Welcome to the Quiz!
This quiz contains 8 questions from a mix of 1 subtopics.
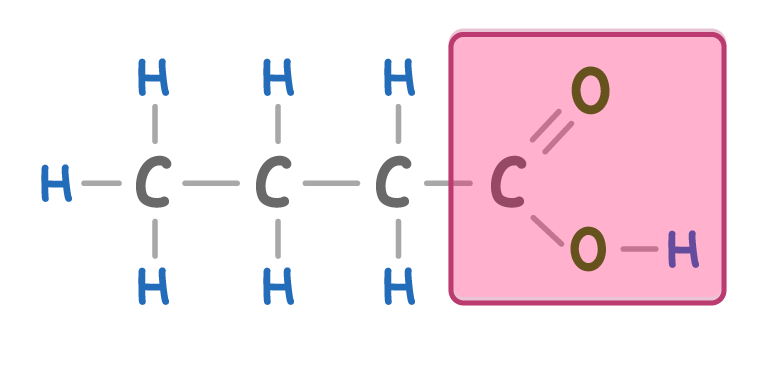
alkane / alkene / homologous / heterogeneous
Carboxylic acids are a series. They are basically chains with a COOH group on one end.
|

Carboxylic acids have a similar name to alkanes, but the 'e' at the end is replaced with 'oic acid'.
What is the name of the above carboxylic acid?
|
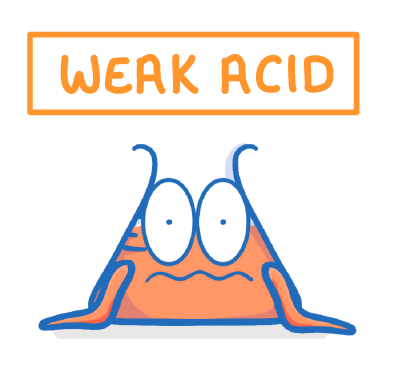
Carboxylic acids are weak acids:
oxygen / hydrogen / weak / ionises
- All carboxylic acids are weak acids. Weak acids do not fully ionise in water. This means that acids don't release all their ions.
- The ionisation of carboxylic acids in water can be shown as an equilibrium reaction like this:
C3H7COOH ⇌ C3H7COO- + H+
- It is always the H+ attached to the OH group that . The other hydrogen atoms are strongly bonded to the carbon atoms.
|
Carboxylic acids partially dissociate in water to form a negative ion and a hydrogen ion.
The negative ion has a name ending with 'anoate ion'.
Butanoic acid will ionise into a ion and a hydrogen ion.
|
oxidising / reducing / alkene / alcohol
Carboxylic acids are made from an with an oxidising agent.
|
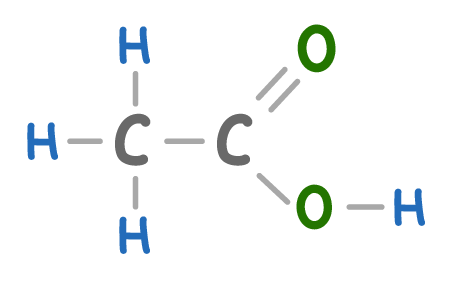
What molecule is shown above?
Butanoic acid
Methanoic acid
Ethanoic Acid
Propanoic acid
|
Butanol can be oxidised to a carboxylic acid.
What will the carboxylic acid be called?
|
What is the general formula for carboxylic acids?
CnHn+1COOH
Cn+1H2nCOOH
CnH2n+1COOH
|