Kidneys 2 - Anatomy & Nephrons
This lesson covers:
- The anatomy of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra
- The anatomy of the nephron, including the glomerulus, and the different parts of the tubule
Blood enters the kidneys via the renal and leaves via the renal .
|
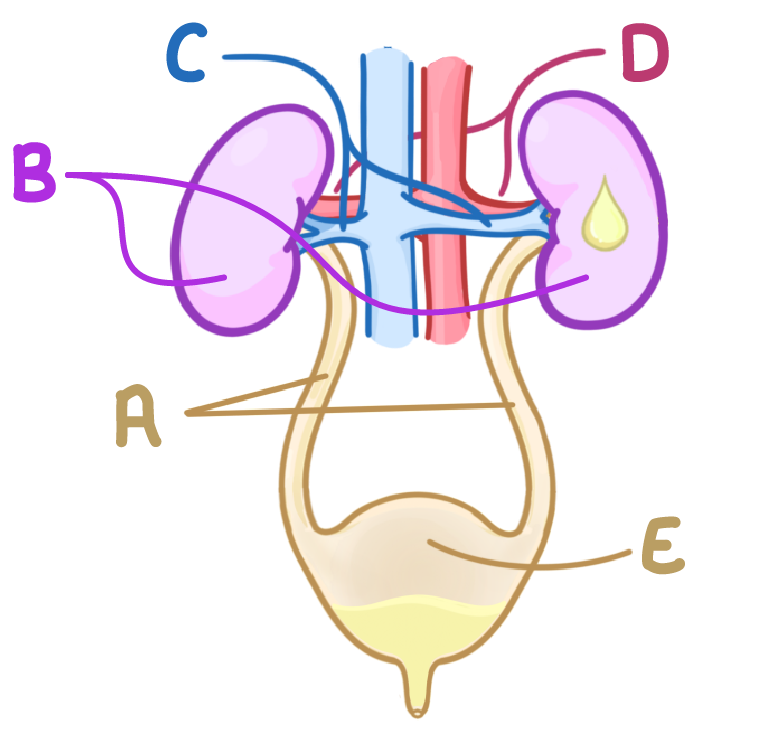
Which letter on this diagram represents the kidneys?
A
B
C
D
E
|
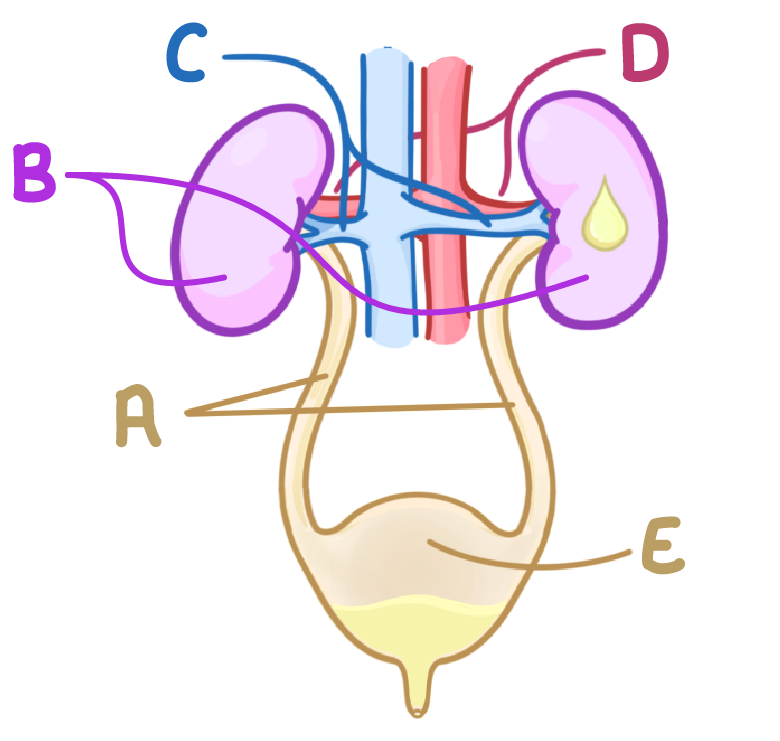
What is A indicating on this diagram?
Ureters
Renal artery
Urethra
Kidney
|
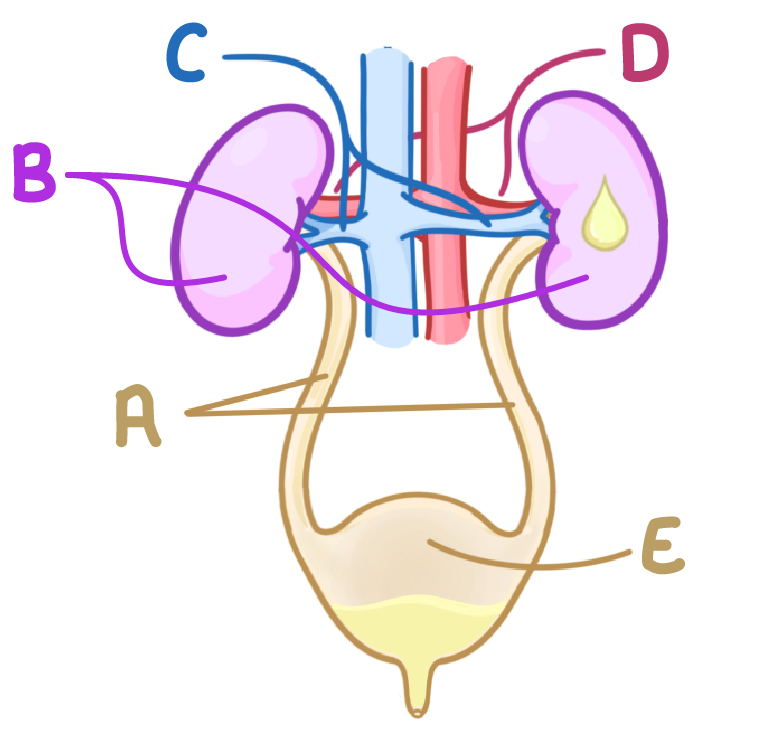
Which letter on this diagram represents the bladder?
A
B
C
D
E
|
Which structure carries urine from the bladder out of the body?
Ureter
Urethra
Nephron
Renal vein
|
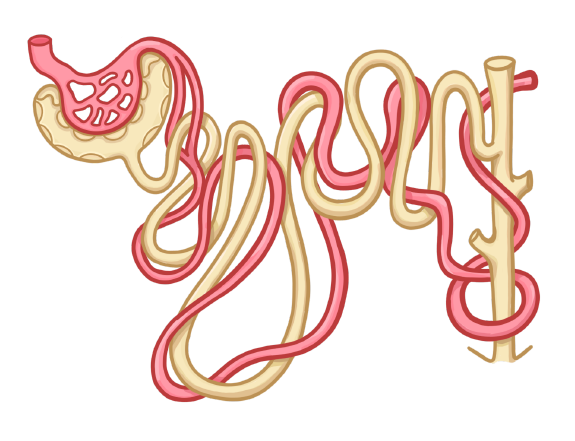
What structure is shown in the diagram above?
|
reabsorption is the process whereby certain molecules (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids), are reabsorbed from the filtrate, as it passes through the nephron.
|
True or false? Selective reabsorption takes place throughout the nephron.
True
False
|
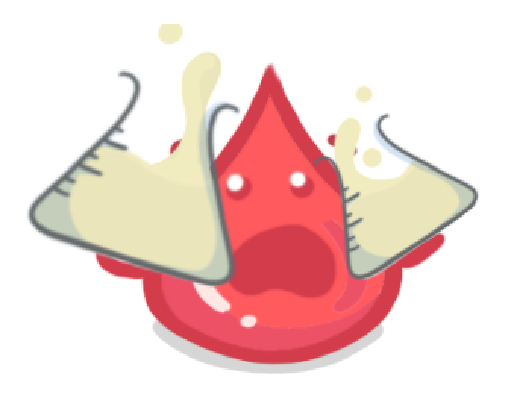

How much urea is selectively reabsorbed?
None
It depends on how much we have in the blood already
Almost all
|
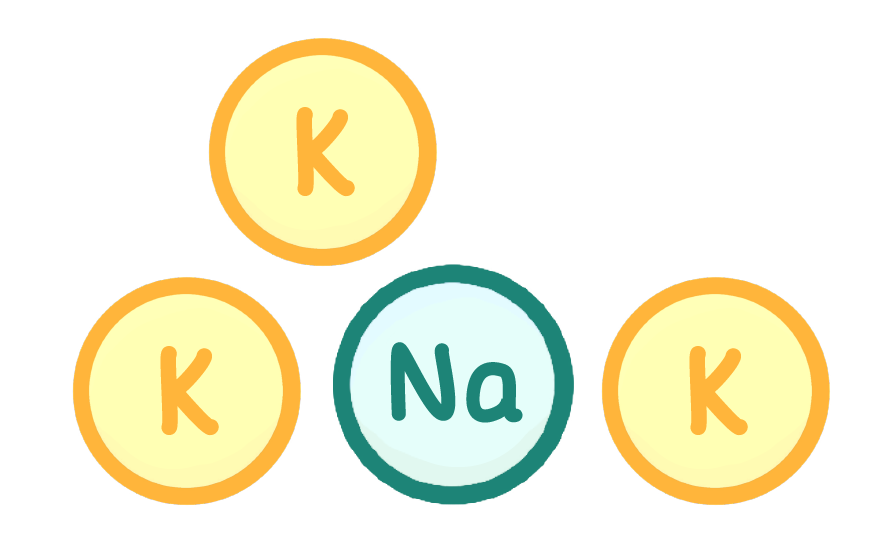
How many ions are selectively reabsorbed?
It depends on how many we already have in the blood
All
None
|
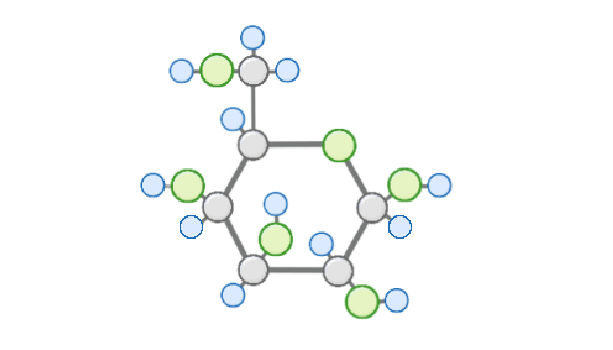
How much glucose is selectively reabsorbed?
It depends on how much we have in the blood already
Almost all
None
|