Welcome to the Quiz!
This quiz contains 8 questions from a mix of 1 subtopics.
What happens to the temperature of a substance whilst it changes state?
The temperature increases
The temperature remains constant
The temperature decreases
|
boiling / form / break / state
When a substance changes from a liquid to a gas, it's called . During boiling, heat energy is used to the forces holding the particles together.
|
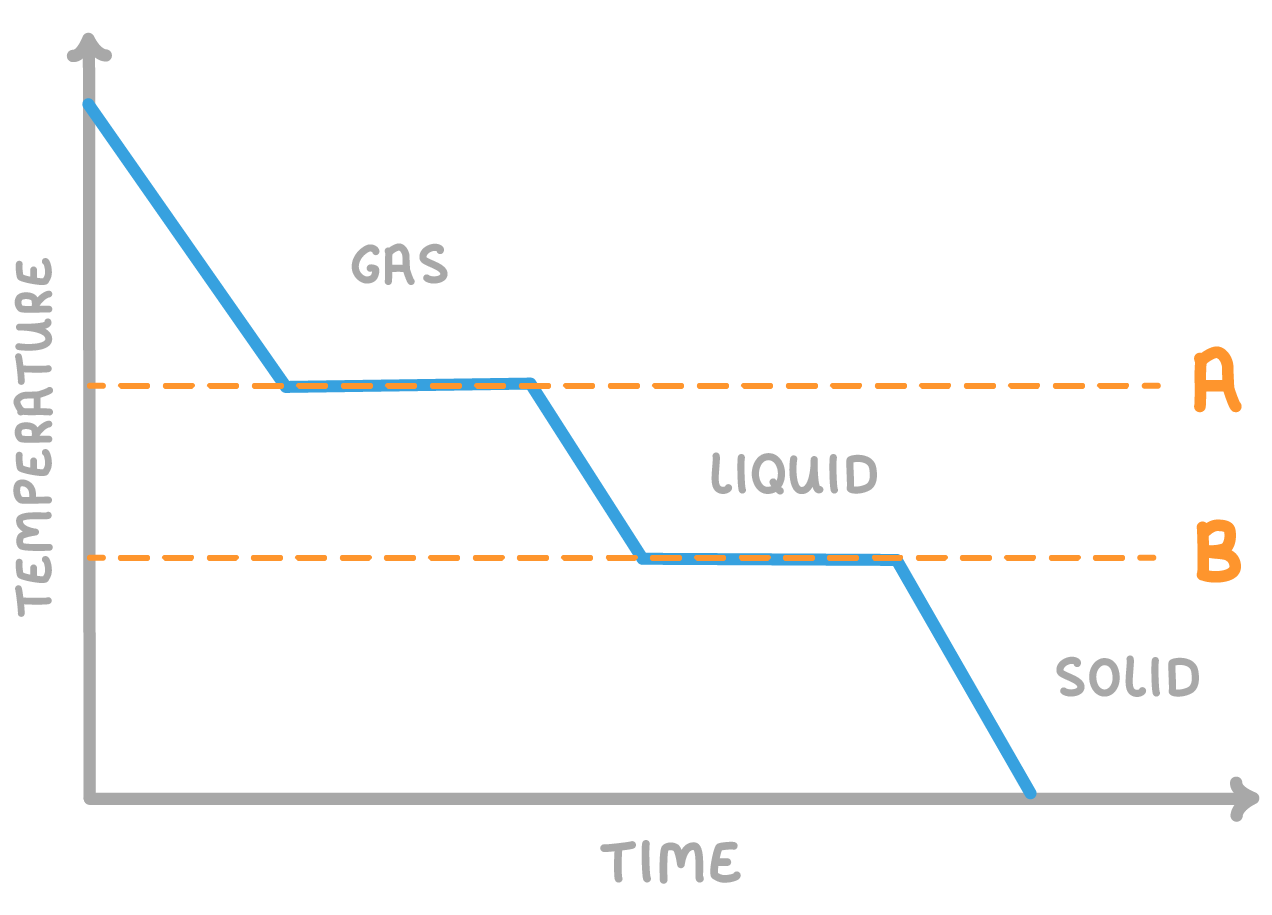
The above graph shows a substance cooling over time, changing state from a gas to a liquid, then from a liquid to a solid.
What is the name of the two temperatures A and B on the graph?
A: point
B: point
|
with / without / state / energy
The specific latent heat is the required to change 1kg of a particular substance from one to another, a change in temperature.
|
fusion / fission / vaporisation
The specific latent heat of refers to when a substance changes from a solid to a liquid (or vice versa).
The specific latent heat of refers to when a substance changes from a liquid to a gas (or vice versa).
|
The specific latent heat has the symbol L and the units J/kg.
What is the formula for specific latent heat?
(Note: this formula applies for both specific latent heat of fusion and specific latent heat of vaporisation)
|
2 kg of ice melts and becomes water.
How much energy did it take to melt the ice?
The latent heat of fusion of ice is 334,000 J/kg.
J
|
0.4 kg of water at 100°C boils to become steam.
How much energy did it take to boil the water?
The latent heat of vaporisation of water is 2,260,000 J/kg.
J
|