Kingdoms of Life
This lesson covers:
- The key features and differences between animals, plants, fungi, protoctists, bacteria, and viruses
This lesson is not in your course, but we have included it here because you may find it helpful for understanding other parts of the course.
Feel free to skip it.
Which of the following are included in the '5 kingdoms of life'?
(Select all that apply)
Protoctists
Animals
Viruses
Fungi
Plants
Bacteria
|
Which of the following are considered 'eukaryotes'?
(Select all that apply)
Plants
Protoctists
Bacteria
Viruses
Fungi
Animals
|
Which of the following is considered 'prokaryotic'?
Viruses
Plants
Fungi
Bacteria
Animals
Protoctists
|
A key difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, is eukaryotic cells all have:
Cytoplasm
A nucleus
A cell membrane
Plasmids
|
Which of the following are features of animals?
(Select all that apply)
Unicellular
Reproduce asexually
Autotrophs
Multicellular
Reproduce sexually
Heterotrophs
|

Which of the following are features of plants?
(Select all that apply)
Heterotrophs
Multicellular
Saprotrophs
Autotrophs
Unicellular
|
Fungi can be unicellular or multicellular.
Is yeast unicellular or multicellular?
Unicellular
Multicellular
|
Saprotrophic nutrition
excrete / absorb / digestive / nutrients / heterotrophic / waste
- Fungi feed by a special type of nutrition called 'saprotrophic' nutrition.
- First, they secrete enzymes out of their body, onto the food.
- These break down and digest the food.
- They then the small into their cells.
|
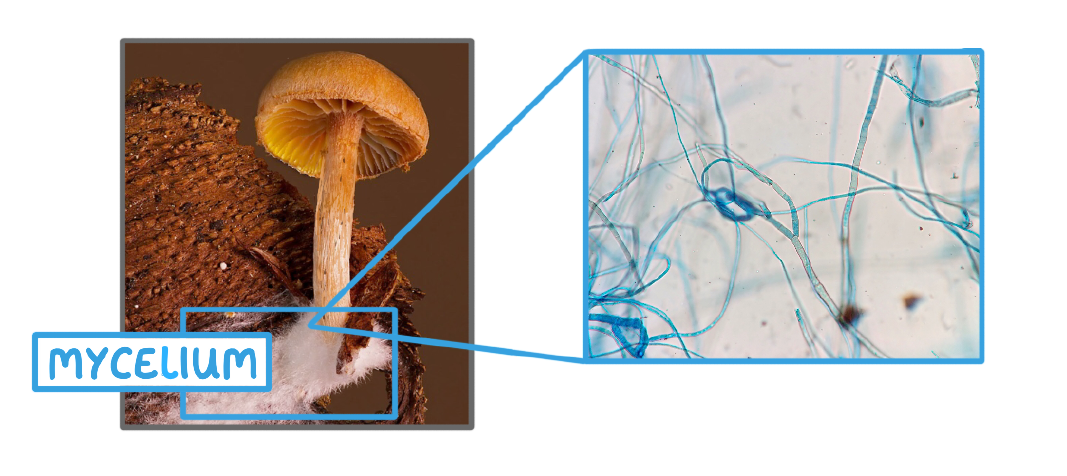

Some fungi (for example mushrooms) have a body known as a mycelium, which is made up of loads of tiny thread like structures called __________.
hairs
hydras
hyphae
|
unicellular / multicellular
The large majority of protoctists are .
|
True or false? Only some protoctists can photosynthesise.
True
False
|

True or false? Bacteria only live in a few specific environments.
True
False
|
True or false? The majority of bacteria don't have anything to do with humans (i.e. they don't help us, or cause us any problems).
True
False
|
plants / bacteria
Humans have in their intestines which help them break down food.
|
Would it be correct to say viruses are 'tiny cells'?
Yes
No
|
Viruses are considered parasites.
What does the term 'parasite' mean?
An organism that transports pathogens from one host to another
An organism that depends on another organism to grow and reproduce
A microorganism that causes disease
|
Which of the following can act as pathogens?
(Select all that apply)
Viruses
Animals
Plants
Bacteria
Protoctists
Fungi
|