Factors Affecting Enzyme Action
This lesson covers:
- How temperature affects the rate of enzyme controlled reactions
- How pH affects the rate of enzyme controlled reactions

What does the term 'optimum' mean for enzyme temperature?
The highest temperature before denaturing occurs
The temperature at which enzyme activity is highest
The lowest temperature at which the enzyme works
|
What is pH?
A measure of salt concentation
A measure of pressure
A measure of acidity
|
What affect does extremely high pH have on enzymes?
Denatures them
Destroys them
Inactivates them
|
Which of these statements about enzymes is true?
They all have an optimum pH of 7
Temperature has no effect on their activity
They can be reused
|
Which two of the following statements about enzymes are true?
Enzymes break down food during digestion
The shape of an enzyme is crucial for its activity
Enzymes are reactants in chemical reactions
Enzymes are metals
|
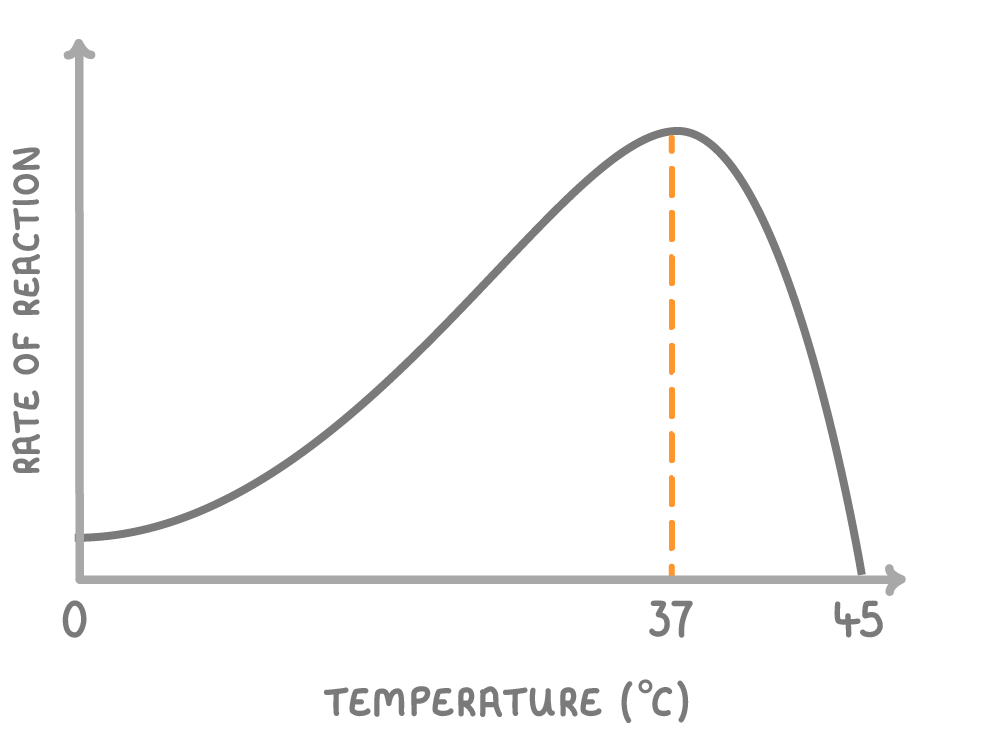 The graph above shows that as temperature increases from 0°C to 37°C, the rate of reaction ________. Decreases Stays the same Increases
|
Reading from the graph, what's the optimum temperature for enzyme activity? °C
|
Once the temperature rises above 37°C, enzyme activity begins to .
|
|
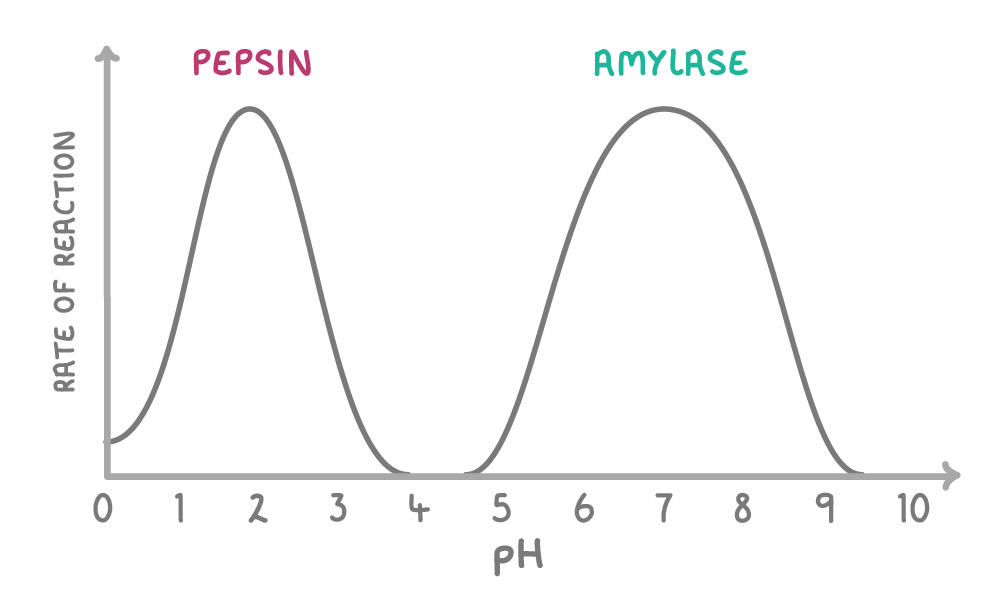
Pepsin is found in the stomach, amylase is found elsewhere in the body.
Using the graph above, what is the optimum pH for pepsin?
|
Explain how increasing the temperature can cause an enzyme to denature.
|