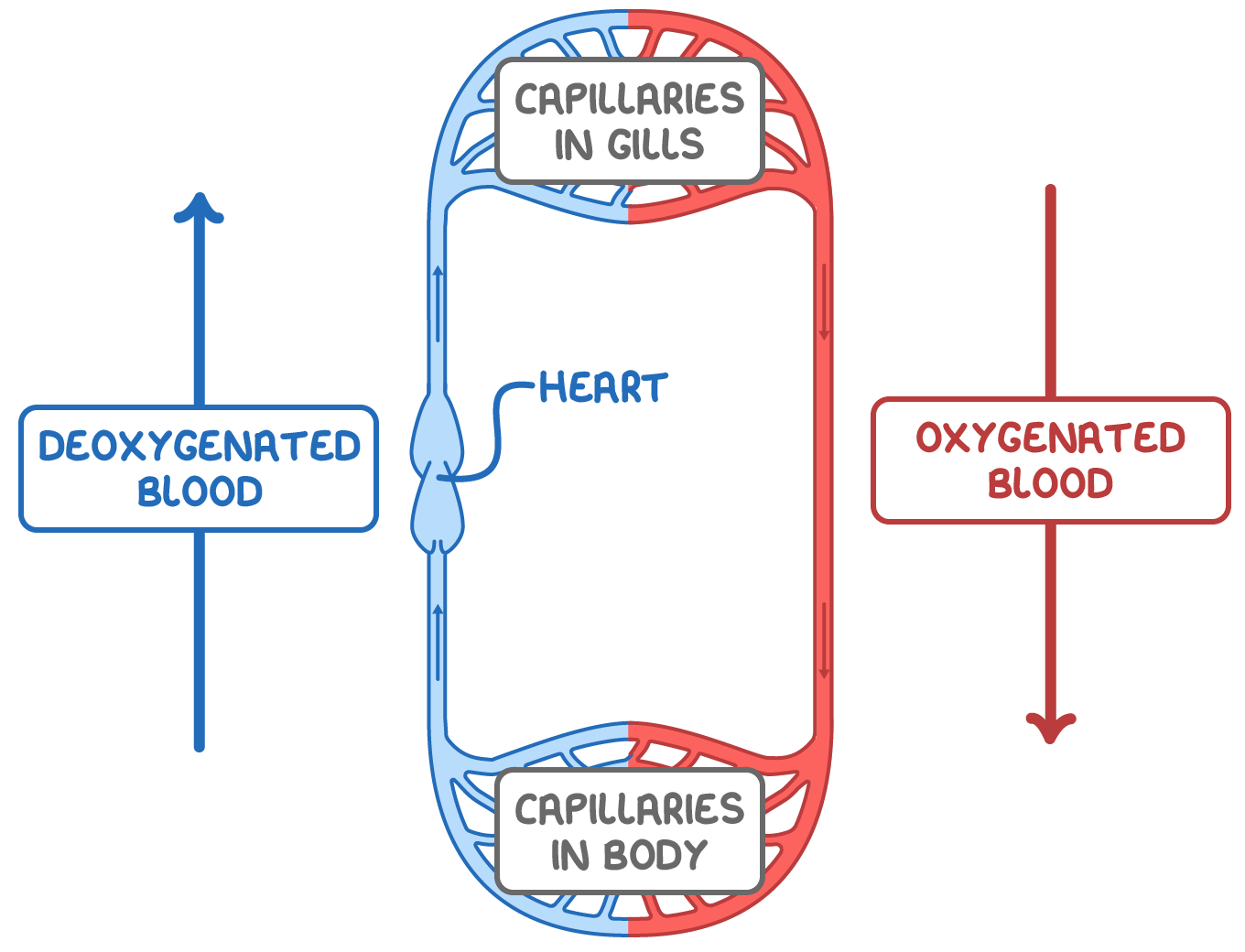 Fish have single circulatory systems:
|
Mammals have a double circulatory system In double circulatory systems, the blood travels around two separate loops per complete circuit.
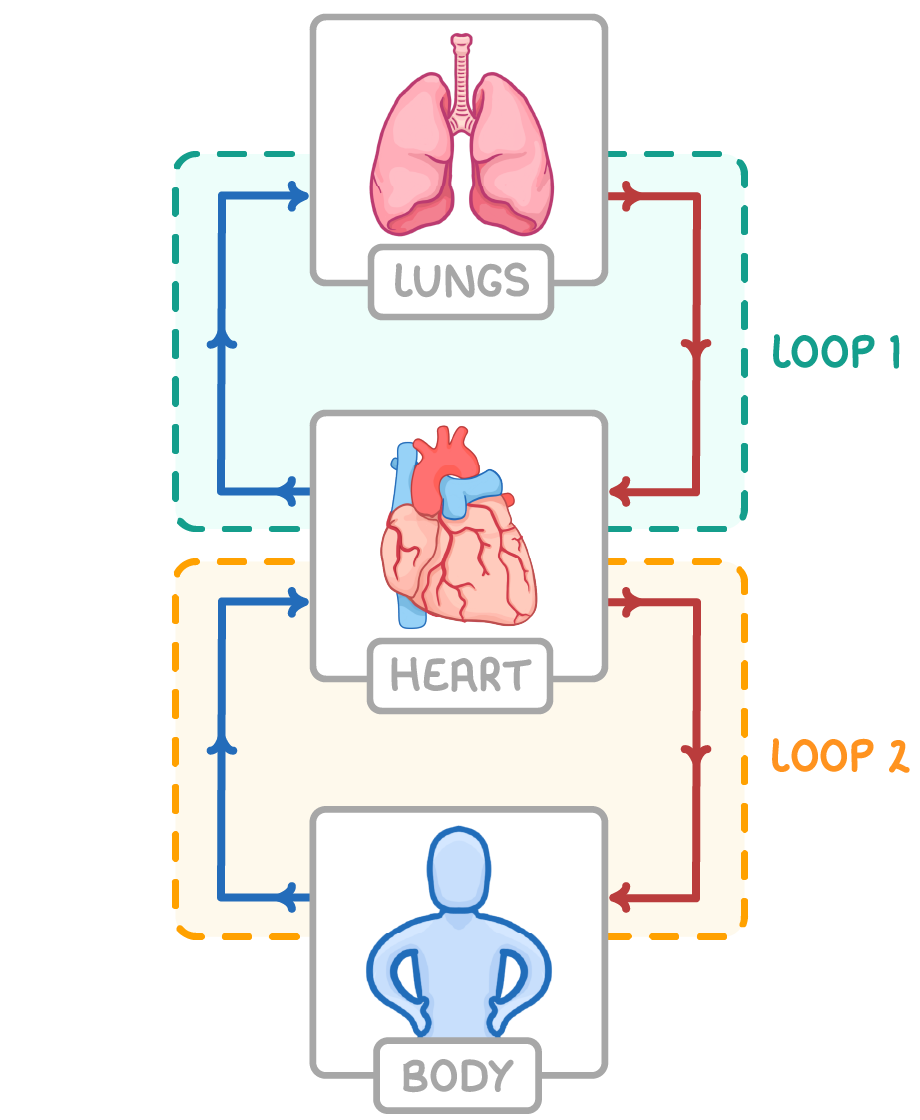 Mammals have a double circulatory system:
|
Advantages of double circulation
|
The three parts of the circulatory system are the b, the b v, and the h.
|
Our double circulatory system has two loops:
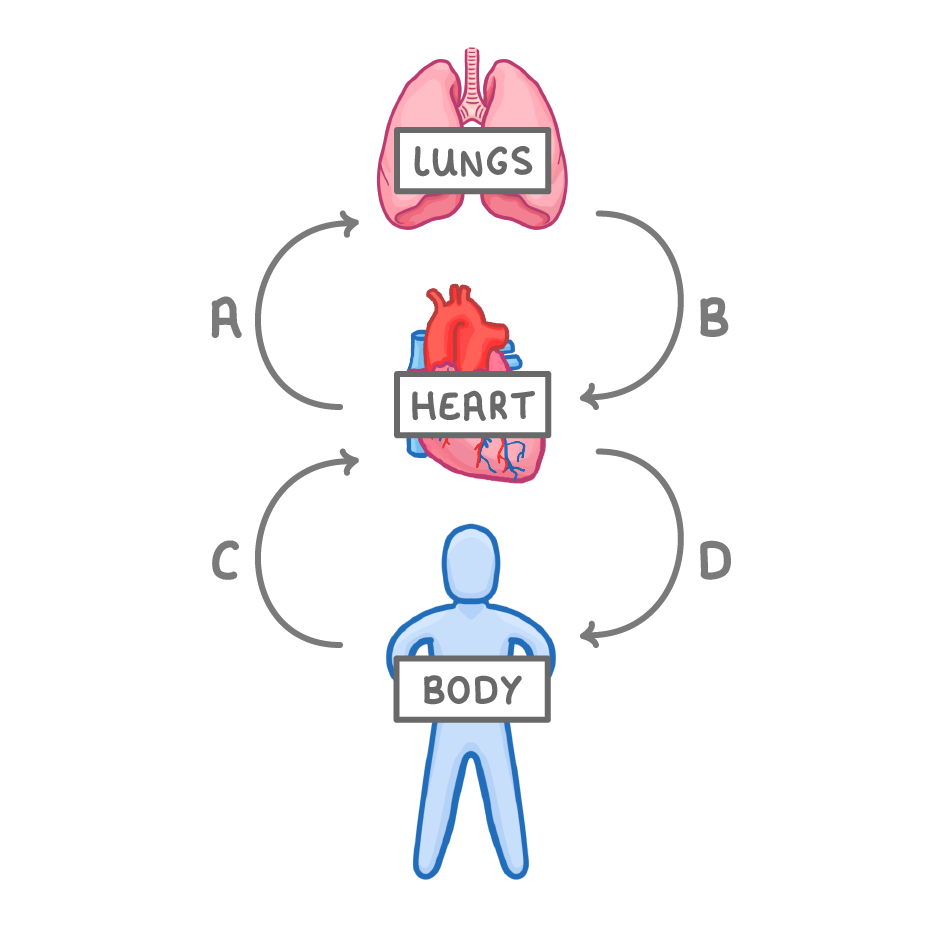
Which letters represent the movement of deoxygenated blood?
(Select all that apply)
A
B
C
D
|
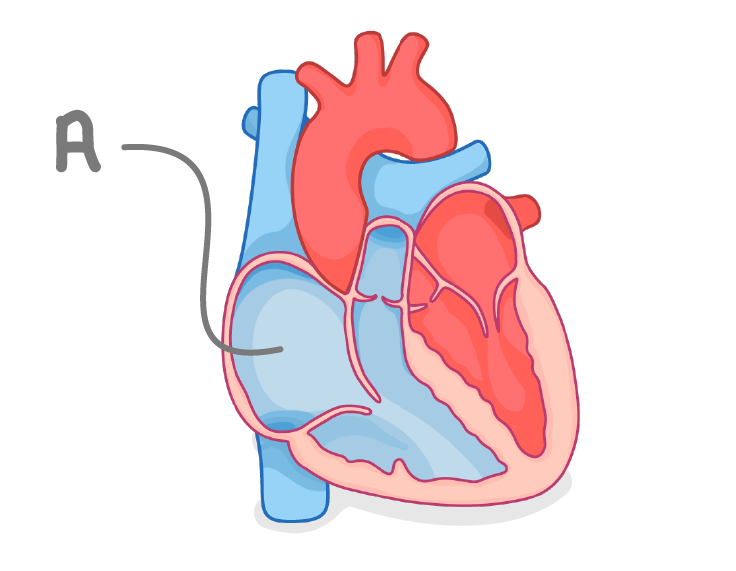
Name the chamber labelled 'A' on the diagram above.
|
On each side of the heart, the atrium and ventricle are separated by a , which prevents the blood from flowing b.
|
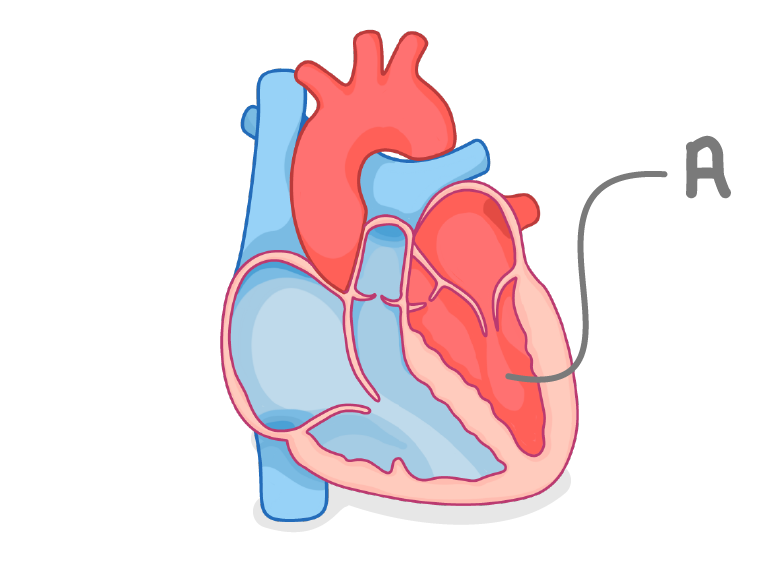
What is the name of the chamber labelled 'A' on the diagram above?
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Left ventricle
|
The _______ ventricle has thicker walls because it has to pump blood all the way around the body.
right
left
|
Which blood vessel carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs?
Vena cava
Aorta
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
|
The journey of blood around the body
left ventricle / pulmonary artery / right atrium / pulmonary vein
Body tissues ➔ vena cava ➔ ➔ right ventricle ➔ ➔ lungs ➔ ➔ left atrium ➔ ➔ aorta ➔ body tissues
|
Which blood vessel carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body?
Pulmonary Artery
Aorta
Pulmonary Vein
Vena cava
|
The movement of blood between the ventricles and atria:
contract / relax / ventricles / atria / aorta
- The walls of the atria , pushing blood into the relaxed ventricles.
- The walls of the contract, pushing blood out of the heart. At the same time, more blood will enter the now-relaxed .
- The cycle repeats.
|
Pacemaker cells are found in which chamber of the heart?
|
Which statement is always true regarding arteries?
They carry blood towards the heart
They carry oxygenated blood
They carry blood away from the heart
They carry deoxygenated blood
|
Which statements is always true for veins?
They carry blood away from the heart
They usually carry deoxygenated blood
They carry blood towards the heart
They usually carry oxygenated blood
|
The c arteries supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients.
|