Decay
This lesson covers:
- What 'decomposition' is
- The ideal conditions for decomposition
- The role of decomposition in making compost and biogas
Decomposition Decomposition, often called 'rotting', is the process by which dead organic matter is broken down into simpler organic or inorganic substances, such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars, and minerals. Decomposition is essential for the recycling of elements throughout an ecosystem. |
 For example, when leaves fall from a tree and are slowly broken down in the soil, we say that they are decomposing. This recycles the carbon, nitrogen, magnesium etc. and makes them available for the plants to absorb and use again. |
Detritus feeders and decomposers Decomposition is carried out by two groups of organisms: detritus feeders (detritivores), and decomposers.  |
Detritus feeders - small animals like worms and woodlice that feed on dead organic matter. |
Decomposers - microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. |
What is decay?
The breakdown of organic matter by the action of decomposers
The production of glucose from carbon dioxide and water
The formation of urea by the liver
|
Which of the following are detritus feeders?
Bacteria
Fungi
Woodlice
Worms
|
Factors that affect the rate of decomposition The rate of decomposition is affected by 3 environmental conditions: |
 1Oxygen availability Higher oxygen ➔ more aerobic respiration ➔ more energy available ➔ faster growth and decomposition |
 2Temperature Higher temperature ➔ particles have more kinetic energy & enzymes are closer to optimum temperature ➔ higher rate of reactions ➔ more decomposition However, if temperature rises too high, it will denature enzymes, decreasing the rate of reaction and therefore decreasing the rate of decomposition. |
 3Water content Decomposers need water to survive, so the rate of decomposition increases in moist conditions. However, if the soil becomes waterlogged then the oxygen levels will fall, which will decrease the rate of decomposition. |
What effect would lowering the temperature have on the rate of decay of an apple?
Increase the rate of decay
Decrease the rate of decay
No effect on the rate of decay
|
Oxygen is important for decomposition.
What process do bacteria need oxygen for?
|
Why could the rate of decomposition fall if soil becomes waterlogged?
|
Compost
Compost is a mixture of decayed organic material that is used to fertilise and improve the soil. It is commonly prepared by leaving dead plant waste in ideal conditions (plenty of oxygen, warm, moist) until it is mostly decomposed. It can then be spread across soil, where it provides nutrients for the plants.

The image above shows how the mixture changes over time as it decomposes. At first there are whole pieces of food, but over time it breaks into smaller pieces, and in the end starts to look like soil.
What is compost made of?
Mud
Manure
Dead plants
|
Biogas generators |
 Some decomposing microorganisms can break down organic material without oxygen. In these cases, the microorganisms carry out anaerobic respiration and so it is called 'anaerobic decay'. |
The mixture of gases this produces is known as 'biogas', and the most important of the gases is methane. When methane is combusted (burned), it releases a lot of energy, which can be used for cooking, heating, or generating electricity. 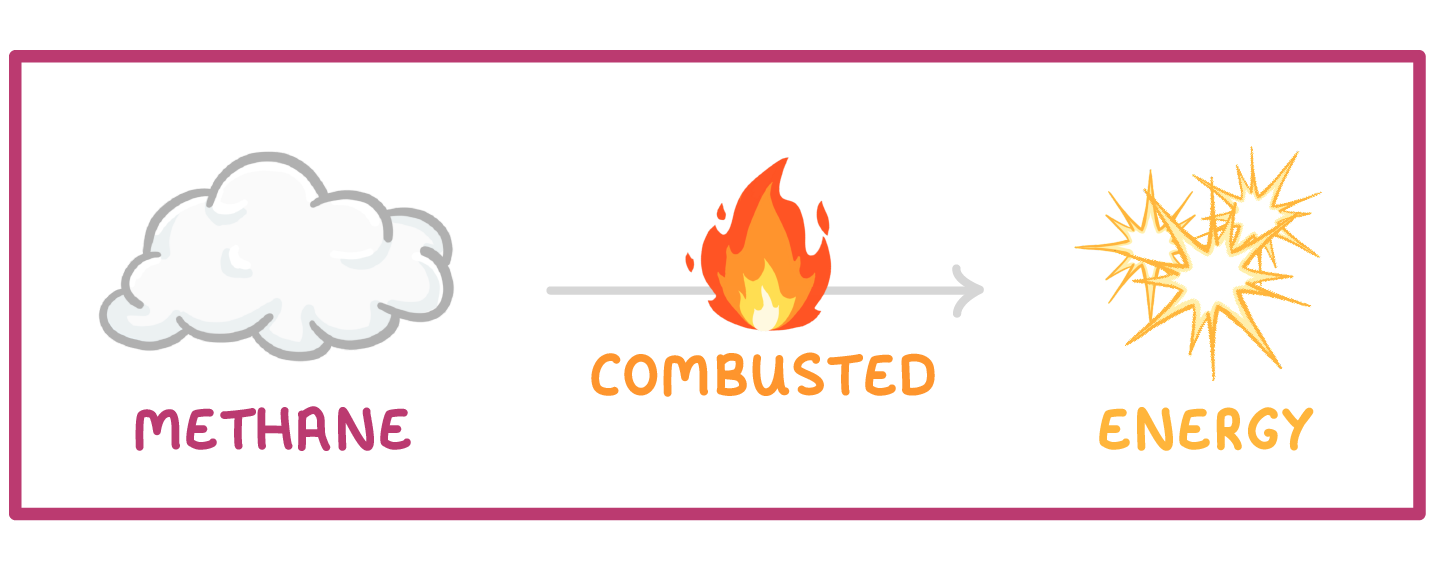 |
Biogas generators are large containers in which animal or plant waste is left to decay anaerobically. Importantly, there cannot be any oxygen in the container. If there is oxygen, the microorganisms will respire aerobically and won't produce as much methane. |
 Once the biogas is removed from the tank, a sludgy material is left over, which contains a high density of useful minerals. This can be spread on fields like fertiliser. |
What does anaerobic mean?
Without air
With oxygen
With air
Without oxygen
|
Do biogas generators carry out aerobic or anaerobic decay?
Aerobic
Anaerobic
|
What is the main gas in biogas?
|
Once the gas has been removed from a biogas generator, a sludgy material is left over.
What is this sludgy material used for and why?
|