Cloning Animals
This lesson covers:
- An outline of how to clone an animal by transplanting a cell nucleus
- An outline of how to clone an animal by transplanting embryos
- What a 'transgenic' organism is
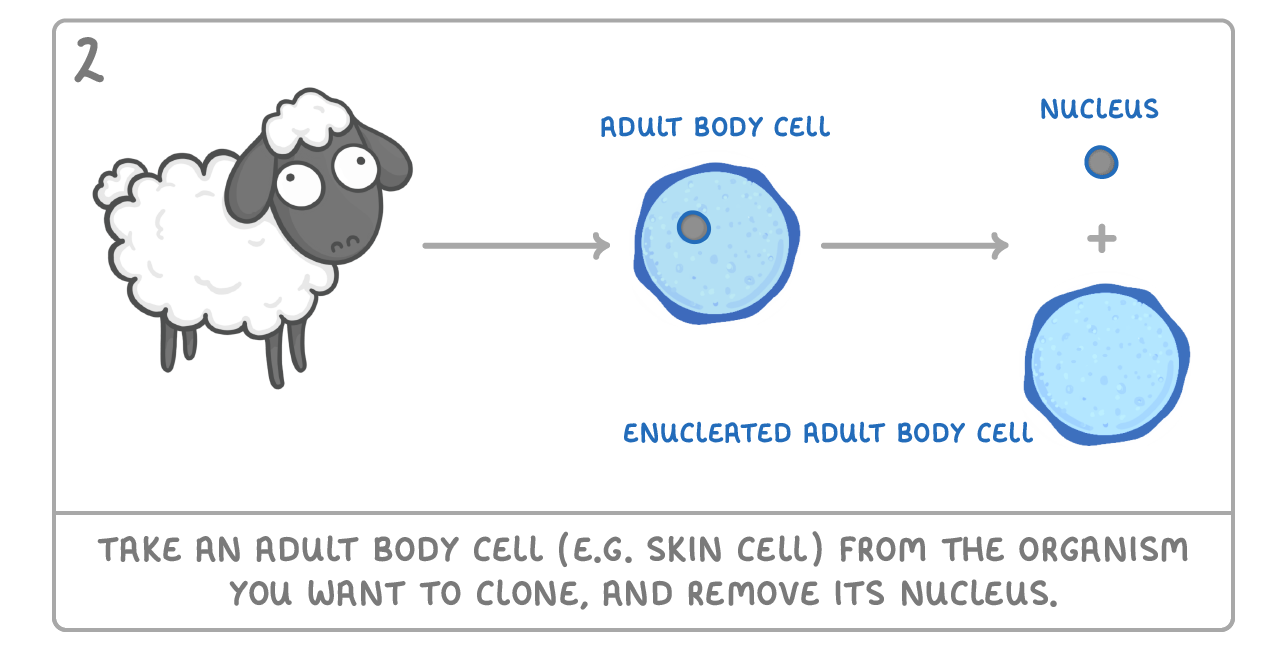
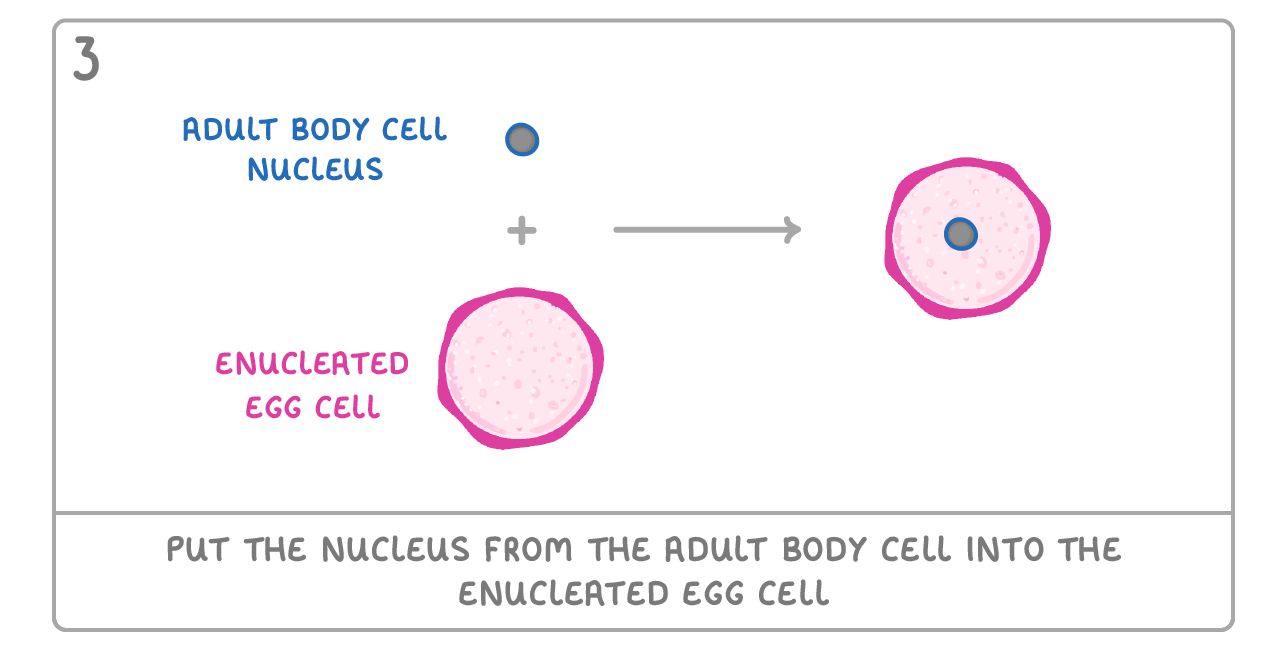
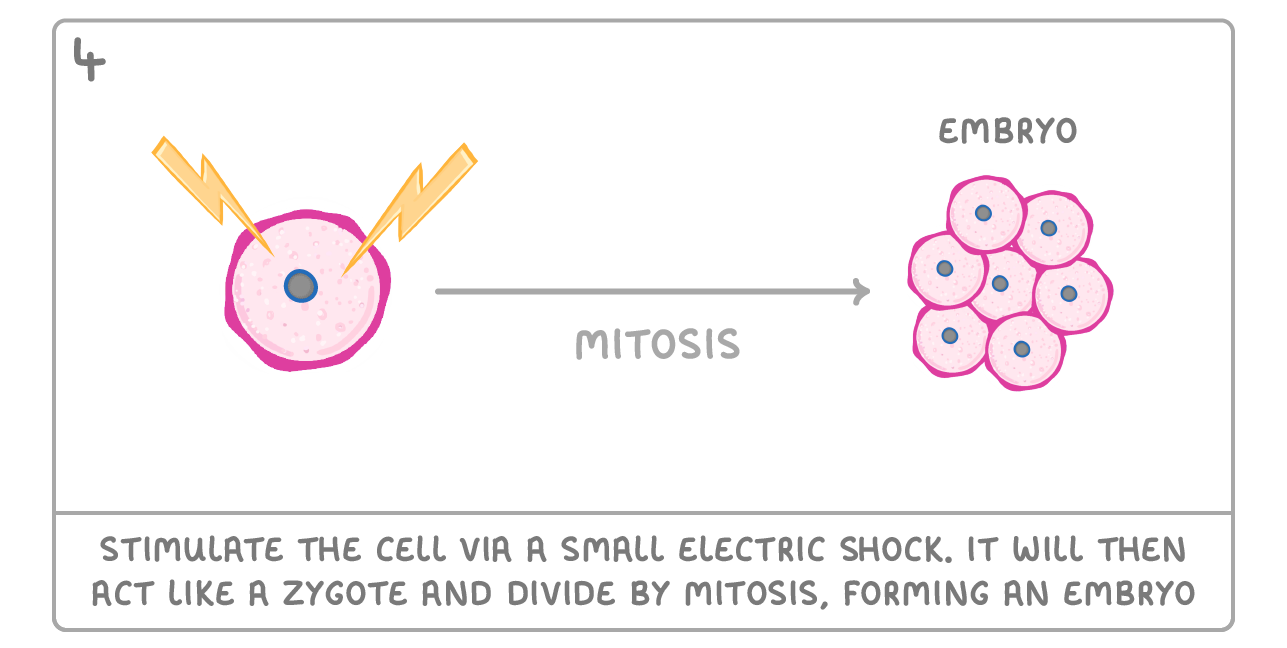
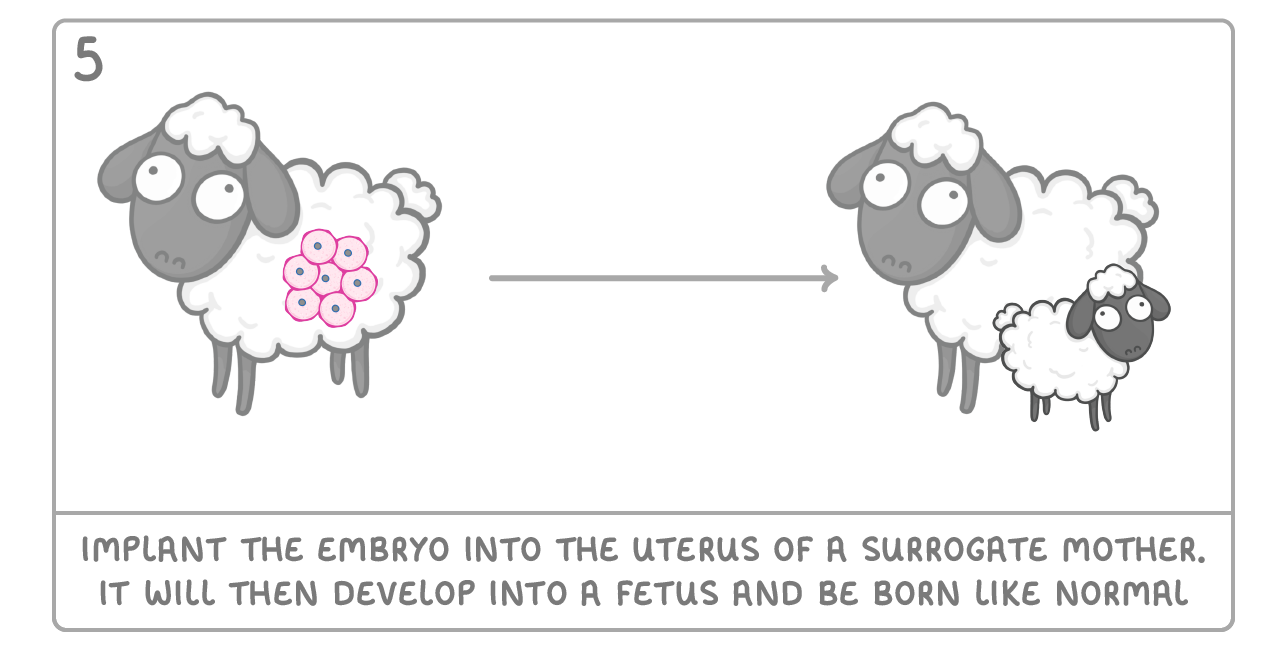
Cloning animals by transplanting a cell nucleus It is now possible to clone an animal. This was first done in 1996 with a sheep named Dolly. Although she had health issues, she did survive, and the process has been repeated in lots of other mammals. Below are the steps involved: |
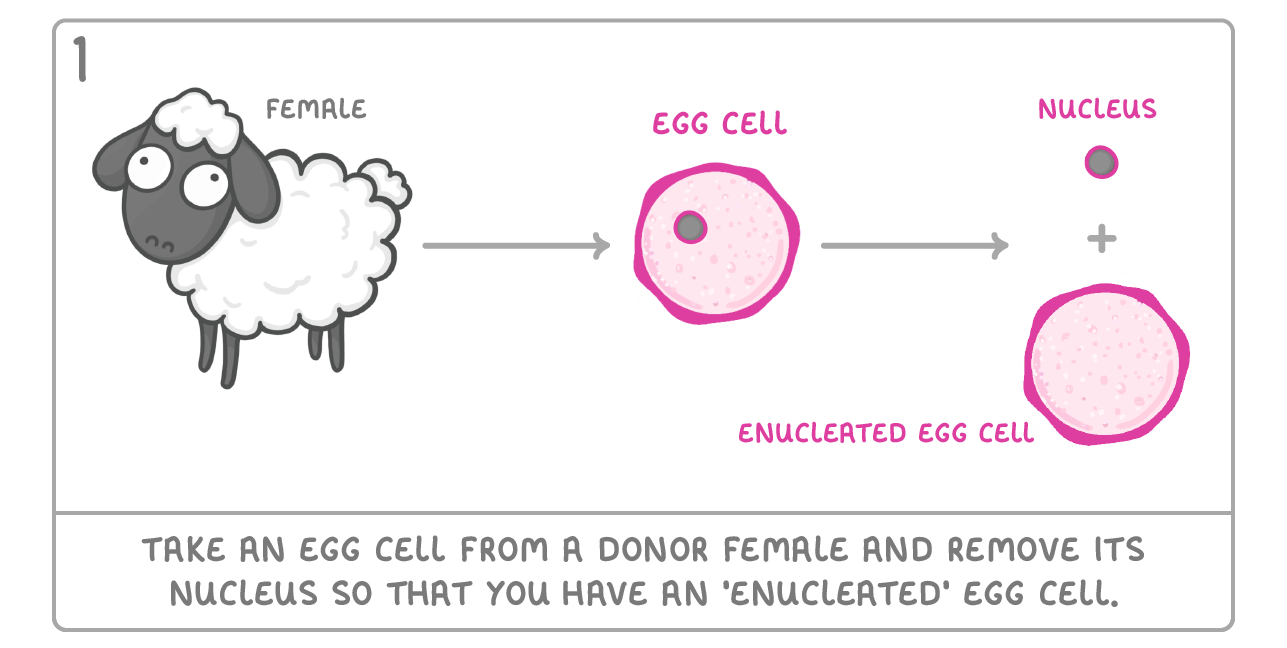 |
A is an individual which is genetically identical to another individual.
|
When you 'enucleate' a cell, what do you remove?
Ribosome
Nucleus
Cell wall
|
What is the animal that gives birth to the cloned animal known as?
A suffragette
A transplant
A carrier
A surrogate
|
In adult cell cloning, where does the foetus develop?
Uterus (womb)
Ovary
Laboratory
|
In adult cell cloning, what type of cell do you take from the organism you want to clone?
Adult body cell (e.g. skin cell)
Egg cell
Sperm cell
|
How was 'Dolly the sheep' produced?
Genetic modification
Selective breeding
Adult cell cloning
|
What type of nucleus is used in adult cell cloning?
A haploid nucleus
A diploid nucleus
|
Cloning transgenic animals to produce human proteins |
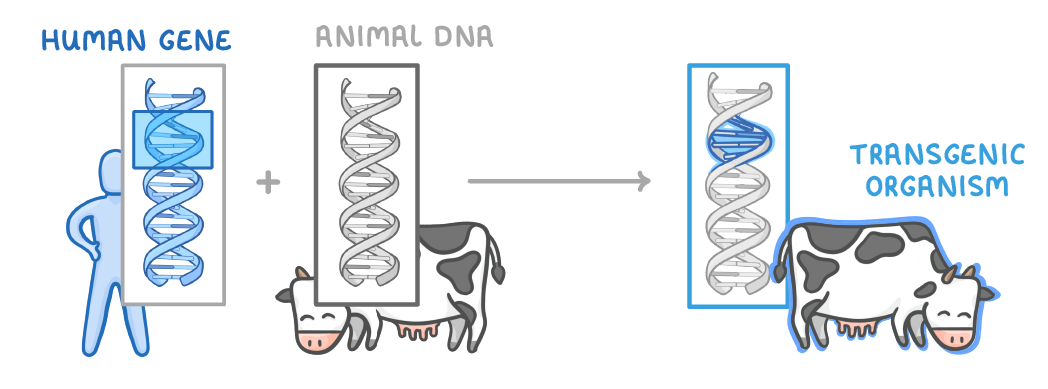 Using genetic engineering, scientists have managed to place human genes into the DNA of other organisms, such as cows, sheep, and goats. For example, scientists could put the human insulin gene into a cow. Once an organism has DNA from another species, we say that the organism is 'transgenic'. |
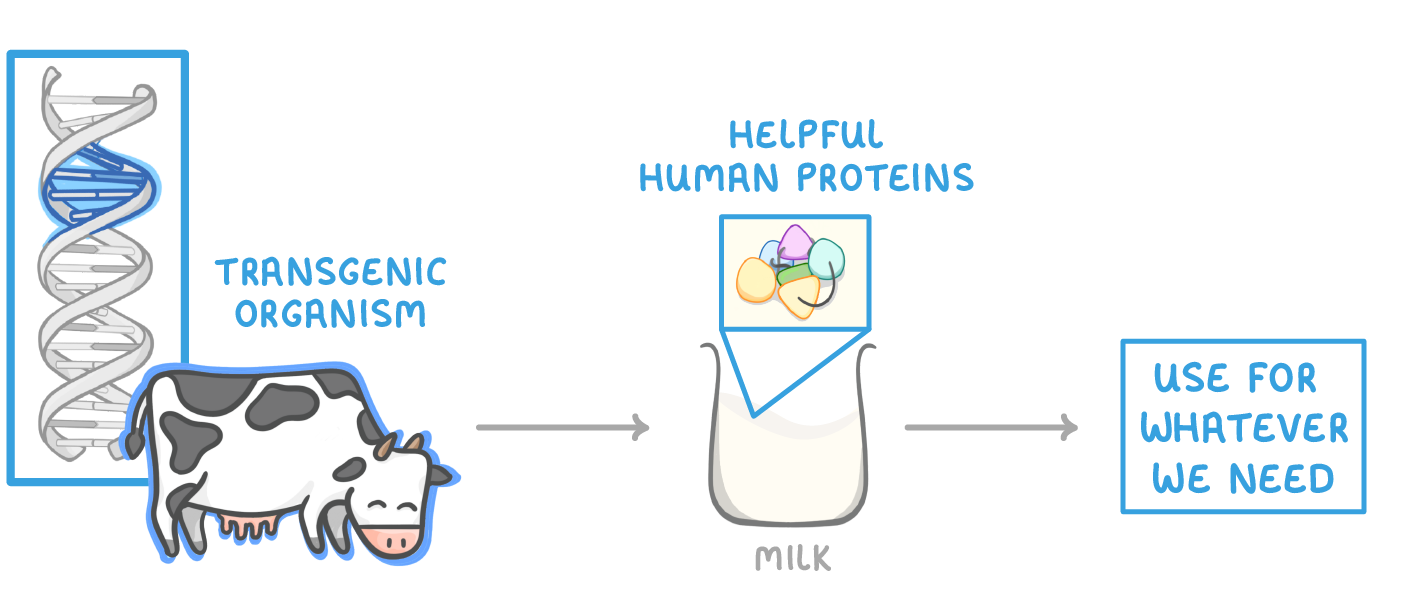 A real world example of transgenic organisms is genetically engineering cows, sheep, and goats, so that they produce helpful human proteins in their milk. For example, if a cow had the human insulin gene, it would produce the human insulin protein. We can then easily extract the proteins and use them for whatever we need, for example medicines. |
Rather than genetically engineering new organisms each time, scientists often clone the transgenic organisms they've already made. |
What is a transgenic organism?
An organism with DNA from another organism.
An organism with DNA from another species
An organism that has had some of its DNA removed
|
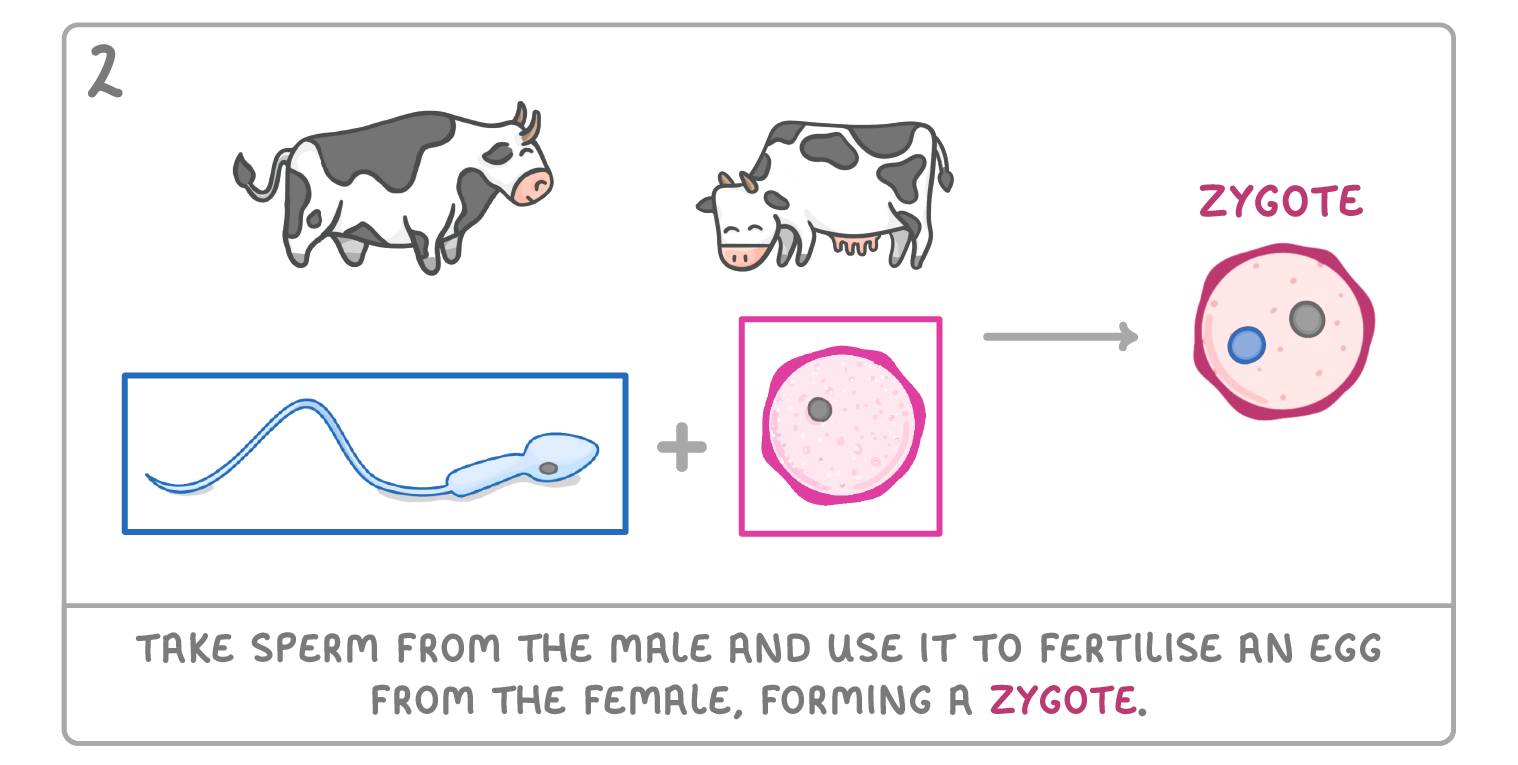
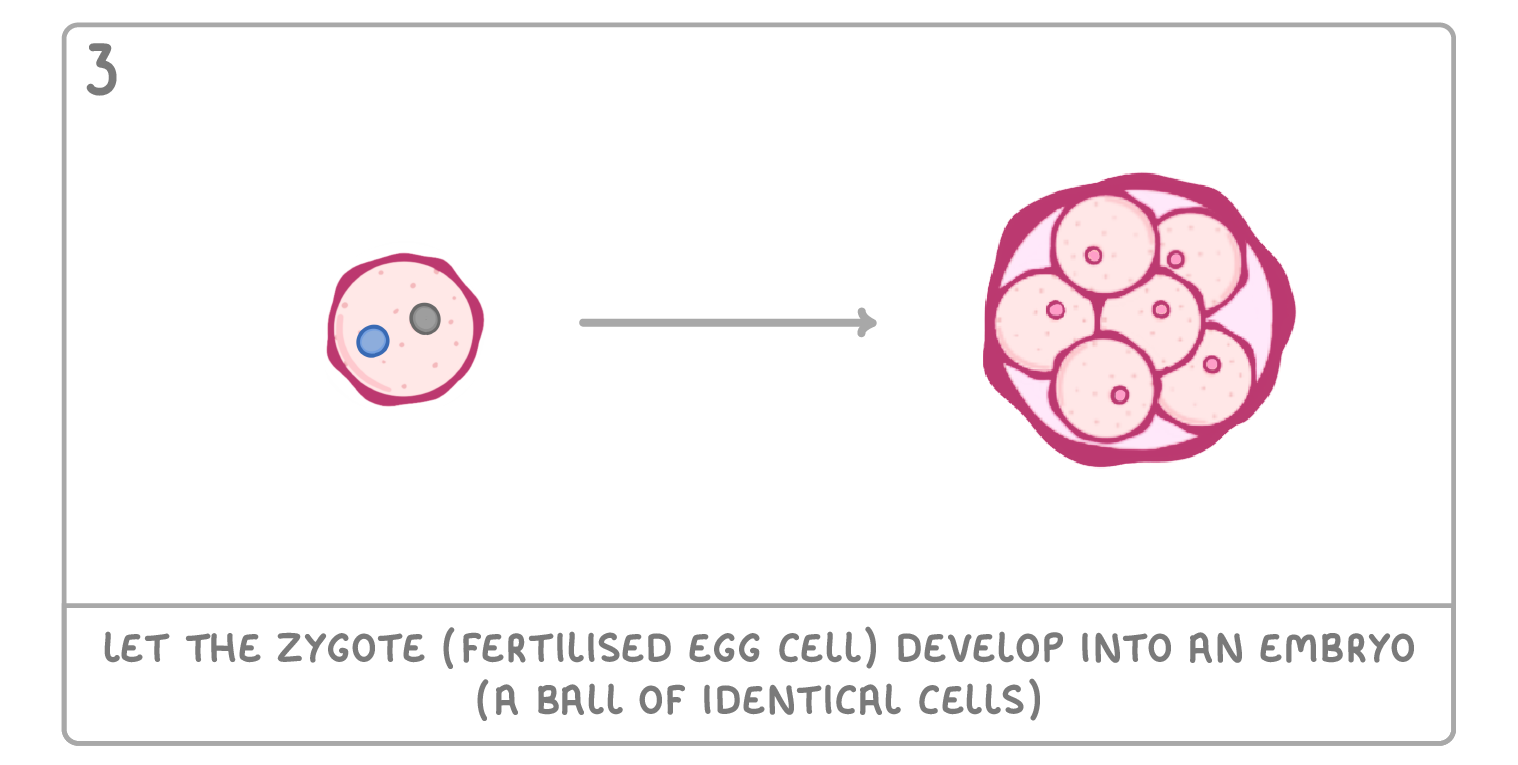
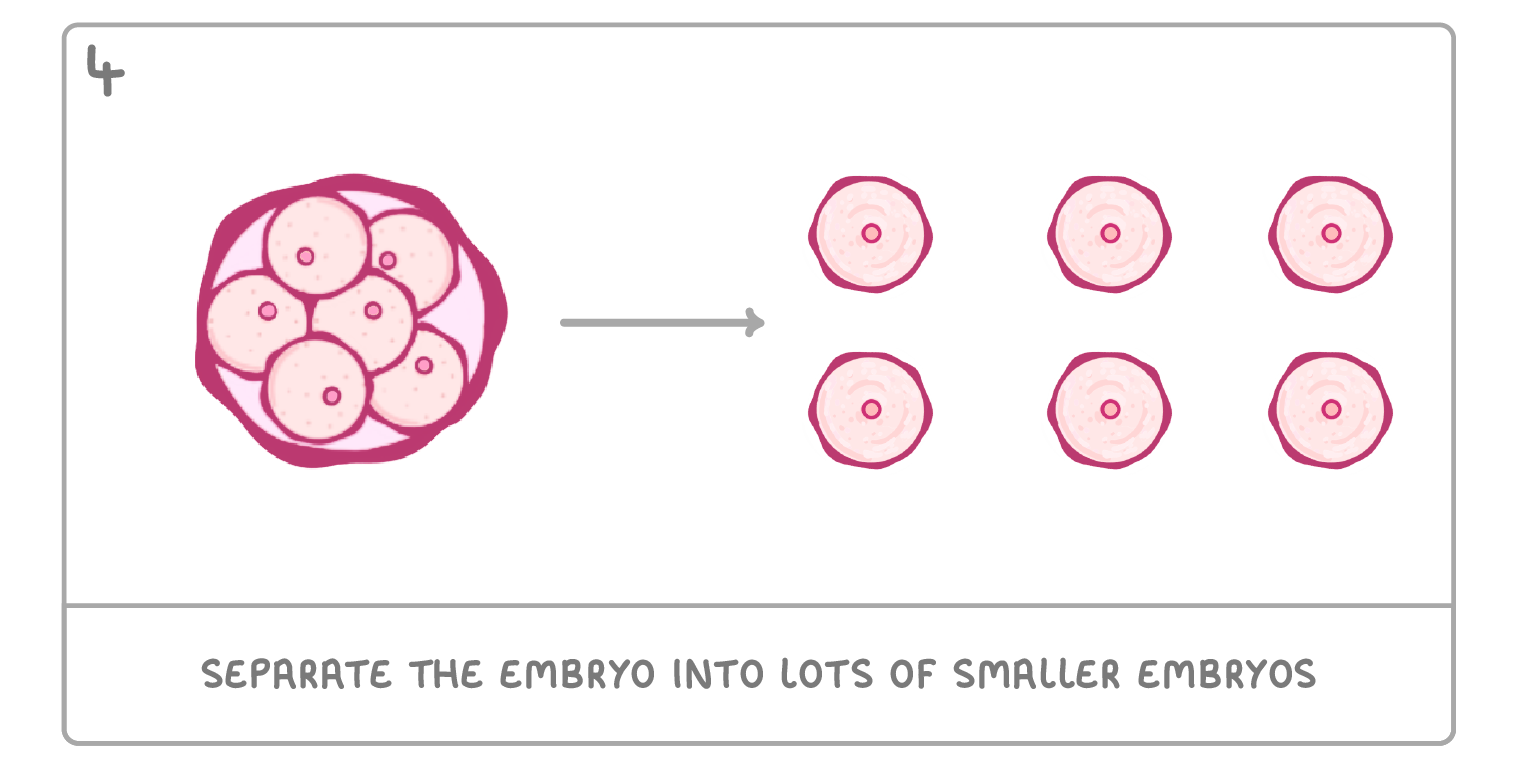
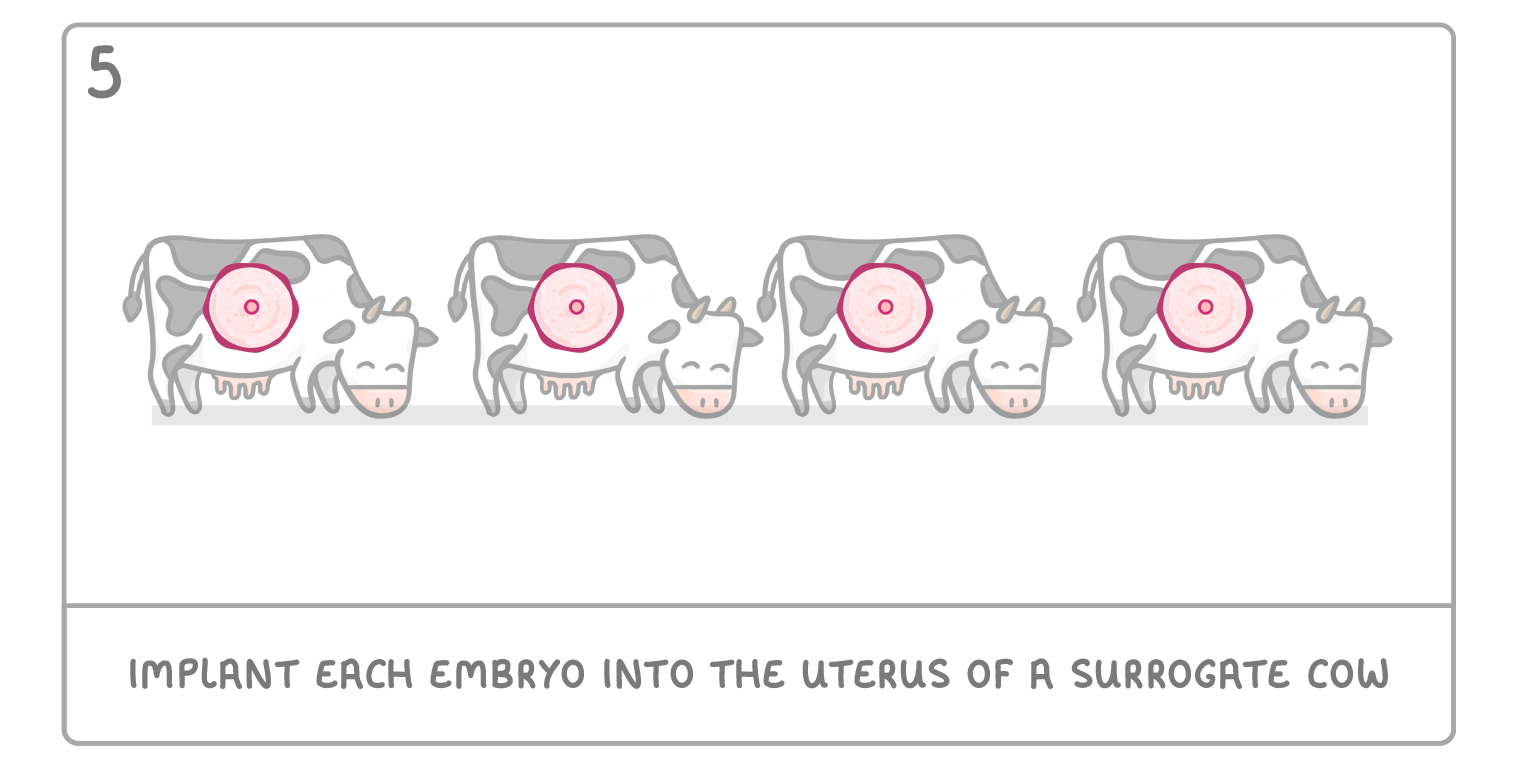
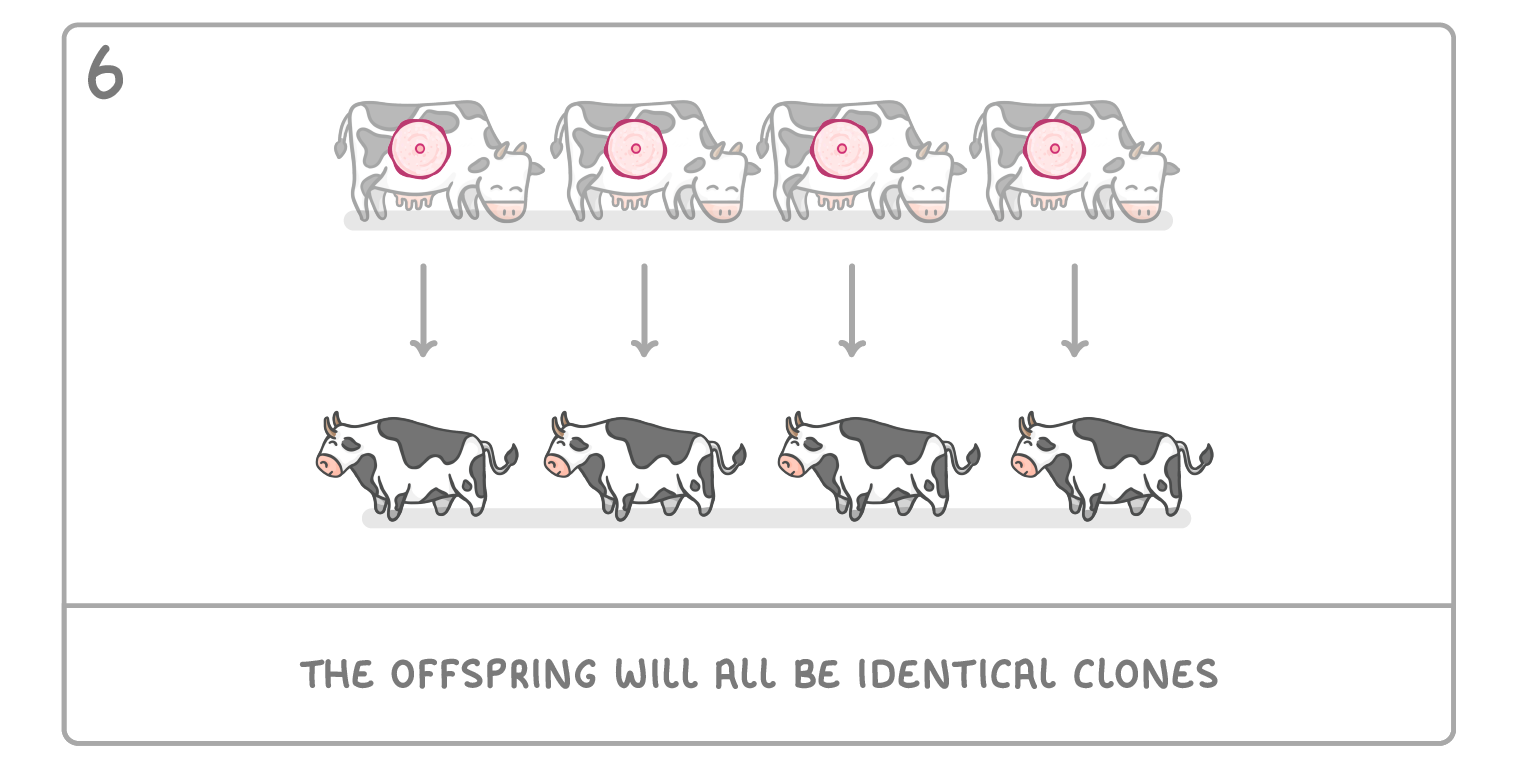
Cloning by embryo transplants It's possible to clone an organism when it is an embryo. This is done by separating the cells of an embryo, and letting each cell develop individually. The steps for doing this are as follows: |
 |
Suggest three advantages of producing cows with desirable characteristics via embryo cloning, rather than via selective breeding.
|
Name the type of cell division that produces an embryo from an individual cell
|