Welcome to the Quiz!
This quiz contains 15 questions from a mix of 1 subtopics.
combine / separate / mixture / element
Chromatography is a chemical analysis technique used to substances in a .
|
What is paper chromatography used for?
To separate a mixtures of soluble substances in liquids
To separate solids
To separate gases
|
What is the name given for the pencil line?
The bottom line
The horizontal line
The baseline
|
Why should we use pencil for the baseline rather than pen?
Pen ink would damage the filter paper which could break
Pencil can be erased
Pen ink would dissolve in the solvent and move up the paper
|
Should the baseline be submerged in the solvent?
Yes
No
|
What are some solvents commonly used in chromatography?
(Select all that apply)
Ethanol
Water
Milk
Fruit juice
|
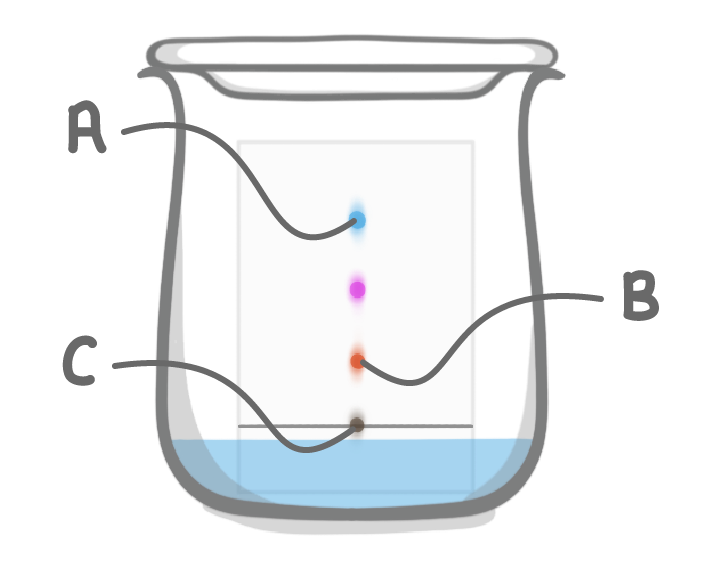
Match the letters A to C on the diagram above with the following descriptions:
Insoluble parts of the ink:
Substance with the a relatively slow rate of travel:
Substance with a relatively fast rate of travel:
|

What is the name of the resulting paper we end up with?
A chromatogram
A colourgram
A line chart
|
The 'mobile phase' refers to the molecules that can move.
Which is the mobile phase in paper chromatography?
The paper
The solvent
|
faster / slower / more / less / further / shorter
A substance which is soluble in the mobile phase will spend more time in the mobile phase. This means it will move , and travel a distance up the paper.
|
The 'stationary phase' refers to the molecules that can't move.
Which is the stationary phase in paper chromatography?
The solvent
The paper
|
mobile / stationary / faster / slower
A substance which is less soluble in the mobile phase will spend more time in the phase, so move , and not travel very far up the paper.
|
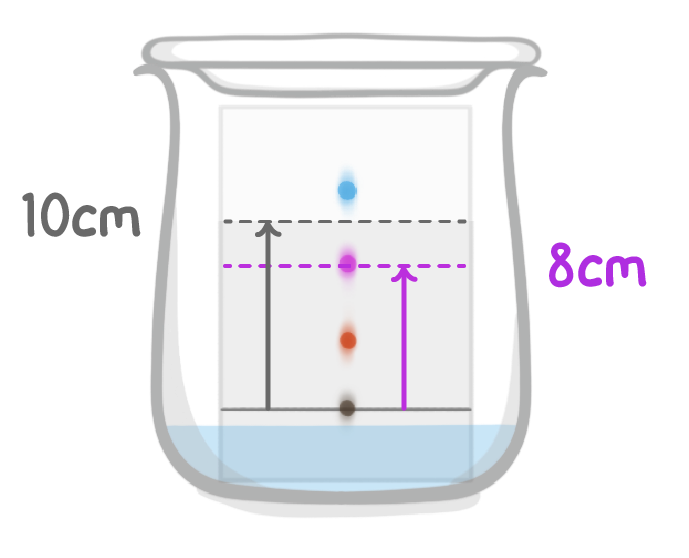
What is the Rf value of the purple substance?
|
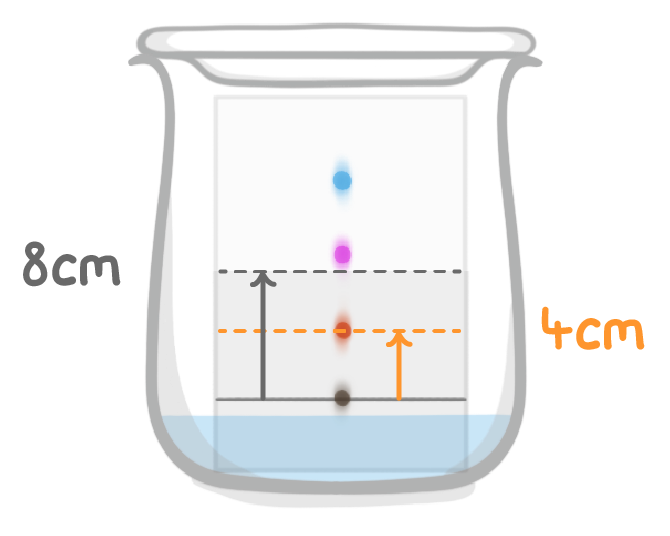
What is the Rf value of the orange substance?
|
True or false? The Rf value for a substance is specific to a particular mobile phase (solvent) and stationary phase (paper).
If you change either the mobile or stationary phase, you'll get a different Rf value.
False
True
|