Welcome to the Quiz!
This quiz contains 13 questions from a mix of 1 subtopics.
What is the definition of corrosion?
|
Rusting is a special type of corrosion. It refers to the corrosion of which of the following metals?
Iron
Nickel
Vanadium
Magnesium
|
Complete the word equation for rusting.
Iron + + water ➔ iron (III)
|
During the process of rusting, iron undergoes the following half equation:
Fe ➔ Fe3+ + 3e-
Has the iron (Fe) been oxidised or reduced?
Oxidised
Reduced
|
Balance the half equation for the reduction of oxygen.
O2 + e- ➔ O2-
|
The rusting of iron involves both oxidation and reduction. This means that it is considered a reaction.
|
Which of the following are required for rusting of iron to take place?
(Select all that apply)
Catalyst
Salt
Water
Oxygen
|
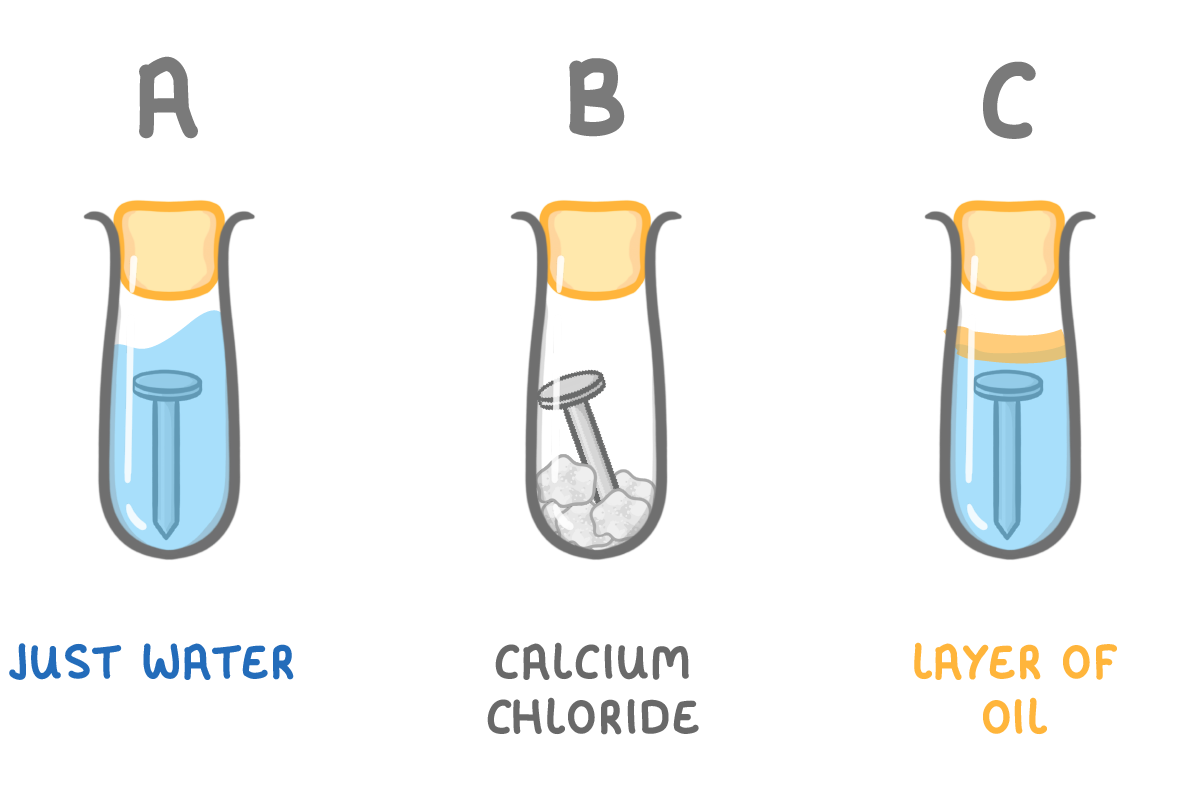
The image above shows three test tubes, each with an iron nail in, but in different conditions.
In which test tube would the iron nail rust?
A
B
C
|
Why doesn't aluminium break down as it corrodes like iron does?
Aluminium doesn't oxidise
Aluminium isn't exposed to oxygen
The aluminium oxide forms a protective layer, preventing further oxidation
|
There are two main ways to prevent iron from rusting: barrier methods and sacrificial methods.
Which of the following describes barrier methods?
Coat the iron in something to prevent the oxygen and water from touching the iron
Regularly scrape off any rust that forms so that it does not accumulate
Adding a more reactive metal to the iron, so that metal reacts with oxygen instead
|
Give three examples of using barrier methods to prevent iron from rusting.
|
There are two main ways to prevent iron from rusting: barrier methods and sacrificial methods.
Which of the following describes sacrificial methods?
Adding a more reactive metal to the iron, so that metal reacts with oxygen instead
Regularly scrape off any rust that forms so that it does not accumulate
Coat the iron in something to prevent the oxygen and water from touching the iron
|
Galvanisation
- Galvanising can prevent iron from r. It involves coating the iron in a thin layer of .
- The layer acts as a physical barrier to prevent water or from reaching the iron (barrier method).
- If the zinc gets scratched though, then the zinc will still react with any nearby oxygen as it is reactive than iron (sacrificial method).
|